大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
一、输入
1. 单个输入
n = input() #无参数 默认返回字符串
n = input(“有提示参数的输入”) #有提示性输入语句的输入,仍是以str类型返回
n = int(input()) #根据给定的类型输入,返回值类型int
n = float(input()) #根据给定的类型输入,返回值类型float
n = eval(input()) #eval()函数用来执行一个字符串表达式,并返回表达式的值。也可以用于返回数据本身的类型
2. 多个输入
a, b = input().split(” “) # 输入字符串(默认返回类型)a 和 b 以(空格)分隔
a, b, c = eval(input()) #输入三个值(任何类型)中间由逗号分隔
a, b, c = map(int, input().split(“,”)) #输入三个值(int)中间由逗号分隔
a, b, c = map(eval, input().split(” “)) #输入三个值(任何类型)中间(空格)分隔
3. 一行输入
方法1
lst = list(map(int, input().split(” “))) #输入一行值(int)由(空格)分隔 存入列表
方法2(输入n个数)
n = int(input())
s = input() #将数一行输入 空格分隔
lst = []
for i in s.split(” “):
lst.append(int(i))
#两种输出方式
for i in lst:
print(i, end=” “)
for i in range(n):
print(lst[i], end=” “)
二、输出
1. 直接输出(适用于无特殊输出要求的情况)
2. 加星号拆包(更加适用于一行打印出数组元素)
x = [1,2,3,4,5] print(*x) #输出:1 2 3 4 5 y = {1:'a',2:'b',3:'c',4:'d'} print(*y) #输出:1 2 3 43. 加入%进行格式化控制(适用于保留几位小数、进制、对齐、科学计数法等)
x = 123
print(‘%d’%x)
#输出:123
print(‘这有一个整数%d’%666)
#输出:这有一个整数666
print(‘%.2f’%3.)
#输出:3.14
print(‘%e’%223)
#输出:1.e+13
print(‘%04d’%99)
#输出:000099
print(‘%9s’%’hahaha’)
#输出 hahaha (注意左侧有多个空格)
注:这里的引号都是单引号
4. print()+format()格式化输出(格式化输出推荐用法)
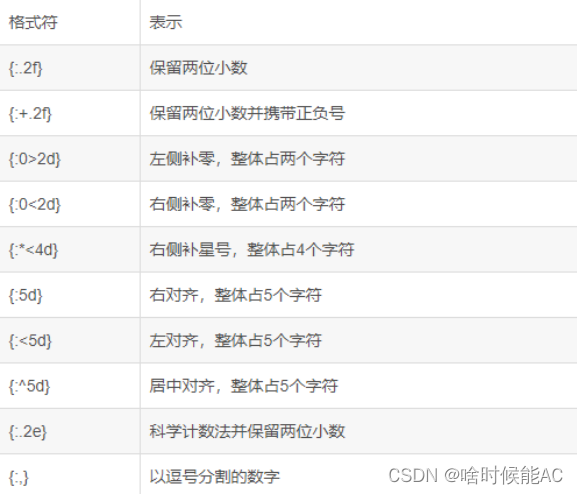
x = 123 print('{}'.format(x)) #输出:123 print('hello!{}'.format('World')) #输出:hello!World print('{}'.format(['1','2','3','4','5'])) #输出:['1','2','3','4','5'] print('{}->{}->{}'.format(1,2,3)) #输出:1->2->3 print('{2}->{0}->{1}'.format(1,2,3)) #输出:3->1->2 print('The Number is {}'.format(666)) #输出:The Number is 666 print('{:.2f}'.format(3.245)) #输出:3.25 print('{:0>4d}'.format(12)) #输出:0012 print('{:>8s}'.format('abc')) #输出: abc(注意abc前面有空格) print('{:<8d}'.format(999)) #输出:999 (注意999后面有空格) print('{:.2e}'.format()) #输出:1.23e+09 x = 123 print(f'The Number is {x:d}') #输出:The Number is 123 y = 3.1415 print(f'PI is {y:.2f} ...') #输出:3.14 z = [1,3,5,7,9] print(f'{z[0]:d} {z}') #输出:1 [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] Eg: 输入:3,5 输出:3+5=8 3-5=-2举例:
a,b=map(int,input().split(",")) print('{}+{}={}'.format(a,b,a+b)) print('{}-{}={}'.format(a,b,a-b))5. print()其他常用搭配以及复杂型输出示例(数组、矩阵、不规则输出等)
(1)打印一行数组
x = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] print(' '.join(map(str,x))) #输出:1 2 3 4 5 6 7(2)打印一行以任意字符分割的数组
x = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] print('*'.join(map(str,x))) #输出:1*2*3*4*5*6*7(3) 打印多行数组/二维数组-两种方法
方法一:
x = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] for i in x: print(*i) #输出: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9方法二:
x = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] for i in x: print(' '.join(map(str,i)))(4)将两个不同行列的二维数组并排打印
二维数组A: 二维数组B:
1 2 3 4 1 3 5
5 6 7 8 2 4 6
6 7 8 9 7 8 9
3 2 1
#定义两个二维数组 a = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[6,7,8,9]] b = [[1,3,5],[2,4,6],[7,8,9],[3,2,1]] #定义组合输出所需列表 out_list = [] sum_len = len(a[0])+len(b[0])+1 while a!=[] or b!=[]: if a!=[]: #取数组a一行 out_list+=a.pop(0)+[' '] if b!=[]: #取数组b一行 out_list+=b.pop(0) if len(out_list)<sum_len and a == []: #取剩下的数组一行 out_list = list(' '*(sum_len-len(out_list)))+out_list print(*out_list) #输出两个二维数组一行的合并内容 out_list = []输出:
1 2 3 4 1 3 5
5 6 7 8 2 4 6
6 7 8 9 7 8 9
3 2 1
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/119118.html