大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
系列文章目录
HEVC视频编解码标准简介
【x264编码器】章节1——x264编码流程及基于x264的编码器demo
【x264编码器】章节2——x264的lookahead流程分析
【x264编码器】章节3——x264的码率控制
【x264编码器】章节4——x264的帧内预测流程
【x264编码器】章节5——x264的帧间预测流程
【x264编码器】章节6——x264的变换量化
【x265编码器】章节1——lookahead模块分析
【x265编码器】章节2——编码流程及基于x265的编码器demo
【x265编码器】章节3——帧内预测流程
【x265编码器】章节4——帧间预测流程
【x265编码器】章节5——x265帧间运动估计流程
【x265编码器】章节6——x265的码率控制
【x265编码器】章节7——滤波模块
【x265编码器】章节8——变换量化模块
目录
2.1CRF模式(Constant Rate Factor恒定码率系数)
2.3CBR模式(Constant Bitrate恒定码率)
2.初始化可重新配置的码率控制相关参数x264_ratecontrol_init_reconfigurable
3.码率控制启动,计算初始QP x264_ratecontrol_start
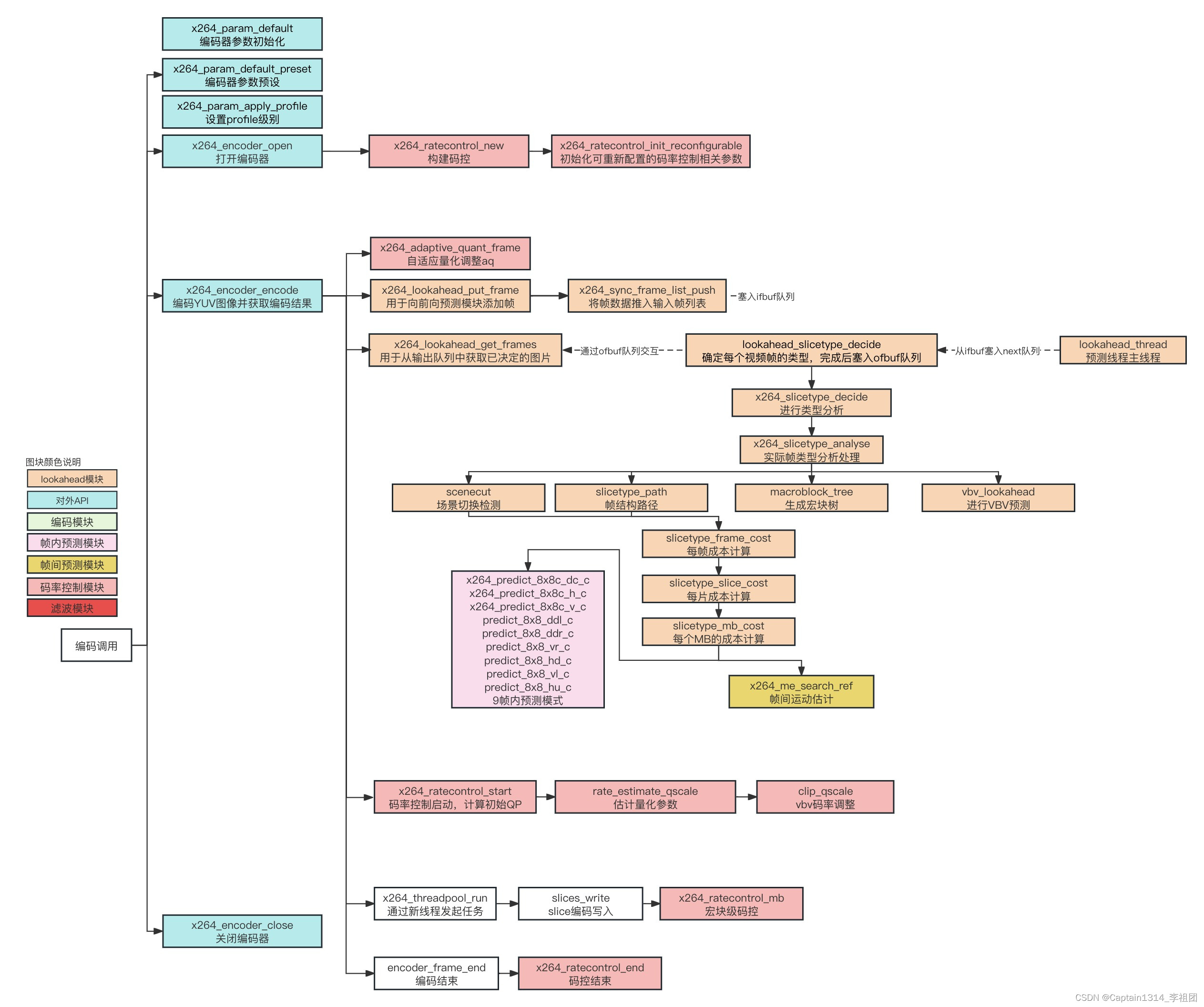
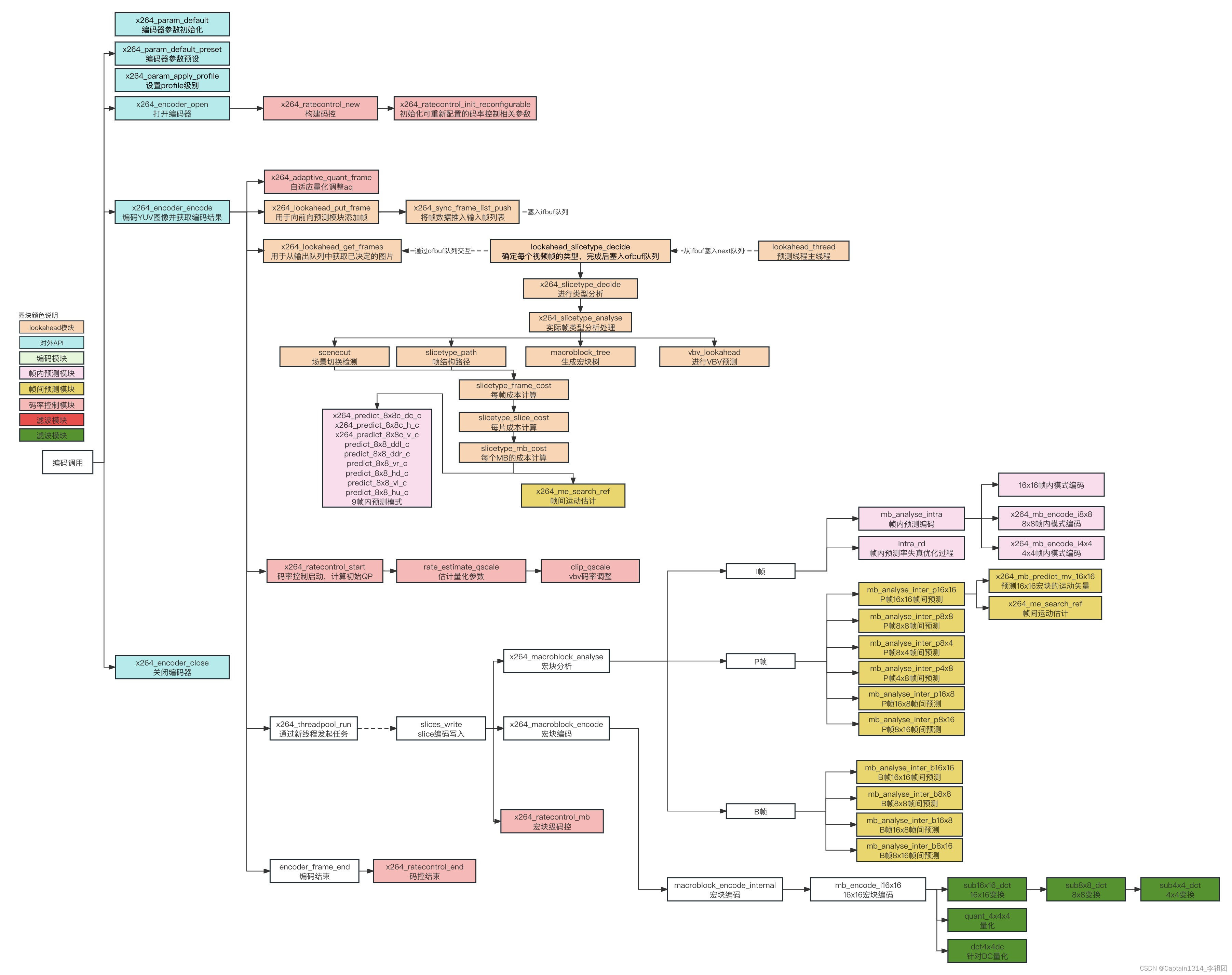
一、码率控制
码控总体的流程如下:
x264完整的流程框架如下:
1.码率控制模型
B帧的QP不同于I/P帧的QP计算,而是由前后参考帧的QP经过偏移得到,详细过程可以查看rate_estimate_qscale;
1.1R-Q模型说明
x264码率控制R-Q模型可以表示为如下:


static float predict_size( predictor_t *p, float q, float var ) { return (p->coeff*var + p->offset) / (q*p->count); }static inline float qscale2qp( float qscale ) { return (12.0f + QP_BD_OFFSET) + 6.0f * log2f( qscale/0.85f ); }其中Complex表示当前帧的编码复杂度,x265中用lookahead模块计算的SATD作为衡量当前帧的复杂度,c为模型参数,qscale是率失真优化中的拉格朗日乘子,R为编码当前帧需要的比特数。

其中

上述公式3对应的代码如下:
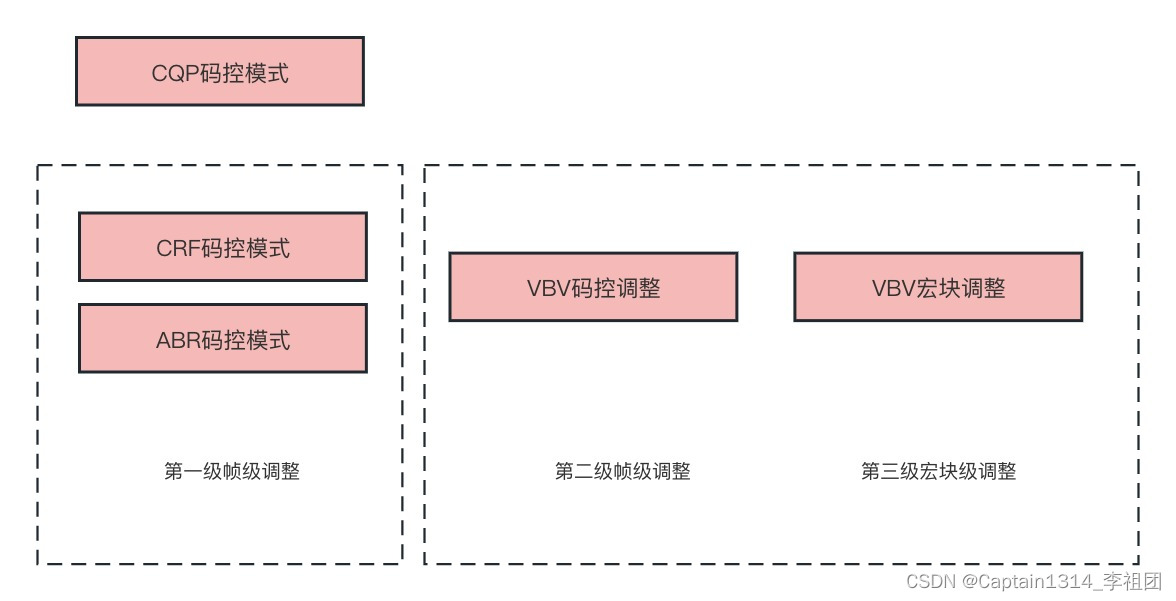
static float rate_estimate_qscale( x264_t *h ) { //省略多余代码 double wanted_bits, overflow = 1; //计算当前帧的复杂度(last_satd),并更新短期复杂度和复杂度计数 rcc->last_satd = x264_rc_analyse_slice( h ); rcc->short_term_cplxsum *= 0.5; rcc->short_term_cplxcount *= 0.5; rcc->short_term_cplxsum += rcc->last_satd / (CLIP_DURATION(h->fenc->f_duration) / BASE_FRAME_DURATION); rcc->short_term_cplxcount ++; rce.tex_bits = rcc->last_satd; rce.blurred_complexity = rcc->short_term_cplxsum / rcc->short_term_cplxcount; rce.mv_bits = 0; rce.p_count = rcc->nmb; rce.i_count = 0; rce.s_count = 0; rce.qscale = 1; rce.pict_type = pict_type; rce.i_duration = h->fenc->i_duration; //如果使用的是恒定质量模式(X264_RC_CRF),则调用get_qscale函数来获取量化参数(q) if( h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CRF ) { q = get_qscale( h, &rce, rcc->rate_factor_constant, h->fenc->i_frame ); } else { //调用get_qscale函数来根据帧的期望比特数和复杂度平均值来获取量化参数(q) q = get_qscale( h, &rce, rcc->wanted_bits_window / rcc->cplxr_sum, h->fenc->i_frame ); //省略多余代码 }//wanted_bits_window和cplxr_sum获取的位置,省略多余代码 int x264_ratecontrol_end( x264_t *h, int bits, int *filler ) { //省略多余代码 if( h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_B ) rc->cplxr_sum += bits * qp2qscale( rc->qpa_rc ) / rc->last_rceq; else { /* Depends on the fact that B-frame's QP is an offset from the following P-frame's. * Not perfectly accurate with B-refs, but good enough. */ rc->cplxr_sum += bits * qp2qscale( rc->qpa_rc ) / (rc->last_rceq * h->param.rc.f_pb_factor); } rc->cplxr_sum *= rc->cbr_decay; rc->wanted_bits_window += h->fenc->f_duration * rc->bitrate; rc->wanted_bits_window *= rc->cbr_decay; //省略多余代码 }2.码控模式
主要是有CQP、CRF、ABR模式,以及他们的相互组合:
1.CRF+VCV
2.ABR+VBV(如果此时设置了最大码率等于平均码率,ABR+VBV=CBR)
对应的代码主要是rate_estimate_qscale(第一级调整)、clip_qscale(第二级调整)和x264_ratecontrol_mb(第三级宏块级调整)
2.1CRF模式(Constant Rate Factor恒定码率系数)
对于CRF模式而言,右边这部分是是固定值rate_factor_constant,在初始化的时候确定,跟分辨率,qCompress这个参数是外部可设参数,默认值0.6,因此QP的选择只跟编码复杂度有关,跟码率无关,编码复杂度越高,QP值越高,因此可以一定程度上说CRF模式是恒定质量的编码模式。
从公式3上可以得出:
1.当qCompress=1,此时QP选择跟编码复杂度无关,即固定QP,CQP;
2.当qCompress=0,此时QP跟编码复杂度成正比,分配给复杂高和复杂度低帧的QP相同,行为接近CBR;
对于CRF而言,rate_factor_constant由下面代码赋值;
void x264_ratecontrol_init_reconfigurable( x264_t *h, int b_init ) { //多余代码 if( h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CRF ) { /* Arbitrary rescaling to make CRF somewhat similar to QP. * Try to compensate for MB-tree's effects as well. */ double base_cplx = h->mb.i_mb_count * (h->param.i_bframe ? 120 : 80); double mbtree_offset = h->param.rc.b_mb_tree ? (1.0-h->param.rc.f_qcompress)*13.5 : 0; rc->rate_factor_constant = pow( base_cplx, 1 - rc->qcompress ) / qp2qscale( h->param.rc.f_rf_constant + mbtree_offset + QP_BD_OFFSET ); } }2.2ABR模式(Average Bitrate平均码率)
对于CRF模式而言,经过上述的调整即可,而对于ABR模式而言,上面对于qscale的处理属于第一次调整,qscale还会经过下面第二次调整:


overflow的范围是0.5-2之间,利用overflow对总目标比特和编码时间比特之间的差距,进行调整,其中


static float rate_estimate_qscale( x264_t *h ) { // FIXME is it simpler to keep track of wanted_bits in ratecontrol_end? int i_frame_done = h->i_frame; double time_done = i_frame_done / rcc->fps; if( h->param.b_vfr_input && i_frame_done > 0 ) time_done = ((double)(h->fenc->i_reordered_pts - h->i_reordered_pts_delay)) * h->param.i_timebase_num / h->param.i_timebase_den; wanted_bits = time_done * rcc->bitrate;//计算已编码帧的时间(time_done)和期望比特数(wanted_bits) if( wanted_bits > 0 ) { abr_buffer *= X264_MAX( 1, sqrt( time_done ) ); overflow = x264_clip3f( 1.0 + (predicted_bits - wanted_bits) / abr_buffer, .5, 2 ); q *= overflow;//根据预测的比特数与期望比特数之间的差异以及ABR缓冲区的大小调整量化参数(q)的值 } }//伪代码 static float rate_estimate_qscale( x264_t *h ) { //第一次调整 q = get_qscale( h, &rce, rcc->wanted_bits_window / rcc->cplxr_sum, h->fenc->i_frame ); //第二次调整 overflow = x264_clip3f( 1.0 + (predicted_bits - wanted_bits) / abr_buffer, .5, 2 ); q *= overflow;//根据预测的比特数与期望比特数之间的差异以及ABR缓冲区的大小调整量化参数(q)的值 //第三次调整 q = clip_qscale( h, pict_type, q ); }2.3CBR模式(Constant Bitrate恒定码率)
CBR模式,是在ABR模式的基础上再做限制,当允许的最大码率等于平均码率,此时即CBR模式
3.自适应量化模块aq-mode
根据宏块复杂度的不同,调整宏块的qp偏移,其中复杂度的计算方式类似方差的计算如下(与方差的不同,仅差倍数关系):
static ALWAYS_INLINE uint32_t ac_energy_var( uint64_t sum_ssd, int shift, x264_frame_t *frame, int i, int b_store ) { uint32_t sum = sum_ssd; uint32_t ssd = sum_ssd >> 32; if( b_store ) { frame->i_pixel_sum[i] += sum; frame->i_pixel_ssd[i] += ssd; }//类方差的计算,与方差唯一的不同是方差=ssd >> shift - ((uint64_t)sum * sum >> shift*2) return ssd - ((uint64_t)sum * sum >> shift); }aq-mode总共有四种方案,分别是:X264_AQ_NONE、X264_AQ_VARIANCE、X264_AQ_AUTOVARIANCE和X264_AQ_AUTOVARIANCE_BIASED;
1.X264_AQ_NONE:不做任何调整;
2.X264_AQ_VARIANCE:仅会考虑自身宏块的方差和设置strength强度参数,不考虑其他宏块;
3.X264_AQ_AUTOVARIANCE:会考虑所有宏块的qp调整的均值,公式=f_aq_strength * avg_adj * (qp_adj -(avg_adj – 0.5f * (avg_adj_pow2 – 14.f) / avg_adj))
其中f_aq_strength为设置的调整的强度,avg_adj为由energy第一轮计算得到的宏块qp调整的均值,avg_adj_pow2为宏块qp调整平方和的均值;
4.X264_AQ_AUTOVARIANCE_BIASED:会考虑所有宏块的qp调整的均值,公式=f_aq_strength * avg_adj * (qp_adj -(avg_adj – 0.5f * (avg_adj_pow2 – 14.f) / avg_adj)) + f_aq_strength * (1.f – 14.f / (qp_adj * qp_adj))
代码如下:
void x264_adaptive_quant_frame( x264_t *h, x264_frame_t *frame, float *quant_offsets ) { /* Actual adaptive quantization */ else { /* constants chosen to result in approximately the same overall bitrate as without AQ. * FIXME: while they're written in 5 significant digits, they're only tuned to 2. */ float strength; float avg_adj = 0.f; float bias_strength = 0.f; //通过判断自适应量化模式(h->param.rc.i_aq_mode)的取值,确定使用不同的自适应量化策略 if( h->param.rc.i_aq_mode == X264_AQ_AUTOVARIANCE || h->param.rc.i_aq_mode == X264_AQ_AUTOVARIANCE_BIASED ) { //计算位深度校正因子(bit_depth_correction),用于将能量值转换为QP调整因子 float bit_depth_correction = 1.f / (1 << (2*(BIT_DEPTH-8))); float avg_adj_pow2 = 0.f; for( int mb_y = 0; mb_y < h->mb.i_mb_height; mb_y++ ) for( int mb_x = 0; mb_x < h->mb.i_mb_width; mb_x++ ) { uint32_t energy = ac_energy_mb( h, mb_x, mb_y, frame ); float qp_adj = powf( energy * bit_depth_correction + 1, 0.125f ); frame->f_qp_offset[mb_x + mb_y*h->mb.i_mb_stride] = qp_adj; avg_adj += qp_adj; avg_adj_pow2 += qp_adj * qp_adj; } avg_adj /= h->mb.i_mb_count; avg_adj_pow2 /= h->mb.i_mb_count; strength = h->param.rc.f_aq_strength * avg_adj; avg_adj = avg_adj - 0.5f * (avg_adj_pow2 - 14.f) / avg_adj; bias_strength = h->param.rc.f_aq_strength; } else strength = h->param.rc.f_aq_strength * 1.0397f; for( int mb_y = 0; mb_y < h->mb.i_mb_height; mb_y++ ) for( int mb_x = 0; mb_x < h->mb.i_mb_width; mb_x++ ) { float qp_adj; int mb_xy = mb_x + mb_y*h->mb.i_mb_stride; if( h->param.rc.i_aq_mode == X264_AQ_AUTOVARIANCE_BIASED ) { qp_adj = frame->f_qp_offset[mb_xy]; qp_adj = strength * (qp_adj - avg_adj) + bias_strength * (1.f - 14.f / (qp_adj * qp_adj)); } else if( h->param.rc.i_aq_mode == X264_AQ_AUTOVARIANCE ) { qp_adj = frame->f_qp_offset[mb_xy]; qp_adj = strength * (qp_adj - avg_adj); } else { //计算 X264_AQ_VARIANCE 方差的方案,仅会考虑自身宏块的方差和设置strength强度参数,不考虑其他宏块 uint32_t energy = ac_energy_mb( h, mb_x, mb_y, frame ); qp_adj = strength * (x264_log2( X264_MAX(energy, 1) ) - (14.427f + 2*(BIT_DEPTH-8))); } if( quant_offsets ) qp_adj += quant_offsets[mb_xy]; frame->f_qp_offset[mb_xy] = frame->f_qp_offset_aq[mb_xy] = qp_adj; if( h->frames.b_have_lowres ) frame->i_inv_qscale_factor[mb_xy] = x264_exp2fix8(qp_adj); } } }二、代码模块分析
1.构建码控x264_ratecontrol_new
主要进行参数的初始化,如果是ABR码控,还会进行cplxr_sum以及wanted_bits_window此类参数的初始化,代码如下:
int x264_ratecontrol_new( x264_t *h ) { //声明一个指向x264_ratecontrol_t结构的指针rc,用于指向当前编码器上的码率控制数据结构 x264_ratecontrol_t *rc; //调用x264_emms()函数,确保在SSE指令之后使用emms指令以恢复FPU(浮点运算单元)的状态 x264_emms(); //使用CHECKED_MALLOCZERO宏分配并初始化大小为h->param.i_threads * sizeof(x264_ratecontrol_t)的内存块,并将指针赋值给h->rc CHECKED_MALLOCZERO( h->rc, h->param.i_threads * sizeof(x264_ratecontrol_t) ); rc = h->rc;//将rc指向h->rc,方便后续代码的使用 //rc->b_abr表示是否使用平均比特率(Average Bit Rate)控制方法,条件是不使用恒定QP(Constant QP)控制方法并且不读取统计信息 rc->b_abr = h->param.rc.i_rc_method != X264_RC_CQP && !h->param.rc.b_stat_read; rc->b_2pass = h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_ABR && h->param.rc.b_stat_read; //如果编码参数中指定了帧率(h->param.i_fps_num和h->param.i_fps_den),则计算帧率的浮点数值并赋给rc->fps;否则,默认帧率为25.0 /* FIXME: use integers */ if( h->param.i_fps_num > 0 && h->param.i_fps_den > 0 ) rc->fps = (float) h->param.i_fps_num / h->param.i_fps_den; else rc->fps = 25.0; //如果编码参数中启用了宏块树模式(h->param.rc.b_mb_tree),则设置相关的参数 if( h->param.rc.b_mb_tree ) { h->param.rc.f_pb_factor = 1;//表示宏块树模式下的P帧和B帧之间的PB因子 rc->qcompress = 1;//表示宏块树模式下的量化压缩系数 } else rc->qcompress = h->param.rc.f_qcompress; //将编码参数中的比特率乘以一个缩放因子(1000或1024,取决于h->param.i_avcintra_class的值)赋给rc->bitrate,得到实际的比特率值 rc->bitrate = h->param.rc.i_bitrate * (h->param.i_avcintra_class ? 1024. : 1000.); rc->rate_tolerance = h->param.rc.f_rate_tolerance;//将编码参数中的帧间码率容差系数赋给rc->rate_tolerance,表示允许的帧间码率波动范围 rc->nmb = h->mb.i_mb_count;//表示总的宏块数 rc->last_non_b_pict_type = -1;//表示最近一个非B帧的图像类型,初始值为无效值 rc->cbr_decay = 1.0;//表示恒定比特率模式下的比特率衰减系数 if( h->param.rc.i_rc_method != X264_RC_ABR && h->param.rc.b_stat_read ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "CRF/CQP is incompatible with 2pass.\n" ); return -1; } //码率控制初始化 x264_ratecontrol_init_reconfigurable( h, 1 ); if( h->param.i_nal_hrd ) { uint64_t denom = (uint64_t)h->sps->vui.hrd.i_bit_rate_unscaled * h->sps->vui.i_time_scale; uint64_t num = 90000; x264_reduce_fraction64( &num, &denom ); rc->hrd_multiply_denom = 90000 / num; double bits_required = log2( num ) + log2( h->sps->vui.i_time_scale ) + log2( h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_size_unscaled ); if( bits_required >= 63 ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "HRD with very large timescale and bufsize not supported\n" ); return -1; } } if( rc->rate_tolerance < 0.01 ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "bitrate tolerance too small, using .01\n" ); rc->rate_tolerance = 0.01; } //表示是否使用可变QP h->mb.b_variable_qp = rc->b_vbv || h->param.rc.i_aq_mode; if( rc->b_abr )//如果使用ABR(Average Bit Rate)控制方法 { //定义了一个宏ABR_INIT_QP,根据不同的码率控制方法设置初始QP值 /* FIXME ABR_INIT_QP is actually used only in CRF */ #define ABR_INIT_QP (( h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CRF ? h->param.rc.f_rf_constant : 24 ) + QP_BD_OFFSET) rc->accum_p_norm = .01; rc->accum_p_qp = ABR_INIT_QP * rc->accum_p_norm; /* estimated ratio that produces a reasonable QP for the first I-frame */ rc->cplxr_sum = .01 * pow( 7.0e5, rc->qcompress ) * pow( h->mb.i_mb_count, 0.5 ); rc->wanted_bits_window = 1.0 * rc->bitrate / rc->fps; rc->last_non_b_pict_type = SLICE_TYPE_I; } rc->ip_offset = 6.0 * log2f( h->param.rc.f_ip_factor ); rc->pb_offset = 6.0 * log2f( h->param.rc.f_pb_factor ); rc->qp_constant[SLICE_TYPE_P] = h->param.rc.i_qp_constant; rc->qp_constant[SLICE_TYPE_I] = x264_clip3( h->param.rc.i_qp_constant - rc->ip_offset + 0.5, 0, QP_MAX ); rc->qp_constant[SLICE_TYPE_B] = x264_clip3( h->param.rc.i_qp_constant + rc->pb_offset + 0.5, 0, QP_MAX ); h->mb.ip_offset = rc->ip_offset + 0.5; rc->lstep = pow( 2, h->param.rc.i_qp_step / 6.0 ); rc->last_qscale = qp2qscale( 26 + QP_BD_OFFSET ); int num_preds = h->param.b_sliced_threads * h->param.i_threads + 1; CHECKED_MALLOC( rc->pred, 5 * sizeof(predictor_t) * num_preds ); CHECKED_MALLOC( rc->pred_b_from_p, sizeof(predictor_t) ); static const float pred_coeff_table[3] = { 1.0, 1.0, 1.5 }; for( int i = 0; i < 3; i++ ) { rc->last_qscale_for[i] = qp2qscale( ABR_INIT_QP ); rc->lmin[i] = qp2qscale( h->param.rc.i_qp_min ); rc->lmax[i] = qp2qscale( h->param.rc.i_qp_max ); for( int j = 0; j < num_preds; j++ ) { rc->pred[i+j*5].coeff_min = pred_coeff_table[i] / 2; rc->pred[i+j*5].coeff = pred_coeff_table[i]; rc->pred[i+j*5].count = 1.0; rc->pred[i+j*5].decay = 0.5; rc->pred[i+j*5].offset = 0.0; } for( int j = 0; j < 2; j++ ) { rc->row_preds[i][j].coeff_min = .25 / 4; rc->row_preds[i][j].coeff = .25; rc->row_preds[i][j].count = 1.0; rc->row_preds[i][j].decay = 0.5; rc->row_preds[i][j].offset = 0.0; } } rc->pred_b_from_p->coeff_min = 0.5 / 2; rc->pred_b_from_p->coeff = 0.5; rc->pred_b_from_p->count = 1.0; rc->pred_b_from_p->decay = 0.5; rc->pred_b_from_p->offset = 0.0; if( parse_zones( h ) < 0 ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "failed to parse zones\n" ); return -1; } /* Load stat file and init 2pass algo */ if( h->param.rc.b_stat_read ) { char *p, *stats_in, *stats_buf; /* read 1st pass stats */ assert( h->param.rc.psz_stat_in ); stats_buf = stats_in = x264_slurp_file( h->param.rc.psz_stat_in ); if( !stats_buf ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "ratecontrol_init: can't open stats file\n" ); return -1; } if( h->param.rc.b_mb_tree ) { char *mbtree_stats_in = strcat_filename( h->param.rc.psz_stat_in, ".mbtree" ); if( !mbtree_stats_in ) return -1; rc->p_mbtree_stat_file_in = x264_fopen( mbtree_stats_in, "rb" ); x264_free( mbtree_stats_in ); if( !rc->p_mbtree_stat_file_in ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "ratecontrol_init: can't open mbtree stats file\n" ); return -1; } } /* check whether 1st pass options were compatible with current options */ if( strncmp( stats_buf, "#options:", 9 ) ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "options list in stats file not valid\n" ); return -1; } float res_factor, res_factor_bits; { int i, j; uint32_t k, l; char *opts = stats_buf; stats_in = strchr( stats_buf, '\n' ); if( !stats_in ) return -1; *stats_in = '\0'; stats_in++; if( sscanf( opts, "#options: %dx%d", &i, &j ) != 2 ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "resolution specified in stats file not valid\n" ); return -1; } else if( h->param.rc.b_mb_tree ) { rc->mbtree.srcdim[0] = i; rc->mbtree.srcdim[1] = j; } res_factor = (float)h->param.i_width * h->param.i_height / (i*j); /* Change in bits relative to resolution isn't quite linear on typical sources, * so we'll at least try to roughly approximate this effect. */ res_factor_bits = powf( res_factor, 0.7 ); if( !