大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
注: 机翻,未校。
Nvidia GPUs through the ages: The history of Nvidia’s graphics cards
By Adrian Willings
Updated Mar 25, 2023
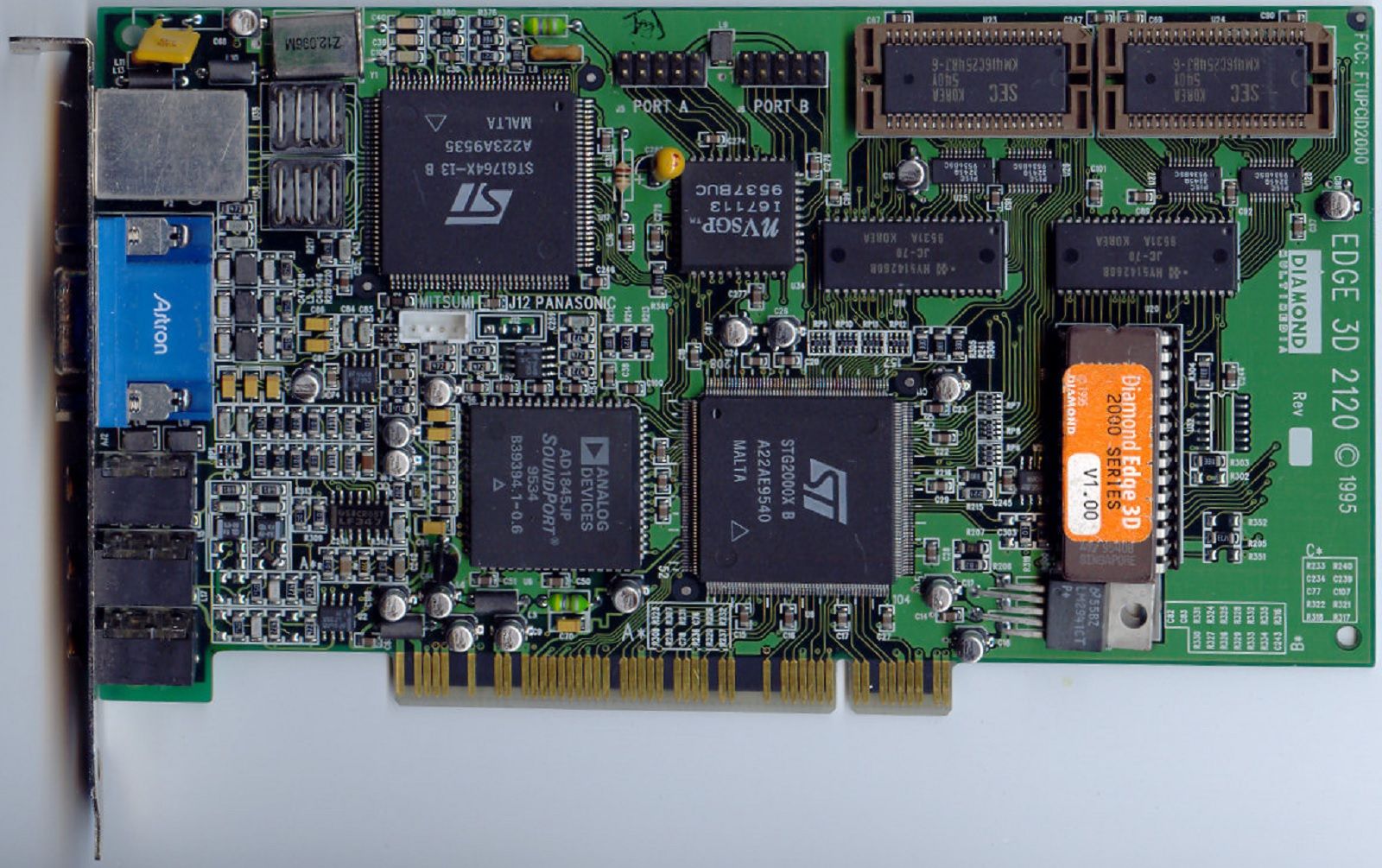
Nvidia NV1 英伟达 NV1(1995)
Swaaye/Wikipedia
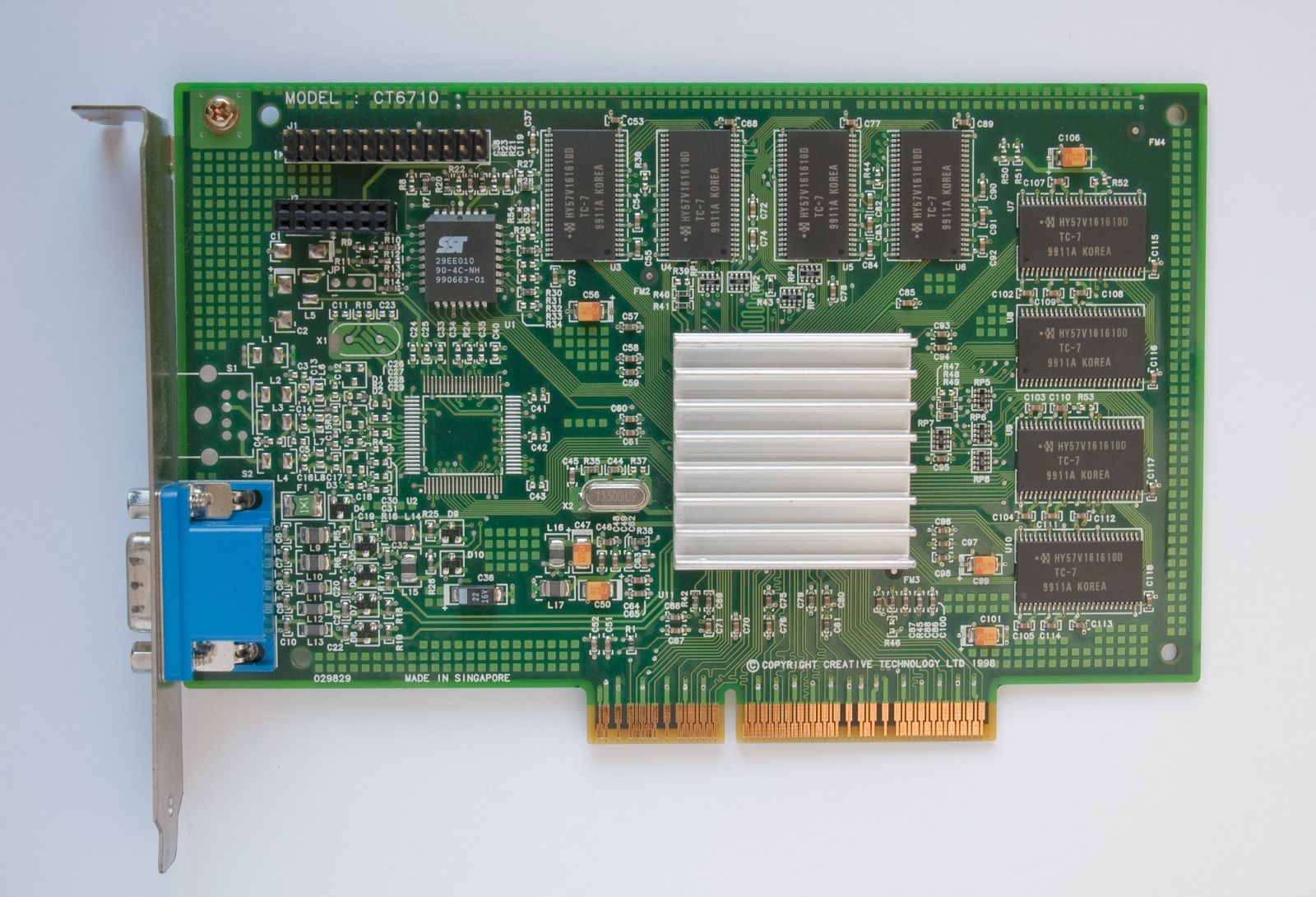
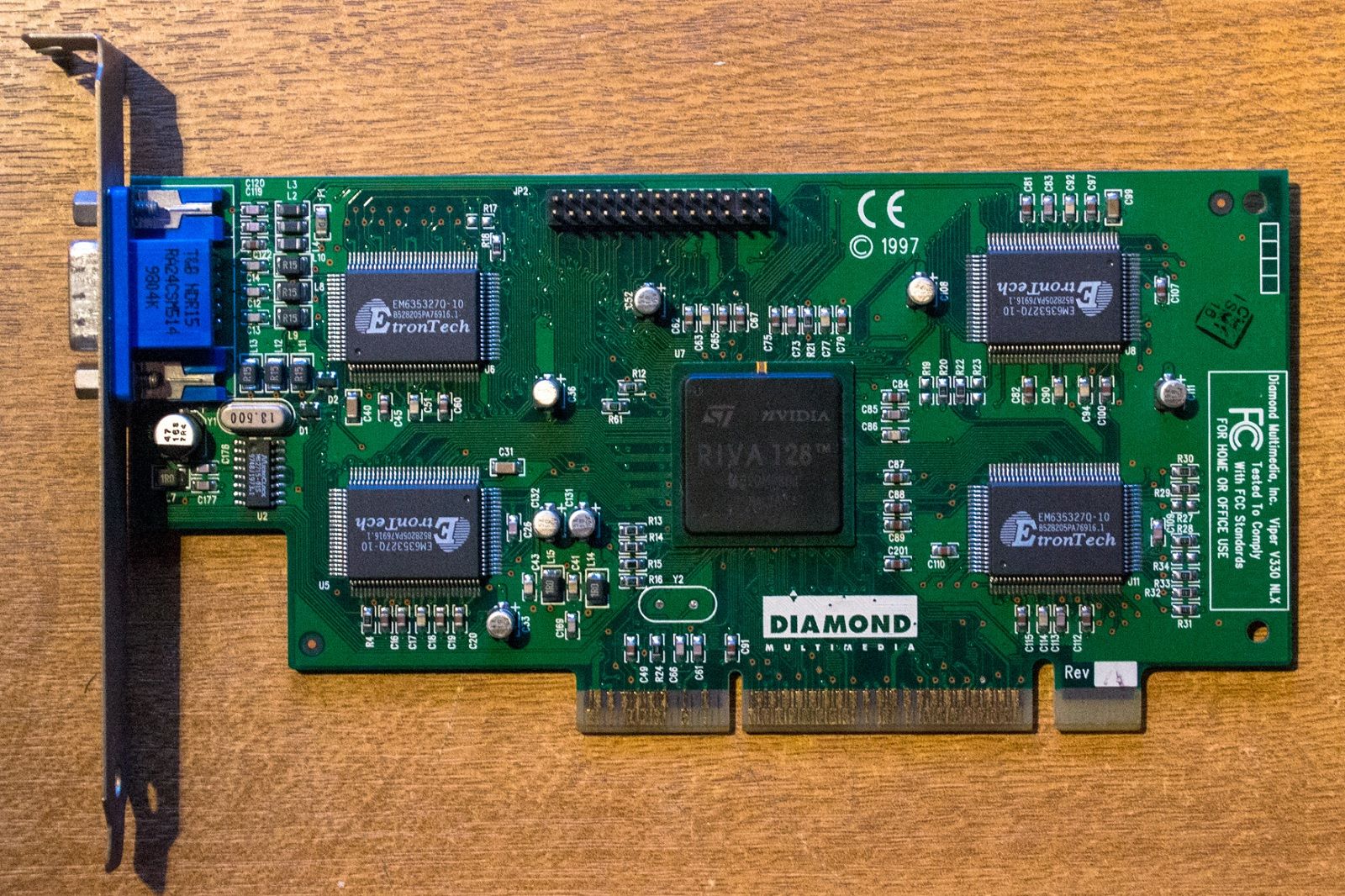
Nvidia RIVA 128 英伟达 RIVA 128(1997)
Mathías Tabó/Wikipedia
Nvidia NV4 英伟达 NV4(1998)
Tors/Wikipedia
Nvidia NV5 英伟达 NV5(1999)
Uwe Hermann/Wikipedia
Nvidia GeForce 256 英伟达 GeForce 256(1999)
Hyins/Wikipedia
Nvidia GeForce2 英伟达 GeForce2(2000)
Hyins/Wikipedia
Nvidia GeForce3 英伟达 GeForce3
Hyins/Wikipedia
Nvidia GeForce FX series Nvidia GeForce FX 系列(2003)
Hyins/Wikipedia
Nvidia GeForce 6 series Nvidia GeForce 6 系列(2004)
Hyins/Wikipedia
Nvidia GeForce7 series Nvidia GeForce7 系列(2005)
FxJ/Wikipedia
Nvidia GeForce8 series Nvidia GeForce8 系列(2006)
Shooke/Wikipedia
Nvidia GeForce9 series Nvidia GeForce9 系列(2008)
Sk/Wikipedia
Nvidia GeForce 400 series Nvidia GeForce 400 系列(2010)
Amazon
Nvidia GeForce 600 series Nvidia GeForce 600 系列(2012)
HanyNAR
Nvidia GeForce 700 series Nvidia GeForce 700 系列(2013)
