大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。

🎬 鸽芷咕:个人主页
🔥 个人专栏: 《C++干货基地》《粉丝福利》
⛺️生活的理想,就是为了理想的生活!
引入
哈喽各位铁汁们好啊,我是博主鸽芷咕《C++干货基地》是由我的襄阳家乡零食基地有感而发,不知道各位的城市有没有这种实惠又全面的零食基地呢?C++ 本身作为一门篇底层的一种语言,世面的免费课程大多都没有教明白。所以本篇专栏的内容全是干货让大家从底层了解C++,把更多的知识由抽象到简单通俗易懂。
⛳️ 推荐
前些天发现了一个巨牛的人工智能学习网站,通俗易懂,风趣幽默,忍不住分享一下给大家。点击跳转到网站。
文章目录
一、STL是什么?
STL我相信各位学C++的肯定都不会陌生,C++自从模版出来之后就发生了革命性的意义。有了模版这个东西我们就可以只书写一个库来不给不同类型的数据使用。
STL(standard template libaray-标准模板库):是C++标准库的重要组成部分,不仅是一个可复用的组件库,而且是一个包罗数据结构与算法的软件框架。
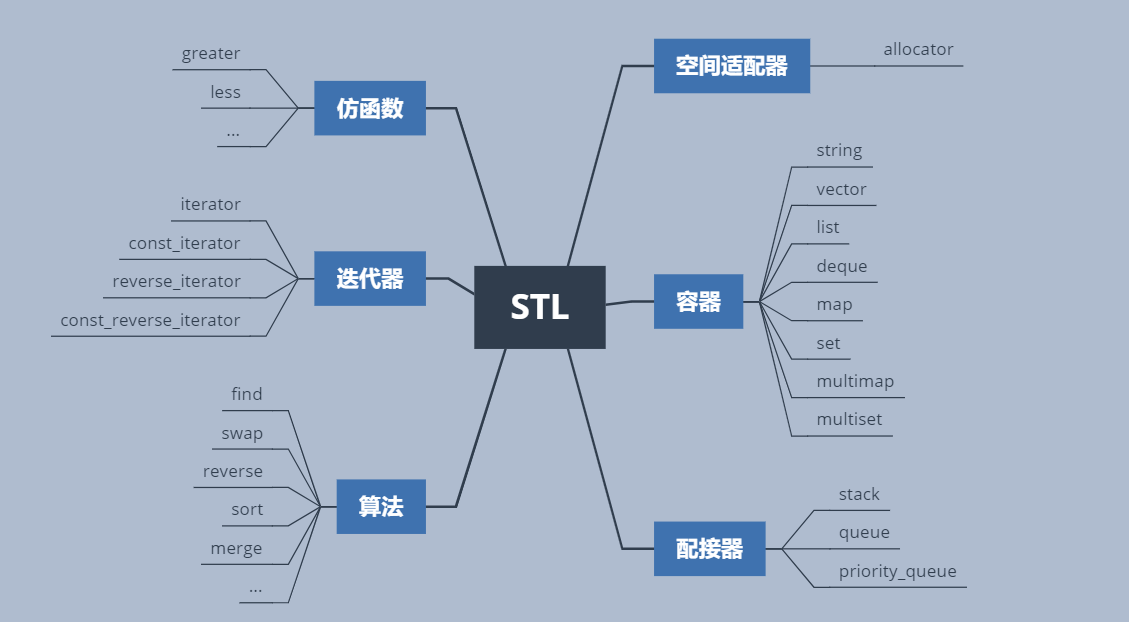
二、STL的六大组件
STL主要是由四大组件组成的,前面说了STL 是一个包罗数据结构与算法的软件框架 其中里面的容器就是数据结构库含有各种常用的数据结构
- 例如 顺序表 链表 队列 二叉树 等等常用数据结构
- 其中今天介绍的string 其实也算是 STL 的一员是 存放字符的顺序表
但是由于历史原因,string是先出来的 STL 是后面由惠普实验室后开发出来开源所以人们并没有把string 归类到STL 之中。
三、我们为什么要学string?
在C语言中,字符串是以’\0’结尾的一些字符的集合,为了操作方便,C标准库中提供了一些str系列的库函数。
- 但是这些库函数与字符串是分离开的,不太符合OOP的思想.