( p = strstr( opts, "timebase=" ) ) || sscanf( p, "timebase=%u/%u", &k, &l ) != 2 ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "timebase specified in stats file not valid\n" ); return -1; } if( k != h->param.i_timebase_num || l != h->param.i_timebase_den ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "timebase mismatch with 1st pass (%u/%u vs %u/%u)\n", h->param.i_timebase_num, h->param.i_timebase_den, k, l ); return -1; } CMP_OPT_FIRST_PASS( "bitdepth", BIT_DEPTH ); CMP_OPT_FIRST_PASS( "weightp", X264_MAX( 0, h->param.analyse.i_weighted_pred ) ); CMP_OPT_FIRST_PASS( "bframes", h->param.i_bframe ); CMP_OPT_FIRST_PASS( "b_pyramid", h->param.i_bframe_pyramid ); CMP_OPT_FIRST_PASS( "intra_refresh", h->param.b_intra_refresh ); CMP_OPT_FIRST_PASS( "open_gop", h->param.b_open_gop ); CMP_OPT_FIRST_PASS( "bluray_compat", h->param.b_bluray_compat ); CMP_OPT_FIRST_PASS( "mbtree", h->param.rc.b_mb_tree ); if( (p = strstr( opts, "interlaced=" )) ) { char *current = h->param.b_interlaced ? h->param.b_tff ? "tff" : "bff" : h->param.b_fake_interlaced ? "fake" : "0"; char buf[5]; sscanf( p, "interlaced=%4s", buf ); if( strcmp( current, buf ) ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "different interlaced setting than first pass (%s vs %s)\n", current, buf ); return -1; } } if( (p = strstr( opts, "keyint=" )) ) { p += 7; char buf[13] = "infinite "; if( h->param.i_keyint_max != X264_KEYINT_MAX_INFINITE ) sprintf( buf, "%d ", h->param.i_keyint_max ); if( strncmp( p, buf, strlen(buf) ) ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "different keyint setting than first pass (%.*s vs %.*s)\n", strlen(buf)-1, buf, strcspn(p, " "), p ); return -1; } } if( strstr( opts, "qp=0" ) && h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_ABR ) x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "1st pass was lossless, bitrate prediction will be inaccurate\n" ); if( !strstr( opts, "direct=3" ) && h->param.analyse.i_direct_mv_pred == X264_DIRECT_PRED_AUTO ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "direct=auto not used on the first pass\n" ); h->mb.b_direct_auto_write = 1; } if( ( p = strstr( opts, "b_adapt=" ) ) && sscanf( p, "b_adapt=%d", &i ) && i >= X264_B_ADAPT_NONE && i <= X264_B_ADAPT_TRELLIS ) h->param.i_bframe_adaptive = i; else if( h->param.i_bframe ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "b_adapt method specified in stats file not valid\n" ); return -1; } if( (h->param.rc.b_mb_tree || h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size) && ( p = strstr( opts, "rc_lookahead=" ) ) && sscanf( p, "rc_lookahead=%d", &i ) ) h->param.rc.i_lookahead = i; } /* find number of pics */ p = stats_in; int num_entries; for( num_entries = -1; p; num_entries++ ) p = strchr( p + 1, ';' ); if( !num_entries ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "empty stats file\n" ); return -1; } rc->num_entries = num_entries; if( h->param.i_frame_total < rc->num_entries && h->param.i_frame_total > 0 ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "2nd pass has fewer frames than 1st pass (%d vs %d)\n", h->param.i_frame_total, rc->num_entries ); } if( h->param.i_frame_total > rc->num_entries ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "2nd pass has more frames than 1st pass (%d vs %d)\n", h->param.i_frame_total, rc->num_entries ); return -1; } CHECKED_MALLOCZERO( rc->entry, rc->num_entries * sizeof(ratecontrol_entry_t) ); CHECKED_MALLOC( rc->entry_out, rc->num_entries * sizeof(ratecontrol_entry_t*) ); /* init all to skipped p frames */ for( int i = 0; i < rc->num_entries; i++ ) { ratecontrol_entry_t *rce = &rc->entry[i]; rce->pict_type = SLICE_TYPE_P; rce->qscale = rce->new_qscale = qp2qscale( 20 + QP_BD_OFFSET ); rce->misc_bits = rc->nmb + 10; rce->new_qp = 0; rc->entry_out[i] = rce; } /* read stats */ p = stats_in; double total_qp_aq = 0; for( int i = 0; i < rc->num_entries; i++ ) { ratecontrol_entry_t *rce; int frame_number = 0; int frame_out_number = 0; char pict_type = 0; int e; char *next; float qp_rc, qp_aq; int ref; next= strchr(p, ';'); if( next ) *next++ = 0; //sscanf is unbelievably slow on long strings e = sscanf( p, " in:%d out:%d ", &frame_number, &frame_out_number ); if( frame_number < 0 || frame_number >= rc->num_entries ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "bad frame number (%d) at stats line %d\n", frame_number, i ); return -1; } if( frame_out_number < 0 || frame_out_number >= rc->num_entries ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "bad frame output number (%d) at stats line %d\n", frame_out_number, i ); return -1; } rce = &rc->entry[frame_number]; rc->entry_out[frame_out_number] = rce; rce->direct_mode = 0; e += sscanf( p, " in:%*d out:%*d type:%c dur:%"SCNd64" cpbdur:%"SCNd64" q:%f aq:%f tex:%d mv:%d misc:%d imb:%d pmb:%d smb:%d d:%c", &pict_type, &rce->i_duration, &rce->i_cpb_duration, &qp_rc, &qp_aq, &rce->tex_bits, &rce->mv_bits, &rce->misc_bits, &rce->i_count, &rce->p_count, &rce->s_count, &rce->direct_mode ); rce->tex_bits *= res_factor_bits; rce->mv_bits *= res_factor_bits; rce->misc_bits *= res_factor_bits; rce->i_count *= res_factor; rce->p_count *= res_factor; rce->s_count *= res_factor; p = strstr( p, "ref:" ); if( !p ) goto parse_error; p += 4; for( ref = 0; ref < 16; ref++ ) { if( sscanf( p, " %d", &rce->refcount[ref] ) != 1 ) break; p = strchr( p+1, ' ' ); if( !p ) goto parse_error; } rce->refs = ref; /* find weights */ rce->i_weight_denom[0] = rce->i_weight_denom[1] = -1; char *w = strchr( p, 'w' ); if( w ) { int count = sscanf( w, "w:%hd,%hd,%hd,%hd,%hd,%hd,%hd,%hd", &rce->i_weight_denom[0], &rce->weight[0][0], &rce->weight[0][1], &rce->i_weight_denom[1], &rce->weight[1][0], &rce->weight[1][1], &rce->weight[2][0], &rce->weight[2][1] ); if( count == 3 ) rce->i_weight_denom[1] = -1; else if( count != 8 ) rce->i_weight_denom[0] = rce->i_weight_denom[1] = -1; } if( pict_type != 'b' ) rce->kept_as_ref = 1; switch( pict_type ) { case 'I': rce->frame_type = X264_TYPE_IDR; rce->pict_type = SLICE_TYPE_I; break; case 'i': rce->frame_type = X264_TYPE_I; rce->pict_type = SLICE_TYPE_I; break; case 'P': rce->frame_type = X264_TYPE_P; rce->pict_type = SLICE_TYPE_P; break; case 'B': rce->frame_type = X264_TYPE_BREF; rce->pict_type = SLICE_TYPE_B; break; case 'b': rce->frame_type = X264_TYPE_B; rce->pict_type = SLICE_TYPE_B; break; default: e = -1; break; } if( e < 14 ) { parse_error: x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "statistics are damaged at line %d, parser out=%d\n", i, e ); return -1; } rce->qscale = qp2qscale( qp_rc ); total_qp_aq += qp_aq; p = next; } if( !h->param.b_stitchable ) h->pps->i_pic_init_qp = SPEC_QP( (int)(total_qp_aq / rc->num_entries + 0.5) ); x264_free( stats_buf ); if( h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_ABR ) { if( init_pass2( h ) < 0 ) return -1; } /* else we're using constant quant, so no need to run the bitrate allocation */ } /* Open output file */ /* If input and output files are the same, output to a temp file * and move it to the real name only when it's complete */ if( h->param.rc.b_stat_write )//需要写入统计信息文件,则进行以下操作 { char *p; rc->psz_stat_file_tmpname = strcat_filename( h->param.rc.psz_stat_out, ".temp" ); if( !rc->psz_stat_file_tmpname ) return -1; rc->p_stat_file_out = x264_fopen( rc->psz_stat_file_tmpname, "wb" ); if( rc->p_stat_file_out == NULL ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "ratecontrol_init: can't open stats file\n" ); return -1; } p = x264_param2string( &h->param, 1 ); if( p ) fprintf( rc->p_stat_file_out, "#options: %s\n", p ); x264_free( p ); if( h->param.rc.b_mb_tree && !h->param.rc.b_stat_read ) { rc->psz_mbtree_stat_file_tmpname = strcat_filename( h->param.rc.psz_stat_out, ".mbtree.temp" ); rc->psz_mbtree_stat_file_name = strcat_filename( h->param.rc.psz_stat_out, ".mbtree" ); if( !rc->psz_mbtree_stat_file_tmpname || !rc->psz_mbtree_stat_file_name ) return -1; rc->p_mbtree_stat_file_out = x264_fopen( rc->psz_mbtree_stat_file_tmpname, "wb" ); if( rc->p_mbtree_stat_file_out == NULL ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "ratecontrol_init: can't open mbtree stats file\n" ); return -1; } } } if( h->param.rc.b_mb_tree && (h->param.rc.b_stat_read || h->param.rc.b_stat_write) ) { if( !h->param.rc.b_stat_read ) { rc->mbtree.srcdim[0] = h->param.i_width; rc->mbtree.srcdim[1] = h->param.i_height; } if( macroblock_tree_rescale_init( h, rc ) < 0 ) return -1; } for( int i = 0; i<h->param.i_threads; i++ ) { //将h->thread[i]->rc指向rc+i,即为每个线程分配一个独立的rc结构体 h->thread[i]->rc = rc+i; if( i )//如果i不为0,即对于除第一个线程以外的线程 { //将rc[i]的内容复制为rc[0],使每个线程的rc结构体内容相同 rc[i] = rc[0]; h->thread[i]->param = h->param;//将h->thread[i]->param赋值为h->param,将线程的编码参数与主线程保持一致 h->thread[i]->mb.b_variable_qp = h->mb.b_variable_qp;//将h->thread[i]->mb.b_variable_qp赋值为h->mb.b_variable_qp,将线程的宏块的QP变量性质与主线程保持一致 h->thread[i]->mb.ip_offset = h->mb.ip_offset;//将h->thread[i]->mb.ip_offset赋值为h->mb.ip_offset,将线程的宏块的内部像素偏移与主线程保持一致 } } return 0; fail: return -1; }2.初始化可重新配置的码率控制相关参数x264_ratecontrol_init_reconfigurable
这段代码根据参数和配置对VBV(Video Buffering Verifier)参数进行了设置和调整。VBV是一种用于控制比特率和缓冲区大小的机制,用于确保视频编码过程中的比特率和缓冲区管理,代码如下:
void x264_ratecontrol_init_reconfigurable( x264_t *h, int b_init ) { x264_ratecontrol_t *rc = h->rc; if( !b_init && rc->b_2pass ) return; if( h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CRF ) { /* Arbitrary rescaling to make CRF somewhat similar to QP. * Try to compensate for MB-tree's effects as well. */ double base_cplx = h->mb.i_mb_count * (h->param.i_bframe ? 120 : 80); double mbtree_offset = h->param.rc.b_mb_tree ? (1.0-h->param.rc.f_qcompress)*13.5 : 0; rc->rate_factor_constant = pow( base_cplx, 1 - rc->qcompress ) / qp2qscale( h->param.rc.f_rf_constant + mbtree_offset + QP_BD_OFFSET ); } if( h->param.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate > 0 && h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size > 0 ) { /* We don't support changing the ABR bitrate right now, so if the stream starts as CBR, keep it CBR. */ if( rc->b_vbv_min_rate )//如果设置了最小码率,则此时变为CBR模式 h->param.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate = h->param.rc.i_bitrate; if( h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size < (int)(h->param.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate / rc->fps) ) { //打印警告消息,指示VBV缓冲区大小不能小于一个帧的比特率 h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size = h->param.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate / rc->fps; x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "VBV buffer size cannot be smaller than one frame, using %d kbit\n", h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size ); } int kilobit_size = h->param.i_avcintra_class ? 1024 : 1000; int vbv_buffer_size = h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size * kilobit_size; int vbv_max_bitrate = h->param.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate * kilobit_size; /* Init HRD */ if( h->param.i_nal_hrd && b_init ) { h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_cnt = 1; h->sps->vui.hrd.b_cbr_hrd = h->param.i_nal_hrd == X264_NAL_HRD_CBR; h->sps->vui.hrd.i_time_offset_length = 0; #define BR_SHIFT 6 #define CPB_SHIFT 4 // normalize HRD size and rate to the value / scale notation h->sps->vui.hrd.i_bit_rate_scale = x264_clip3( x264_ctz( vbv_max_bitrate ) - BR_SHIFT, 0, 15 ); h->sps->vui.hrd.i_bit_rate_value = vbv_max_bitrate >> ( h->sps->vui.hrd.i_bit_rate_scale + BR_SHIFT ); h->sps->vui.hrd.i_bit_rate_unscaled = h->sps->vui.hrd.i_bit_rate_value << ( h->sps->vui.hrd.i_bit_rate_scale + BR_SHIFT ); h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_size_scale = x264_clip3( x264_ctz( vbv_buffer_size ) - CPB_SHIFT, 0, 15 ); h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_size_value = vbv_buffer_size >> ( h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_size_scale + CPB_SHIFT ); h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_size_unscaled = h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_size_value << ( h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_size_scale + CPB_SHIFT ); #undef CPB_SHIFT #undef BR_SHIFT // arbitrary #define MAX_DURATION 0.5 int max_cpb_output_delay = X264_MIN( h->param.i_keyint_max * MAX_DURATION * h->sps->vui.i_time_scale / h->sps->vui.i_num_units_in_tick, INT_MAX ); int max_dpb_output_delay = h->sps->vui.i_max_dec_frame_buffering * MAX_DURATION * h->sps->vui.i_time_scale / h->sps->vui.i_num_units_in_tick; int max_delay = (int)(90000.0 * (double)h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_size_unscaled / h->sps->vui.hrd.i_bit_rate_unscaled + 0.5); h->sps->vui.hrd.i_initial_cpb_removal_delay_length = 2 + x264_clip3( 32 - x264_clz( max_delay ), 4, 22 ); h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_removal_delay_length = x264_clip3( 32 - x264_clz( max_cpb_output_delay ), 4, 31 ); h->sps->vui.hrd.i_dpb_output_delay_length = x264_clip3( 32 - x264_clz( max_dpb_output_delay ), 4, 31 ); #undef MAX_DURATION vbv_buffer_size = h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_size_unscaled; vbv_max_bitrate = h->sps->vui.hrd.i_bit_rate_unscaled; } else if( h->param.i_nal_hrd && !b_init ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "VBV parameters cannot be changed when NAL HRD is in use\n" ); return; } h->sps->vui.hrd.i_bit_rate_unscaled = vbv_max_bitrate; h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_size_unscaled = vbv_buffer_size; if( rc->b_vbv_min_rate ) rc->bitrate = (double)h->param.rc.i_bitrate * kilobit_size; rc->buffer_rate = vbv_max_bitrate / rc->fps; rc->vbv_max_rate = vbv_max_bitrate; rc->buffer_size = vbv_buffer_size; rc->single_frame_vbv = rc->buffer_rate * 1.1 > rc->buffer_size; if( rc->b_abr && h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_ABR ) rc->cbr_decay = 1.0 - rc->buffer_rate / rc->buffer_size * 0.5 * X264_MAX(0, 1.5 - rc->buffer_rate * rc->fps / rc->bitrate); if( h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CRF && h->param.rc.f_rf_constant_max ) { rc->rate_factor_max_increment = h->param.rc.f_rf_constant_max - h->param.rc.f_rf_constant; if( rc->rate_factor_max_increment <= 0 ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "CRF max must be greater than CRF\n" ); rc->rate_factor_max_increment = 0; } } if( b_init ) { if( h->param.rc.f_vbv_buffer_init > 1. ) h->param.rc.f_vbv_buffer_init = x264_clip3f( h->param.rc.f_vbv_buffer_init / h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size, 0, 1 ); h->param.rc.f_vbv_buffer_init = x264_clip3f( X264_MAX( h->param.rc.f_vbv_buffer_init, rc->buffer_rate / rc->buffer_size ), 0, 1); rc->buffer_fill_final = rc->buffer_fill_final_min = rc->buffer_size * h->param.rc.f_vbv_buffer_init * h->sps->vui.i_time_scale; rc->b_vbv = 1; rc->b_vbv_min_rate = !rc->b_2pass && h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_ABR && h->param.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate <= h->param.rc.i_bitrate;//如果最大码率等于平均码率,此时也是CBR模式 } } }3.码率控制启动,计算初始QP x264_ratecontrol_start
此代码段的目的是为了在编码每一帧之前,根据所需的比特率和视频质量,选择适当的量化参数(QP)进行编码,根据不同的条件选择适当的量化参数(QP)值,并进行相关的变量和结构体的设置,以便在编码每一帧之前进行适当的控制和调整代码如下(示例):
/* Before encoding a frame, choose a QP for it */ void x264_ratecontrol_start( x264_t *h, int i_force_qp, int overhead ) { x264_ratecontrol_t *rc = h->rc; ratecontrol_entry_t *rce = NULL; x264_zone_t *zone = get_zone( h, h->fenc->i_frame ); float q; x264_emms(); if( h->param.rc.b_stat_read ) { int frame = h->fenc->i_frame; assert( frame >= 0 && frame < rc->num_entries ); rce = rc->rce = &rc->entry[frame]; if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B && h->param.analyse.i_direct_mv_pred == X264_DIRECT_PRED_AUTO ) { h->sh.b_direct_spatial_mv_pred = ( rce->direct_mode == 's' ); h->mb.b_direct_auto_read = ( rce->direct_mode == 's' || rce->direct_mode == 't' ); } } if( rc->b_vbv ) { //重置行位数、行QP值、行量化参数值,更新VBV计划,包括计算缓冲区速率(rc->buffer_rate)和根据开销(overhead)更新VBV预测 memset( h->fdec->i_row_bits, 0, h->mb.i_mb_height * sizeof(int) ); memset( h->fdec->f_row_qp, 0, h->mb.i_mb_height * sizeof(float) ); memset( h->fdec->f_row_qscale, 0, h->mb.i_mb_height * sizeof(float) ); rc->row_pred = rc->row_preds[h->sh.i_type]; rc->buffer_rate = h->fenc->i_cpb_duration * rc->vbv_max_rate * h->sps->vui.i_num_units_in_tick / h->sps->vui.i_time_scale; update_vbv_plan( h, overhead ); //根据编码级别(h->param.i_level_idc)设置帧大小上限(rc->frame_size_maximum) const x264_level_t *l = x264_levels; while( l->level_idc != 0 && l->level_idc != h->param.i_level_idc ) l++; int mincr = l->mincr; if( h->param.b_bluray_compat ) mincr = 4; //根据编码级别(h->param.i_level_idc)设置帧大小上限 /* Profiles above High don't require minCR, so just set the maximum to a large value. */ if( h->sps->i_profile_idc > PROFILE_HIGH ) rc->frame_size_maximum = 1e9; else { /* The spec has a bizarre special case for the first frame. */ if( h->i_frame == 0 ) { //384 * ( Max( PicSizeInMbs, fR * MaxMBPS ) + MaxMBPS * ( tr( 0 ) - tr,n( 0 ) ) ) / MinCR double fr = 1. / (h->param.i_level_idc >= 60 ? 300 : 172); int pic_size_in_mbs = h->mb.i_mb_width * h->mb.i_mb_height; rc->frame_size_maximum = 384 * BIT_DEPTH * X264_MAX( pic_size_in_mbs, fr*l->mbps ) / mincr; } else { //384 * MaxMBPS * ( tr( n ) - tr( n - 1 ) ) / MinCR rc->frame_size_maximum = 384 * BIT_DEPTH * ((double)h->fenc->i_cpb_duration * h->sps->vui.i_num_units_in_tick / h->sps->vui.i_time_scale) * l->mbps / mincr; } } } //如果是非B帧,则将rc->bframes设置为编码器的B帧数(h->fenc->i_bframes)。这是为了在非B帧的情况下保持与B帧相关的设置一致 if( h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_B ) rc->bframes = h->fenc->i_bframes; //如果启用了ABR(平均码率控制),则根据码率估计的量化参数(qscale)计算QP值。rate_estimate_qscale(h)用于估计当前帧的qscale值。然后使用qscale2qp()将qscale转换为QP if( rc->b_abr ) { q = qscale2qp( rate_estimate_qscale( h ) ); } else if( rc->b_2pass ) { rce->new_qscale = rate_estimate_qscale( h ); q = qscale2qp( rce->new_qscale ); } else /* CQP */ { //如果不是ABR和二次编码,则根据不同的条件选择QP值。如果当前切片类型是B帧,并且前一帧被保留为参考帧(h->fdec->b_kept_as_ref为真),则使用B帧和P帧的QP常数的平均值作为QP。否则,根据切片类型选择相应的QP常数 if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B && h->fdec->b_kept_as_ref ) q = ( rc->qp_constant[ SLICE_TYPE_B ] + rc->qp_constant[ SLICE_TYPE_P ] ) / 2; else q = rc->qp_constant[ h->sh.i_type ]; if( zone ) { if( zone->b_force_qp ) q += zone->i_qp - rc->qp_constant[SLICE_TYPE_P]; else q -= 6*log2f( zone->f_bitrate_factor ); } } if( i_force_qp != X264_QP_AUTO )//如果传入的i_force_qp不等于X264_QP_AUTO,则将强制指定的QP值减去1 q = i_force_qp - 1; //将计算得到的QP值q限制在规定的QP范围内(h->param.rc.i_qp_min和h->param.rc.i_qp_max) q = x264_clip3f( q, h->param.rc.i_qp_min, h->param.rc.i_qp_max ); rc->qpa_rc = rc->qpa_rc_prev = rc->qpa_aq = rc->qpa_aq_prev = 0; h->fdec->f_qp_avg_rc = h->fdec->f_qp_avg_aq = rc->qpm = q; if( rce ) rce->new_qp = q; accum_p_qp_update( h, rc->qpm ); if( h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_B )//根据当前帧的切片类型,更新rc->last_non_b_pict_type,用于后续的参考帧类型选择 rc->last_non_b_pict_type = h->sh.i_type; }4.估计量化参数rate_estimate_qscale
根据总比特数、预测的比特数和期望的比特数之间的差异以及ABR缓冲区的大小来动态调整量化参数,以实现自适应比特率控制,代码如下:
//用于在编码过程中根据已使用的实际比特数更新帧的qscale(量化参数)值 // update qscale for 1 frame based on actual bits used so far static float rate_estimate_qscale( x264_t *h ) { float q; x264_ratecontrol_t *rcc = h->rc; ratecontrol_entry_t rce = {0}; int pict_type = h->sh.i_type; int64_t total_bits = 8*(h->stat.i_frame_size[SLICE_TYPE_I] + h->stat.i_frame_size[SLICE_TYPE_P] + h->stat.i_frame_size[SLICE_TYPE_B]) - rcc->filler_bits_sum;//总比特数通过计算I帧、P帧和B帧的帧大小之和,并减去填充比特数(rcc->filler_bits_sum)而得到 if( rcc->b_2pass ) { rce = *rcc->rce; if( pict_type != rce.pict_type ) { x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "slice=%c but 2pass stats say %c\n", slice_type_to_char[pict_type], slice_type_to_char[rce.pict_type] ); } } if( pict_type == SLICE_TYPE_B ) { /* B-frames don't have independent ratecontrol, but rather get the * average QP of the two adjacent P-frames + an offset */ //获取与当前B帧相邻的两个P帧的信息:是否为I帧(i0和i1) int i0 = IS_X264_TYPE_I(h->fref_nearest[0]->i_type); int i1 = IS_X264_TYPE_I(h->fref_nearest[1]->i_type); int dt0 = abs(h->fenc->i_poc - h->fref_nearest[0]->i_poc);//与当前帧的POC(Presentation Order Count)之差(dt0和dt1) int dt1 = abs(h->fenc->i_poc - h->fref_nearest[1]->i_poc); float q0 = h->fref_nearest[0]->f_qp_avg_rc;//两个P帧的平均QP值(q0和q1) float q1 = h->fref_nearest[1]->f_qp_avg_rc; //如果相邻的P帧是B参考帧(X264_TYPE_BREF),则将其QP值减去偏移量(rcc->pb_offset/2) if( h->fref_nearest[0]->i_type == X264_TYPE_BREF ) q0 -= rcc->pb_offset/2; if( h->fref_nearest[1]->i_type == X264_TYPE_BREF ) q1 -= rcc->pb_offset/2; if( i0 && i1 )//如果两个P帧都是I帧,则将两个P帧的QP值的平均值加上偏移量(rcc->ip_offset)作为当前帧的QP值 q = (q0 + q1) / 2 + rcc->ip_offset; else if( i0 )//如果只有一个P帧是I帧,则将该P帧的QP值作为当前帧的QP值 q = q1; else if( i1 ) q = q0; else//如果两个P帧都不是I帧,则根据相邻P帧的QP值和POC差值的加权平均值作为当前帧的QP值 q = (q0*dt1 + q1*dt0) / (dt0 + dt1); //如果当前帧被保留为参考帧(h->fenc->b_kept_as_ref为真),则将QP值加上偏移量(rcc->pb_offset/2) if( h->fenc->b_kept_as_ref ) q += rcc->pb_offset/2; else//将QP值加上偏移量(rcc->pb_offset) q += rcc->pb_offset; //将QP值转换为qscale值,并存储在变量q中 rcc->qp_novbv = q; q = qp2qscale( q ); if( rcc->b_2pass ) rcc->frame_size_planned = qscale2bits( &rce, q ); else rcc->frame_size_planned = predict_size( rcc->pred_b_from_p, q, h->fref[1][h->i_ref[1]-1]->i_satd ); /* Limit planned size by MinCR */ if( rcc->b_vbv ) rcc->frame_size_planned = X264_MIN( rcc->frame_size_planned, rcc->frame_size_maximum ); rcc->frame_size_estimated = rcc->frame_size_planned; /* For row SATDs */ if( rcc->b_vbv ) rcc->last_satd = x264_rc_analyse_slice( h ); return q; } else { //计算ABR缓冲区的大小 double abr_buffer = 2 * rcc->rate_tolerance * rcc->bitrate; double predicted_bits = total_bits; if( h->i_thread_frames > 1 )//对每个线程的帧进行处理 { int j = rcc - h->thread[0]->rc; for( int i = 1; i < h->i_thread_frames; i++ ) { x264_t *t = h->thread[(j+i) % h->i_thread_frames]; double bits = t->rc->frame_size_planned; if( !t->b_thread_active ) continue; bits = X264_MAX(bits, t->rc->frame_size_estimated); predicted_bits += bits; } } if( rcc->b_2pass ) { double lmin = rcc->lmin[pict_type]; double lmax = rcc->lmax[pict_type]; double diff; /* Adjust ABR buffer based on distance to the end of the video. */ if( rcc->num_entries > h->i_frame ) { double final_bits = rcc->entry_out[rcc->num_entries-1]->expected_bits; double video_pos = rce.expected_bits / final_bits; double scale_factor = sqrt( (1 - video_pos) * rcc->num_entries ); abr_buffer *= 0.5 * X264_MAX( scale_factor, 0.5 ); } diff = predicted_bits - rce.expected_bits; q = rce.new_qscale; q /= x264_clip3f((abr_buffer - diff) / abr_buffer, .5, 2); if( h->i_frame >= rcc->fps && rcc->expected_bits_sum >= 1 ) { /* Adjust quant based on the difference between * achieved and expected bitrate so far */ double cur_time = (double)h->i_frame / rcc->num_entries; double w = x264_clip3f( cur_time*100, 0.0, 1.0 ); q *= pow( (double)total_bits / rcc->expected_bits_sum, w ); } rcc->qp_novbv = qscale2qp( q ); if( rcc->b_vbv ) { /* Do not overflow vbv */ double expected_size = qscale2bits( &rce, q ); double expected_vbv = rcc->buffer_fill + rcc->buffer_rate - expected_size; double expected_fullness = rce.expected_vbv / rcc->buffer_size; double qmax = q*(2 - expected_fullness); double size_constraint = 1 + expected_fullness; qmax = X264_MAX( qmax, rce.new_qscale ); if( expected_fullness < .05 ) qmax = lmax; qmax = X264_MIN(qmax, lmax); while( ((expected_vbv < rce.expected_vbv/size_constraint) && (q < qmax)) || ((expected_vbv < 0) && (q < lmax))) { q *= 1.05; expected_size = qscale2bits(&rce, q); expected_vbv = rcc->buffer_fill + rcc->buffer_rate - expected_size; } rcc->last_satd = x264_rc_analyse_slice( h ); } q = x264_clip3f( q, lmin, lmax ); } else /* 1pass ABR */ { /* Calculate the quantizer which would have produced the desired * average bitrate if it had been applied to all frames so far. * Then modulate that quant based on the current frame's complexity * relative to the average complexity so far (using the 2pass RCEQ). * Then bias the quant up or down if total size so far was far from * the target. * Result: Depending on the value of rate_tolerance, there is a * tradeoff between quality and bitrate precision. But at large * tolerances, the bit distribution approaches that of 2pass. */ double wanted_bits, overflow = 1; //计算当前帧的复杂度(last_satd),并更新短期复杂度和复杂度计数 rcc->last_satd = x264_rc_analyse_slice( h ); rcc->short_term_cplxsum *= 0.5; rcc->short_term_cplxcount *= 0.5; rcc->short_term_cplxsum += rcc->last_satd / (CLIP_DURATION(h->fenc->f_duration) / BASE_FRAME_DURATION); rcc->short_term_cplxcount ++; rce.tex_bits = rcc->last_satd; rce.blurred_complexity = rcc->short_term_cplxsum / rcc->short_term_cplxcount; rce.mv_bits = 0; rce.p_count = rcc->nmb; rce.i_count = 0; rce.s_count = 0; rce.qscale = 1; rce.pict_type = pict_type; rce.i_duration = h->fenc->i_duration; //如果使用的是恒定质量模式(X264_RC_CRF),则调用get_qscale函数来获取量化参数(q) if( h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CRF ) { q = get_qscale( h, &rce, rcc->rate_factor_constant, h->fenc->i_frame ); } else { //调用get_qscale函数来根据帧的期望比特数和复杂度平均值来获取量化参数(q) q = get_qscale( h, &rce, rcc->wanted_bits_window / rcc->cplxr_sum, h->fenc->i_frame ); /* ABR code can potentially be counterproductive in CBR, so just don't bother. * Don't run it if the frame complexity is zero either. */ if( !rcc->b_vbv_min_rate && rcc->last_satd ) { // FIXME is it simpler to keep track of wanted_bits in ratecontrol_end? int i_frame_done = h->i_frame; double time_done = i_frame_done / rcc->fps; if( h->param.b_vfr_input && i_frame_done > 0 ) time_done = ((double)(h->fenc->i_reordered_pts - h->i_reordered_pts_delay)) * h->param.i_timebase_num / h->param.i_timebase_den; wanted_bits = time_done * rcc->bitrate;//计算已编码帧的时间(time_done)和期望比特数(wanted_bits) if( wanted_bits > 0 ) { abr_buffer *= X264_MAX( 1, sqrt( time_done ) ); overflow = x264_clip3f( 1.0 + (predicted_bits - wanted_bits) / abr_buffer, .5, 2 ); q *= overflow;//根据预测的比特数与期望比特数之间的差异以及ABR缓冲区的大小调整量化参数(q)的值 } } } //如果当前帧是关键帧(SLICE_TYPE_I)且最大关键帧间隔(i_keyint_max)大于1,并且上一帧的非B帧的类型不是关键帧,进行以下操作 if( pict_type == SLICE_TYPE_I && h->param.i_keyint_max > 1 /* should test _next_ pict type, but that isn't decided yet */ && rcc->last_non_b_pict_type != SLICE_TYPE_I ) { q = qp2qscale( rcc->accum_p_qp / rcc->accum_p_norm ); q /= h->param.rc.f_ip_factor; } else if( h->i_frame > 0 ) { if( h->param.rc.i_rc_method != X264_RC_CRF ) { //根据溢出值(overflow)和帧类型的上一次量化参数(last_qscale_for)计算量化参数的上下限(lmin和lmax /* Asymmetric clipping, because symmetric would prevent * overflow control in areas of rapidly oscillating complexity */ double lmin = rcc->last_qscale_for[pict_type] / rcc->lstep; double lmax = rcc->last_qscale_for[pict_type] * rcc->lstep; if( overflow > 1.1 && h->i_frame > 3 ) lmax *= rcc->lstep;//如果溢出值大于1.1并且已经处理了3帧以上,则将上限扩大(lmax) else if( overflow < 0.9 ) lmin /= rcc->lstep;//如果溢出值小于0.9,则将下限缩小(lmin) q = x264_clip3f(q, lmin, lmax); } } else if( h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CRF && rcc->qcompress != 1 ) { q = qp2qscale( ABR_INIT_QP ) / h->param.rc.f_ip_factor; } rcc->qp_novbv = qscale2qp( q ); //FIXME use get_diff_limited_q() ? q = clip_qscale( h, pict_type, q ); } rcc->last_qscale_for[pict_type] = rcc->last_qscale = q; if( !(rcc->b_2pass && !rcc->b_vbv) && h->fenc->i_frame == 0 ) rcc->last_qscale_for[SLICE_TYPE_P] = q * h->param.rc.f_ip_factor; if( rcc->b_2pass ) rcc->frame_size_planned = qscale2bits( &rce, q ); else rcc->frame_size_planned = predict_size( &rcc->pred[h->sh.i_type], q, rcc->last_satd ); /* Always use up the whole VBV in this case. */ if( rcc->single_frame_vbv ) rcc->frame_size_planned = rcc->buffer_rate; /* Limit planned size by MinCR */ if( rcc->b_vbv )//如果启用了VBV(b_vbv),将帧大小(frame_size_planned)限制在最大帧大小(frame_size_maximum)和预测帧大小之间,以遵守最小比特率限制(MinCR) rcc->frame_size_planned = X264_MIN( rcc->frame_size_planned, rcc->frame_size_maximum ); rcc->frame_size_estimated = rcc->frame_size_planned; return q; } }5.vbv码率调整clip_qscale