Marcus Burns
Nvidia GeForce 900 series Nvidia GeForce 900 系列(2014)
Marcus Burns
Nvidia GeForce10 series Nvidia GeForce10 系列(2014)
Marcus Burns
Nvidia GeForce20 series Nvidia GeForce20 系列(2018)
Marcus Burns
Nvidia GeForce30 series Nvidia GeForce30 系列(2020)
Pocket-lint
Nvidia GeForce 40-series Nvidia GeForce 40 系列(2022)
Nvidia
via:
- Nvidia GPUs through the ages: The history of Nvidia’s graphics cards
https://www.pocket-lint.com/nvidia-gpu-history/
- Our History: Innovations Over the Years | NVIDIA
https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/about-nvidia/corporate-timeline/
概览一下:英伟达显卡发展简史
英伟达(Nvidia)自成立以来,在图形处理单元(GPU)领域取得了显著的成就。
初创阶段
- 1993 年:英伟达成立,旨在开发高性能图形芯片。
- 1995 年:发布 NV1,这是英伟达首款产品,集成了 2D 和 3D 图形处理能力,但由于技术限制未能获得市场成功。
进入主流市场
- 1996 年:推出 RIVA 128,成为首款支持硬件加速的 2D 和 3D 图形卡,逐渐获得了市场认可。
- 1999 年:推出 GeForce 256,被称为 “世界上第一款真正的 GPU”,引入了硬件光栅化、变换与光照等功能。
GeForce 系列的崛起
- 2000 年:发布 GeForce2 GTS,进一步提升了 3D 图形性能并支持更高的分辨率。
- 2002 年:推出 GeForce4 系列,增强了游戏性能,并引入了新的图形特性,如 Shader 模型。
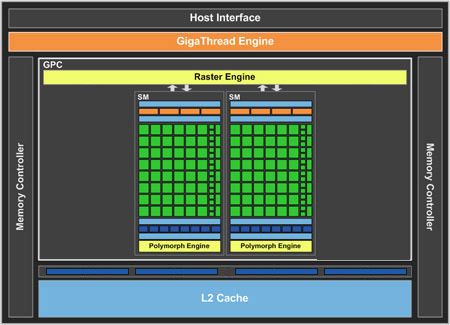
- 2006 年:发布 GeForce 8800 系列,是首款支持 DirectX 10 的 GPU,标志着现代 GPU 架构的开始。