- 而且底层空间需要用户自己管理,稍不留神可能还会越界访问。
所以在C++中 专门把字符串操作封装成了 string 容器,来给开发者更好的调用接口支持。不用去管理底层的空间分配使得使用更加省心。
3.1 string 的定义
- string是表示字符串的字符串类
- 该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。
比特就业课 - string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别名,typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator>
string; - 不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。
在使用string类时,必须包含#include头文件以及using namespace std;
四、string的常用接口使用
4.1 成员函数
构造函数
构造函数介绍我们初始化string 对象的几种方法
- 1. 构造空的string类对象,即空字符串
int main() {
string s1(); return 0; } - 2. 用C-string来构造string类对象
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } - 3.使用string 中的 pos 位置开始,n个字符开始构造
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); string s2(s1, 6, 4); cout << s2 << endl; return 0; } - 4.使用 n 个字符初始化
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1(4,'x'); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } 拷贝构造
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); string s2(s1); cout << s2 << endl; return 0; } operator=
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); string s2= s1; cout << s2 << endl; return 0; } 4.2 迭代器的使用
迭代器是C++提供的一种新的遍历方式,其底层是一种类似指针的实现方式。可能很多人觉得这有什么可说的,但是迭代器不仅可以遍历string还能遍历二叉树链表是一种通用的遍历方式。
string 的三种遍历方式
- 使用迭代器遍历
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); //使用迭代器遍历 string::iterator it1 = s1.begin(); while (it1 != s1.end()) {
cout << *it1 << " "; it1++; } cout << endl; //使用迭代器修改 string::iterator it2 = s1.begin(); while (it2 != s1.end()) {
*it2 -= 1; cout << *it2 << " "; it2++; } cout << endl; return 0; } - 使用方括号遍历 【】
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++) {
cout << s1[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; return 0; } - 使用范围 for 遍历
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); for (auto e : s1) {
cout << e << ' '; } cout << endl; return 0; } rbegin && rend
这俩就是反向迭代器,使用他们打印出来的结果是从后往前
int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); //使用迭代器遍历 string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin(); while (rit != s1.rend()) {
cout << *rit << " "; ++rit; } cout << endl; return 0; } 4.3 容量部分
capacity 获取当前容量
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); cout << s1.capacity() << endl; return 0; } size 获取当前存储了多少字符
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); cout << s1.size() << endl; return 0; } resize 减少字符存储,或填充字符
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); s1.resize(3, 'x'); cout << s1 << endl; s1.resize(5); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } reserve 为string扩容
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); cout << s1.capacity() << endl; s1.reserve(6); cout << s1.capacity() << endl; s1.resize(100); cout << s1.capacity() << endl; return 0; } clear 清空所有字符
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); cout << s1 << endl; s1.clear(); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } empty 判断当前字符串是否为空
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); cout << s1.empty() << endl; return 0; } shrink_to_fit 为当前字符串请求缩容
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); cout << s1.capacity() << endl; s1.reserve(100); cout << s1.capacity() << endl; s1.shrink_to_fit(); cout << s1.capacity() << endl; return 0; } 4.4 元素访问
operator[]
```cpp #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++) {
cout << s1[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; return 0; } 4.5 修改
+= 操作
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); string s2("xxxxx"); s1 += s2; cout << s1 << endl; s1 += "vvvv"; cout << s1 << endl; s1 += 'x'; cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } append 追加字符或字符串
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); string s2("xxxxx"); s1.append(s2); cout << s1 << endl; s1.append("vvvv"); cout << s1 << endl; s1.append(4,'c'); cout << s1 << endl; s1.append("abcdef",3); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } push_back 尾插
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); s1.push_back('x'); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } assign 替换字符串
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); string s2("xxxxxxx"); s1.assign(s2); cout << s1 << endl; s1.assign("Linux C++"); cout << s1 << endl; s1.assign(5,'c'); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } insert 插入
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); string s2("C++"); s1.insert(6, s2); cout << s1 << endl; s1.insert(2, "xxxx"); cout << s1 << endl; s1.insert(6, 2,'v'); cout << s1 << endl; s1.insert(6,"bbbbbb",2); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } erase 删除字符串的一部分,减少其长度
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); cout << s1 << endl; cout << s1.size() << endl; cout << s1.capacity() << endl; s1.erase(5); cout << s1 << endl; cout << s1.size() << endl; cout << s1.capacity() << endl; return 0; } replace 替换
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); s1.replace(5,1,"C++"); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } swap交换
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); string s2("C++ Linux"); cout << s1 << endl; cout << s2 << endl; swap(s1, s2); cout << s1 << endl; cout << s2 << endl; return 0; } 4.6 字符串的操作
find 查找字符或字符串
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); int pos = s1.find('g'); cout << s1[pos]; return 0; } rfind 从后往前查找字符或字符串
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); int pos = s1.rfind('g'); cout << pos << endl; cout << s1[pos]; return 0; } c_str 返回C形式的字符串指针
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {
string s1("hello gugu"); cout << s1.c_str() << endl; return 0; } 结尾
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/121769.html