目的是根据VBV的约束条件对量化参数进行修剪,以控制帧的比特率和缓冲区填充状态,同时根据B帧的复杂度和缓冲区的填充状态来调整量化参数,以控制比特率和缓冲区的使用情况,代码如下:
// apply VBV constraints and clip qscale to between lmin and lmax static double clip_qscale( x264_t *h, int pict_type, double q ) { x264_ratecontrol_t *rcc = h->rc; double lmin = rcc->lmin[pict_type]; double lmax = rcc->lmax[pict_type]; if( rcc->rate_factor_max_increment ) lmax = X264_MIN( lmax, qp2qscale( rcc->qp_novbv + rcc->rate_factor_max_increment ) ); double q0 = q; /* B-frames are not directly subject to VBV, * since they are controlled by the P-frames' QPs. */ if( rcc->b_vbv && rcc->last_satd > 0 ) { double fenc_cpb_duration = (double)h->fenc->i_cpb_duration * h->sps->vui.i_num_units_in_tick / h->sps->vui.i_time_scale; /* Lookahead VBV: raise the quantizer as necessary such that no frames in * the lookahead overflow and such that the buffer is in a reasonable state * by the end of the lookahead. */ if( h->param.rc.i_lookahead ) { int terminate = 0; /* Avoid an infinite loop. */ for( int iterations = 0; iterations < 1000 && terminate != 3; iterations++ ) { double frame_q[3];// 通过qscale,last预估当前帧如果以当前qscale进行编码可能需要用到的比特数 double cur_bits = predict_size( &rcc->pred[h->sh.i_type], q, rcc->last_satd ); double buffer_fill_cur = rcc->buffer_fill - cur_bits;// 当前水池水量buffer_fill减去预计流出的数量(此处没有加上注入的水量) double target_fill;// 期望当前帧编码后的水池水量 double total_duration = 0; double last_duration = fenc_cpb_duration; frame_q[0] = h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_I ? q * h->param.rc.f_ip_factor : q; frame_q[1] = frame_q[0] * h->param.rc.f_pb_factor; frame_q[2] = frame_q[0] / h->param.rc.f_ip_factor; /* Loop over the planned future frames. */ for( int j = 0; buffer_fill_cur >= 0 && buffer_fill_cur <= rcc->buffer_size; j++ ) { total_duration += last_duration; buffer_fill_cur += rcc->vbv_max_rate * last_duration; int i_type = h->fenc->i_planned_type[j]; int i_satd = h->fenc->i_planned_satd[j]; if( i_type == X264_TYPE_AUTO ) break; i_type = IS_X264_TYPE_I( i_type ) ? SLICE_TYPE_I : IS_X264_TYPE_B( i_type ) ? SLICE_TYPE_B : SLICE_TYPE_P; cur_bits = predict_size( &rcc->pred[i_type], frame_q[i_type], i_satd ); buffer_fill_cur -= cur_bits; last_duration = h->fenc->f_planned_cpb_duration[j]; }//让水池里的水最少保持50%的充盈程度 --- 此处target_fill可以理解为下限警戒线的值 /* Try to get to get the buffer at least 50% filled, but don't set an impossible goal. */ target_fill = X264_MIN( rcc->buffer_fill + total_duration * rcc->vbv_max_rate * 0.5, rcc->buffer_size * 0.5 ); if( buffer_fill_cur < target_fill ) { // 如果buffer_fill_cur小于target_fill即已经达到了下限警戒线的阈值,此时会增大qscale q *= 1.01; terminate |= 1; continue; }//让水池里的水不超过80%的容量 --- 此处的target_fill可以理解为上限警戒线的值 /* Try to get the buffer no more than 80% filled, but don't set an impossible goal. */ target_fill = x264_clip3f( rcc->buffer_fill - total_duration * rcc->vbv_max_rate * 0.5, rcc->buffer_size * 0.8, rcc->buffer_size ); if( rcc->b_vbv_min_rate && buffer_fill_cur > target_fill ) { // 在b_vbv_min_rate成立的情况下(即设定了i_vbv_max_bitrate <= h->param.rc.i_bitrate),如果buffer_fill_cur大于target_fill即已经达到了上限警戒线的阈值,此时会降低qscale q /= 1.01; terminate |= 2; continue; } break; } } /* Fallback to old purely-reactive algorithm: no lookahead. */ else { if( ( pict_type == SLICE_TYPE_P || ( pict_type == SLICE_TYPE_I && rcc->last_non_b_pict_type == SLICE_TYPE_I ) ) && rcc->buffer_fill/rcc->buffer_size < 0.5 ) { q /= x264_clip3f( 2.0*rcc->buffer_fill/rcc->buffer_size, 0.5, 1.0 ); } /* Now a hard threshold to make sure the frame fits in VBV. * This one is mostly for I-frames. */ double bits = predict_size( &rcc->pred[h->sh.i_type], q, rcc->last_satd ); /* For small VBVs, allow the frame to use up the entire VBV. */ double max_fill_factor = h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size >= 5*h->param.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate / rcc->fps ? 2 : 1; /* For single-frame VBVs, request that the frame use up the entire VBV. */ double min_fill_factor = rcc->single_frame_vbv ? 1 : 2; if( bits > rcc->buffer_fill/max_fill_factor ) { double qf = x264_clip3f( rcc->buffer_fill/(max_fill_factor*bits), 0.2, 1.0 ); q /= qf; bits *= qf; } if( bits < rcc->buffer_rate/min_fill_factor ) { double qf = x264_clip3f( bits*min_fill_factor/rcc->buffer_rate, 0.001, 1.0 ); q *= qf; } q = X264_MAX( q0, q ); } /* Check B-frame complexity, and use up any bits that would * overflow before the next P-frame. */ if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_P && !rcc->single_frame_vbv ) { //是在P帧类型的情况下,检查B帧的复杂度,并使用在下一个P帧之前可能溢出的任何比特位 int nb = rcc->bframes;//获取了B帧的数量(nb) double bits = predict_size( &rcc->pred[h->sh.i_type], q, rcc->last_satd );//当前帧(P帧)的比特数估计值(bits) double pbbits = bits; double bbits = predict_size( rcc->pred_b_from_p, q * h->param.rc.f_pb_factor, rcc->last_satd );//计算了B帧的比特数估计值 double space; double bframe_cpb_duration = 0; double minigop_cpb_duration; for( int i = 0; i < nb; i++ ) bframe_cpb_duration += h->fenc->f_planned_cpb_duration[i];//计算了B帧的CPB(Coded Picture Buffer)持续时间 if( bbits * nb > bframe_cpb_duration * rcc->vbv_max_rate ) { //并检查是否超过了VBV的最大比特率限制。如果超过了限制,则将B帧的数量设置为0 nb = 0; bframe_cpb_duration = 0; } pbbits += nb * bbits; //计算了整个Mini-GOP(包括B帧和当前帧)的CPB持续时间 minigop_cpb_duration = bframe_cpb_duration + fenc_cpb_duration; space = rcc->buffer_fill + minigop_cpb_duration*rcc->vbv_max_rate - rcc->buffer_size;//可以确定在下一个P帧之前可以填充的比特数 if( pbbits < space ) { //如果预测的帧大小(pbbits)小于剩余空间(space),则将量化参数(q)根据剩余空间的比例进行调整 q *= X264_MAX( pbbits / space, bits / (0.5 * rcc->buffer_size) ); } q = X264_MAX( q0/2, q ); } /* Apply MinCR and buffer fill restrictions */ double bits = predict_size( &rcc->pred[h->sh.i_type], q, rcc->last_satd ); double frame_size_maximum = X264_MIN( rcc->frame_size_maximum, X264_MAX( rcc->buffer_fill, 0.001 ) );//计算了当前帧的比特数估计值(bits)和帧大小的最大限制 if( bits > frame_size_maximum ) q *= bits / frame_size_maximum;//如果预测的帧大小超过了最大限制,将量化参数(q)根据预测的帧大小和最大限制进行调整 if( !rcc->b_vbv_min_rate ) q = X264_MAX( q0, q ); } if( lmin==lmax ) return lmin; else if( rcc->b_2pass ) { double min2 = log( lmin ); double max2 = log( lmax ); q = (log(q) - min2)/(max2-min2) - 0.5; q = 1.0/(1.0 + exp( -4*q )); q = q*(max2-min2) + min2; return exp( q ); } else return x264_clip3f( q, lmin, lmax ); }6.宏块级码控x264_ratecontrol_mb
代码如下:
int x264_ratecontrol_mb( x264_t *h, int bits ) { x264_ratecontrol_t *rc = h->rc; const int y = h->mb.i_mb_y; //将当前宏块的比特数(bits)累加到帧解码器结构体(h->fdec)中的行比特数(h->fdec->i_row_bits[y])中 h->fdec->i_row_bits[y] += bits; rc->qpa_aq += h->mb.i_qp;//将当前宏块的QP值(h->mb.i_qp)累加到(rc)中的AQ(adaptive quantization)变量(rc->qpa_aq)中 //检查当前宏块是否为当前图像的最后一个宏块,如果不是,则返回0 if( h->mb.i_mb_x != h->mb.i_mb_width - 1 ) return 0; //在处理完一行宏块后,执行一些清理操作,调用x264_emms()函数 x264_emms(); rc->qpa_rc += rc->qpm * h->mb.i_mb_width;//将当前宏块的QP值乘以宏块宽度(h->mb.i_mb_width),并累加到RC(ratecontrol)变量(rc->qpa_rc)中 if( !rc->b_vbv ) return 0; //将QP值转换为qscale值并存储到帧解码器结构体中的行QP数组(h->fdec->f_row_qp[y])中 float qscale = qp2qscale( rc->qpm ); h->fdec->f_row_qp[y] = rc->qpm; h->fdec->f_row_qscale[y] = qscale; //更新预测器(predictor),用于根据预测的大小差异调整质量参数 update_predictor( &rc->row_pred[0], qscale, h->fdec->i_row_satd[y], h->fdec->i_row_bits[y] ); if( h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I && rc->qpm < h->fref[0][0]->f_row_qp[y] )//如果当前帧不是I帧且当前QP值小于参考帧的QP值,则更新第二个预测器 update_predictor( &rc->row_pred[1], qscale, h->fdec->i_row_satds[0][0][y], h->fdec->i_row_bits[y] ); /* update ratecontrol per-mbpair in MBAFF */ if( SLICE_MBAFF && !(y&1) )//如果是MBAFF(宏块自适应帧场)模式且当前宏块是帧场对中的第一个宏块,则返回0 return 0; /* FIXME: We don't currently support the case where there's a slice * boundary in between. *///判断是否可以重新编码当前行,即判断是否存在切片边界。如果存在切片边界,暂时不支持该情况,返回0 int can_reencode_row = h->sh.i_first_mb <= ((h->mb.i_mb_y - SLICE_MBAFF) * h->mb.i_mb_stride); //根据先前行的QP值(prev_row_qp)和一些参数计算新的QP范围(qp_min和qp_max)以及步长(step_size) /* tweak quality based on difference from predicted size */ float prev_row_qp = h->fdec->f_row_qp[y]; float qp_absolute_max = h->param.rc.i_qp_max; if( rc->rate_factor_max_increment ) qp_absolute_max = X264_MIN( qp_absolute_max, rc->qp_novbv + rc->rate_factor_max_increment ); float qp_max = X264_MIN( prev_row_qp + h->param.rc.i_qp_step, qp_absolute_max ); float qp_min = X264_MAX( prev_row_qp - h->param.rc.i_qp_step, h->param.rc.i_qp_min ); float step_size = 0.5f; float slice_size_planned = h->param.b_sliced_threads ? rc->slice_size_planned : rc->frame_size_planned; float bits_so_far = row_bits_so_far( h, y );//根据切片大小的计划值(slice_size_planned)和已经编码的比特数(bits_so_far),计算最大帧误差(max_frame_error)和最大帧大小(max_frame_size) float max_frame_error = x264_clip3f( 1.0 / h->mb.i_mb_height, 0.05, 0.25 ); float max_frame_size = rc->frame_size_maximum - rc->frame_size_maximum * max_frame_error; max_frame_size = X264_MIN( max_frame_size, rc->buffer_fill - rc->buffer_rate * max_frame_error ); float size_of_other_slices = 0; if( h->param.b_sliced_threads ) { //如果启用了多线程切片编码,计算其他切片的大小,并根据权重计算其他切片的总大小 float size_of_other_slices_planned = 0; for( int i = 0; i < h->param.i_threads; i++ ) if( h != h->thread[i] ) { size_of_other_slices += h->thread[i]->rc->frame_size_estimated; size_of_other_slices_planned += h->thread[i]->rc->slice_size_planned; } float weight = rc->slice_size_planned / rc->frame_size_planned; size_of_other_slices = (size_of_other_slices - size_of_other_slices_planned) * weight + size_of_other_slices_planned; } if( y < h->i_threadslice_end-1 ) { /* B-frames shouldn't use lower QP than their reference frames. */ if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B ) { //如果当前切片类型为B帧(h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B),将QP下限(qp_min)设置为当前行下一行参考帧的QP值中的较大值 qp_min = X264_MAX( qp_min, X264_MAX( h->fref[0][0]->f_row_qp[y+1], h->fref[1][0]->f_row_qp[y+1] ) ); rc->qpm = X264_MAX( rc->qpm, qp_min ); } //计算剩余缓冲区大小(buffer_left_planned)和码率容忍度(rc_tol) float buffer_left_planned = rc->buffer_fill - rc->frame_size_planned; buffer_left_planned = X264_MAX( buffer_left_planned, 0.f ); /* More threads means we have to be more cautious in letting ratecontrol use up extra bits. */ float rc_tol = buffer_left_planned / h->param.i_threads * rc->rate_tolerance; float b1 = bits_so_far + predict_row_size_to_end( h, y, rc->qpm ) + size_of_other_slices;//根据已经编码的比特数(bits_so_far)和其他切片的大小(size_of_other_slices),计算一个预测的行大小(b1) float trust_coeff = x264_clip3f( bits_so_far / slice_size_planned, 0.0, 1.0 ); //根据当前切片大小的计划值(slice_size_planned)和已经编码的比特数之比(trust_coeff),判断是否可以增加行的QP值 /* Don't increase the row QPs until a sufficient amount of the bits of the frame have been processed, in case a flat */ /* area at the top of the frame was measured inaccurately. */ if( trust_coeff < 0.05f )//如果trust_coeff小于0.05(即编码的比特数较少),将QP上限(qp_max)和QP绝对上限(qp_absolute_max)设置为前一行的QP值(prev_row_qp) qp_max = qp_absolute_max = prev_row_qp; //如果当前切片类型不是I帧,将速率容忍度减半 if( h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I ) rc_tol *= 0.5f; //如果VBV最小速率未启用,则将QP下限(qp_min)设置为QP无VBV(rc->qp_novbv)和当前QP下限(qp_min)中的较大值 if( !rc->b_vbv_min_rate ) qp_min = X264_MAX( qp_min, rc->qp_novbv ); //在循环中,逐步增加QP值(rc->qpm),并根据预测的行大小(predict_row_size_to_end)和其他切片的大小(size_of_other_slices)计算新的行大小(b1) while( rc->qpm < qp_max && ((b1 > rc->frame_size_planned + rc_tol) || (b1 > rc->frame_size_planned && rc->qpm < rc->qp_novbv) || (b1 > rc->buffer_fill - buffer_left_planned * 0.5f)) ) { rc->qpm += step_size; b1 = bits_so_far + predict_row_size_to_end( h, y, rc->qpm ) + size_of_other_slices; } float b_max = b1 + ((rc->buffer_fill - rc->buffer_size + rc->buffer_rate) * 0.90f - b1) * trust_coeff; rc->qpm -= step_size; float b2 = bits_so_far + predict_row_size_to_end( h, y, rc->qpm ) + size_of_other_slices; while( rc->qpm > qp_min && rc->qpm < prev_row_qp && (rc->qpm > h->fdec->f_row_qp[0] || rc->single_frame_vbv) && (b2 < max_frame_size) && ((b2 < rc->frame_size_planned * 0.8f) || (b2 < b_max)) ) { //在循环中,逐步减小QP值(rc->qpm),并根据预测的行大小(predict_row_size_to_end)和其他切片的大小(size_of_other_slices)计算新的行大小(b2) b1 = b2; rc->qpm -= step_size; b2 = bits_so_far + predict_row_size_to_end( h, y, rc->qpm ) + size_of_other_slices; } rc->qpm += step_size; //避免VBV缓冲区下溢或MinCR违规,如果行大小大于最大帧大小,则增加QP值 /* avoid VBV underflow or MinCR violation */ while( rc->qpm < qp_absolute_max && (b1 > max_frame_size) ) { rc->qpm += step_size; b1 = bits_so_far + predict_row_size_to_end( h, y, rc->qpm ) + size_of_other_slices; } //计算估计的帧大小(frame_size_estimated),即行大小减去其他切片的大小 rc->frame_size_estimated = b1 - size_of_other_slices; //如果当前行的QP值超过了QP上限且前一行的QP值小于QP上限,并且可以重新编码当前行,则重新编码当前行 /* If the current row was large enough to cause a large QP jump, try re-encoding it. */ if( rc->qpm > qp_max && prev_row_qp < qp_max && can_reencode_row ) { /* Bump QP to halfway in between... close enough. */ rc->qpm = x264_clip3f( (prev_row_qp + rc->qpm)*0.5f, prev_row_qp + 1.0f, qp_max ); rc->qpa_rc = rc->qpa_rc_prev; rc->qpa_aq = rc->qpa_aq_prev; h->fdec->i_row_bits[y] = 0; h->fdec->i_row_bits[y-SLICE_MBAFF] = 0; return -1; } } else { //处理最后一行的情况。计算估计的帧大小,并进行最后一次尝试重新编码的决策 rc->frame_size_estimated = bits_so_far; /* Last-ditch attempt: if the last row of the frame underflowed the VBV, * try again. */ if( rc->qpm < qp_max && can_reencode_row && (bits_so_far + size_of_other_slices > X264_MIN( rc->frame_size_maximum, rc->buffer_fill )) ) { rc->qpm = qp_max; rc->qpa_rc = rc->qpa_rc_prev; rc->qpa_aq = rc->qpa_aq_prev; h->fdec->i_row_bits[y] = 0; h->fdec->i_row_bits[y-SLICE_MBAFF] = 0; return -1; } } //保存当前的码率控制参数(qpa_rc_prev和qpa_aq_prev) rc->qpa_rc_prev = rc->qpa_rc; rc->qpa_aq_prev = rc->qpa_aq; return 0; }点赞、收藏,会是我继续写作的动力!赠人玫瑰,手有余香
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/127125.html