CUDA 和并行计算
- 2006 年:引入 CUDA 架构,使得 GPU 不仅限于图形处理,而可以用于通用计算,开启了 GPU 计算的新篇章。
- 2010 年:发布 Fermi 架构,进一步扩展了 GPU 的计算能力,成为科学计算和深度学习的核心组件。
深度学习与人工智能的兴起
- 2012 年:发布 Kepler 架构,优化了功耗表现,广泛应用于深度学习训练。
- 2016 年:推出 Pascal 架构,支持新一代深度学习框架,极大地提升了计算性能。
- 2018 年:发布 Turing 架构,首次引入实时光线追踪技术,提升了图形渲染质量。
- 2020 年:推出 Ampere 架构,进一步推动了高性能计算和 AI 的边界。
- 2022 年:发布 Ada Lovelace 架构,……
英伟达的显卡发展历程伴随着不断的技术创新与市场需求的变化。从早期的基础图形处理,到如今的深度学习与实时光线追踪,英伟达始终处于图形计算领域的前沿。随着科技的不断进步,未来的显卡将会实现更多的可能性。
另一篇:Nvidia GPU 的历史:从 NV1 到 Turing
注:机翻,未校。
The History of Nvidia GPUs: NV1 to Turing
By Michael Justin Allen Sexton, Yannick Guerrini & Pierre Dandumont
published August 25, 2018
NV1: Nvidia Enters The Market NV1:Nvidia 进入市场
NV3: Riva 128 NV3: Riva 128
The Riva 128, also known as the NV3, launched in 1997 and was considerably more successful. It switched from using quadrilaterals as the most basic geometric primitive to the far more common polygon. This made it easier to add support for the Riva 128 in games. The GPU also used polygon texture mapping with mixed results. This allowed the GPU to render frames more quickly, but it had reduced image quality.
Riva 128,也被称为 NV3,于 1997 年推出,取得了更大的成功。它从使用四边形作为最基本的几何基元转变为更常见的多边形。这使得在游戏中添加对 Riva 128 的支持变得更加容易。GPU 还使用了多边形纹理映射,结果喜忧参半。这允许 GPU 更快地渲染帧,但会降低图像质量。
NV4: The Plot To Drop The Bomb NV4:投下炸弹的阴谋
NV5: Another Explosion NV5:另一次爆炸
NV10: Use The GeForce Luke! NV10:使用 GeForce Luke!
In late 1999, Nvidia announced the GeForce 256 (code-named “NV10”). Prior to the GeForce 256, essentially all video cards were referred to as “graphics accelerators” or simply as “video cards,” but Nvidia opted to call the GeForce 256 a “GPU.” Nvidia packed in several new features with this card including hardware T&L (Transform and Lighting) processing, which allowed the GPU to perform calculations that were typically relegated to the CPU. Since the T&L Engine was fixed-function hardware designed specifically for this task, its throughput was roughly five times higher than a then high-end Pentium III processor clocked at 550 MHz.
1999 年底,Nvidia 发布了 GeForce 256(代号为“NV10”)。在 GeForce 256 之前,基本上所有的显卡都被称为“图形加速器”或简称为“显卡”,但 Nvidia 选择将 GeForce 256 称为“GPU”。Nvidia 在这款卡中加入了几个新功能,包括硬件 T&L(变换和照明)处理,这使得 GPU 能够执行通常由CPU进行的计算。由于T&L引擎是专为此任务设计的固定功能硬件,其吞吐量大约比当时的高端奔腾III处理器高出五倍,频率为550 MHz。
NV11, NV15, NV16: GeForce2 NV11、NV15、NV16:GeForce2
NV20: The GeForce3 NV20:GeForce3
In 2001, the GeForce3 (codenamed “NV20”) arrived as Nvidia’s first DirectX 8-compatible card. The core contained 60 million transistors manufactured at 150 nm, which could be clocked up to 250 MHz. Nvidia introduced a new memory subsystem on the GeForce3 called “Lightspeed Memory Architecture” (LMA), which was designed to compress the Z-buffer and reduce the overall demand on the memory’s limited bandwidth. It was also designed to accelerate FSAA using a special algorithm called “Quincunx.” Overall performance was higher than the GeForce2, but due to the complexity of the GPU it was fairly expensive to produce, and thus carried a high price tag in comparison.
2001 年,GeForce3(代号为“NV20”)作为 Nvidia 的第一款兼容 DirectX 8 的显卡问世。该内核包含 6000 万个以 150 nm 制造的晶体管,时钟频率可达 250 MHz。Nvidia 在 GeForce3 上引入了一个名为“Lightspeed Memory Architecture”(LMA)的新内存子系统,旨在压缩 Z 缓冲区并降低对内存有限带宽的总体需求。它还旨在使用一种称为“Quincunx”的特殊算法来加速 FSAA。整体性能高于 GeForce2,但由于 GPU 的复杂性,它的生产成本相当高,因此相比之下价格较高。
NV2A: Nvidia And The Xbox NV2A:Nvidia 和 Xbox
NV17: GeForce4 (Part 1) NV17:GeForce4(第 1 部分)
NV25: GeForce4 (Part 2) NV25:GeForce4(第 2 部分)
With the NV17 covering the lower-half of the market, Nvidia launched NV25 to cover the high-end. The NV25 was developed as an improvement upon the GeForce3’s architecture, and essentially had the same resources with four pixel pipelines, eight TMUs, and four ROPs. The NV25 did have twice as many vertex shaders (an increase from one to two), however, and it featured the updated LMA-II system. Overall, the NV25 contained 63 million transistors, just 3 million more than the GeForce3. The GeForce4 NV25 also had a clock speed advantage over the GeForce3, ranging between 225 and 300 MHz. The 128MB DDR memory was clocked between 500 to 650 MHz.
由于 NV17 覆盖了低端市场,Nvidia 推出了 NV25 来覆盖高端市场。NV25 是作为 GeForce3 架构的改进而开发的,基本上具有相同的资源,包括 4 个像素管道、8 个 TMU 和 4 个 ROP。然而,NV25 确实有两倍的顶点着色器(从一个增加到两个),并且它具有更新的 LMA-II 系统。总体而言,NV25 包含 6300 万个晶体管,仅比 GeForce3 多 300 万个。GeForce4 NV25 的时钟速度也优于 GeForce3,范围在 225 到 300 MHz 之间。128MB DDR 内存的时钟频率在 500 到 650 MHz 之间。
NV30: The FX 5000 (Part 1) NV30:FX 5000(第 1 部分)
NV35: The FX 5000 Series (Part 2) NV35:FX 5000 系列(第 2 部分)
NV40: Nvidia GeForce 6800 NV40:英伟达 GeForce 6800
NV43: The GeForce 6600 NV43:GeForce 6600
After Nvidia secured its position at the high-end of the GPU market, it turned its attention to producing a new mid-range graphics chip known as the NV43. This GPU was used inside of the Nvidia GeForce 6600, and it had essentially half of the execution resources of the NV40. It also relied on a narrower 128-bit bus. The NV43 had one key advantage, however, as it was shrunk using 110 nm transistors. The reduced number of resources made the NV43 relatively inexpensive to produce, while he new fabrication technology helped reduce power consumption and boost clock speeds by roughly 20% compared to the GeForce 6600.
在 Nvidia 巩固了其在高端 GPU 市场的地位后,它将注意力转向生产一种名为 NV43 的新型中端图形芯片。该 GPU 用于 Nvidia GeForce 6600 内部,它基本上拥有 NV40 一半的执行资源。它还依赖于更窄的 128 位总线。然而,NV43 有一个关键优势,因为它是使用 110 nm 晶体管缩小的。资源数量的减少使 NV43 的生产成本相对低廉,而与 GeForce 6600 相比,新的制造技术有助于降低功耗并将时钟速度提高约 20%。
G70: The GeForce 7800 GTX And GeForce 7800 GTX 512 G70:GeForce 7800 GTX 和 GeForce 7800 GTX 512
G80: GeForce 8000 Series And The Birth Of Tesla G80:GeForce 8000 系列和特斯拉的诞生
G92: GeForce 9000 Series And Tesla Improved G92:GeForce 9000 系列和特斯拉改进
G92 And G92B: GeForce 9000 Series (Continued) G92 和 G92B:GeForce 9000 系列(续)
G92B: The GeForce 100 Series G92B:GeForce 100 系列
GT200: GeForce 200 Series And Tesla 2.0 GT200:GeForce 200 系列和特斯拉 2.0
GT215: The GeForce 300 Series GT215:GeForce 300 系列
GF100: Fermi Arrises In The GeForce 400 GF100:Fermi 在 GeForce 400 中崛起
GF104, 106, 108: Fermi’s Alterted Cores GF104, 106, 108: 费米改变的核
GF110: Fermi Re-Worked GF110:费米再加工
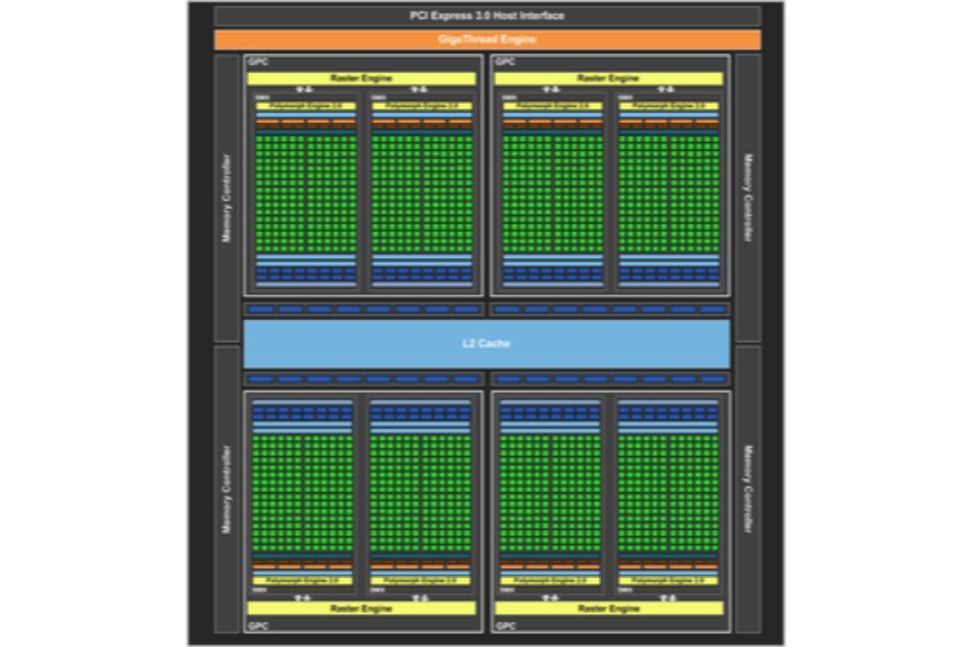
GK104: Kepler And The 600 Series GK104:Kepler 和 600 系列
GK110: Big Kepler GK110: 大开普勒
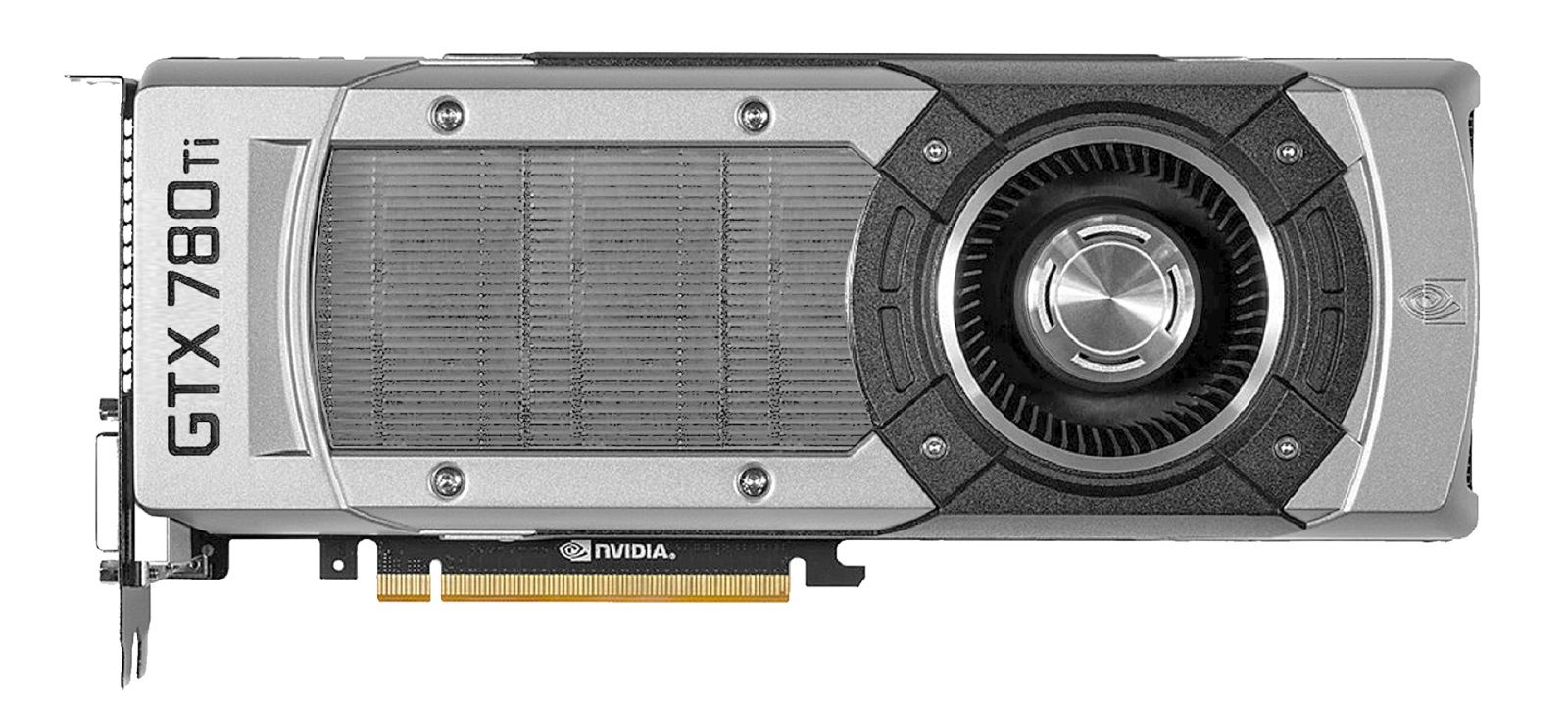
Nvidia’s plan for the GeForce 700 series was essentially to introduce a larger Kepler die. The GK110, which was developed for compute work inside of supercomputers, was perfect for the job. This massive GPU contained 2880 CUDA cores and 240 TMUs. It was first introduced inside the GTX Titan, which had a single SMX disabled, dropping the core count to 2688 CUDA cores, 224 TMUs, and 6GB of RAM. However, the Titan had an unusually high price of $1000, which limited sales. It was later re-introduced as the GTX 780 with just 3GB of RAM and a somewhat more affordable price tag.
Nvidia 对 GeForce 700 系列的计划本质上是引入更大的 Kepler 芯片。GK110 专为超级计算机内部的计算工作而开发,非常适合这项工作。这个巨大的 GPU 包含 2880 个 CUDA 内核和 240 个 TMU。它首先在 GTX Titan 中引入,GTX Titan 禁用了一个 SMX,将核心数量降至 2688 个 CUDA 核心、224 个 TMU 和 6GB RAM。然而,Titan 的 1000 美元价格异常高,这限制了销售。它后来作为 GTX 780 重新推出,只有 3GB 的 RAM,价格更实惠。
GM204: Maxwell GM204: 麦克斯韦
GP104: Pascal GP104: 帕斯卡
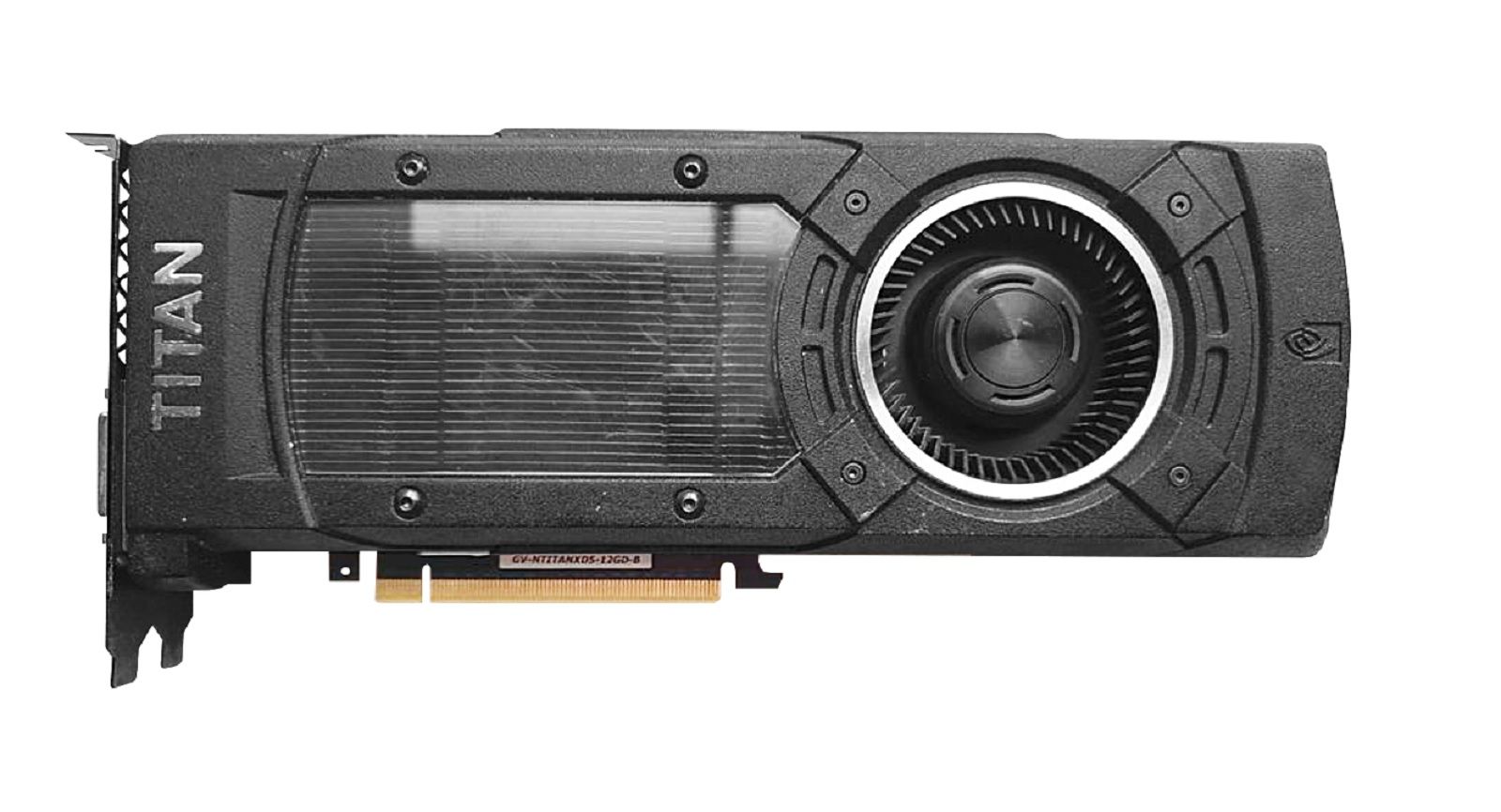
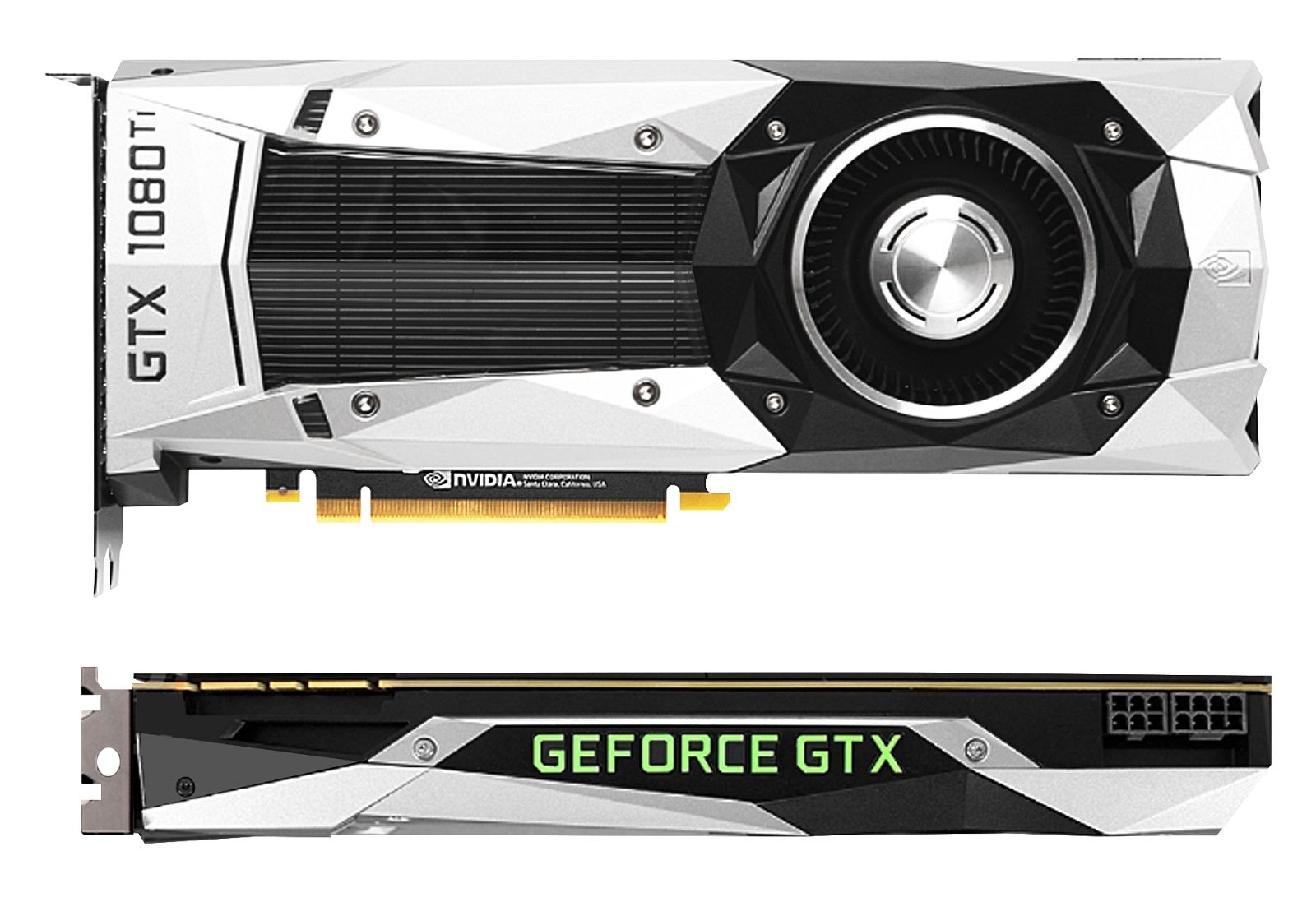
GP102: Titan X, 1080 Ti & Titan XP GP102: Titan X, 1080 Ti&Titan XP
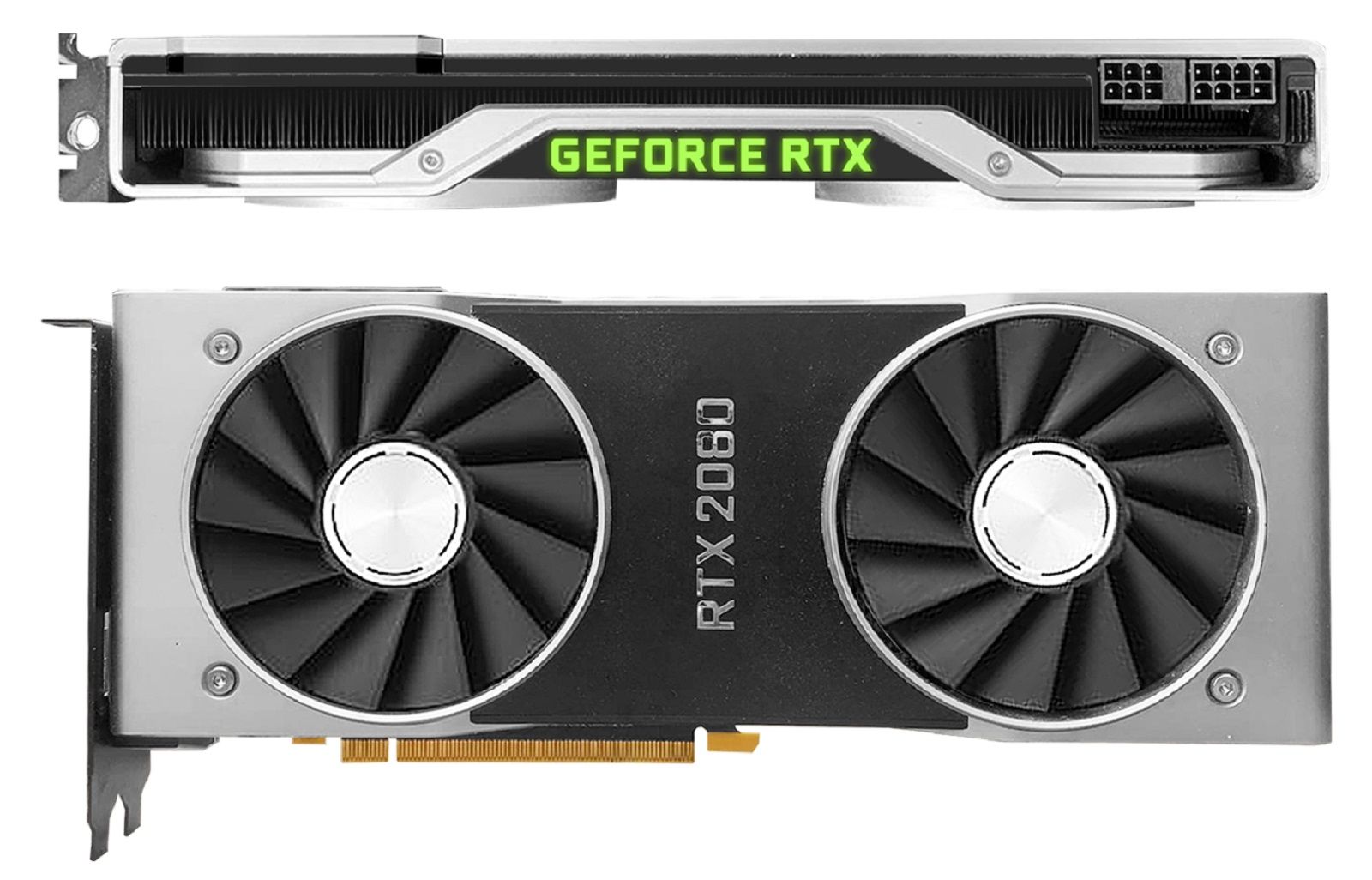
Turing and GeForce RTX Turing 和 GeForce RTX
via:
- The History of Nvidia GPUs: NV1 to Turing | Tom’s Hardware 2018
https://www.tomshardware.com/picturestory/715-history-of-nvidia-gpus.html
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/138319.html