大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。 前面三期我们大略了解了U-Boot的三个常用功能,串口调试输入输出,flash操作,和网络连接,这一期我们来进行U-Boot的改造,我们改造的主题是优化U-Boot的网络功能,我们最终的目的是优化U-Boot的交互界面,最终通过WEB方式与U-Boot进行交互。
U-Boot自带的网络功能都是为了实现从网络上copy数据到本地,并没有引入TCP/IP协议栈的架构,这样限制了很多网络功能的实现,所以我们引进一种新的架构uIP,很多嵌入式领域的人可能都接触过LwIP–一种轻量级的TCP/IP协议栈,其实uIP和LwIP是同一个作者,都是瑞士计算机科学院(Swedish Institute of Computer Science)的Adam Dunkels等开发的,LwIP的含义是Light Weight(轻型)IP协议,uIP的u代表希腊字母的u非常小的意思,也就是说它是比LwIP更小型的TCP/IP协议栈,因为U-Boot不存在任务管理和内存管理,不能算是严格意义的操作系统,所以在U-Boot上移植uIP是更好的选择。在SDK的Tools目录下uip-0-9.zip文件就是uIP的源文件,大家可以解压出来看一下,因为互联网上0.9版本文献比较多,所以没有使用1.0的版本。
uIP是个很实用的东东,比如现在流行的物联网的概念,在前端的信息采集设备通常都是很小的设备,这些小设备与云端的数据通信往往都是基于成熟的IPv4或者IPv6协议,采集设备可能没有自己的操作系统,它的工作任务可能就是在一个时间间隔内上传一次采集数据,这时uIP这种量级的协议栈就有用武之地了,它可以使用很小的内存和CPU资源来完成任务而且不需要底层操作系统支撑。
为了更系统的了解uIP的概念,建议大家阅读一下uIP的参考手册,在源文件的doc目录下。
uIP的代码编写需要遵守一定的结构,而且这种结构最好保持稳定(保持不变)。这个结构主要做以下几个部分任务:1.获得以太网数据包;2.处理ARP报文;3.处理IP报文;4.定期处理TCP和UDP连接;5.定期更新ARP缓冲区。
如果您没有接触过uIP,我建议您阅读一下uIP参考手册的第一章,uIP实际上是一个开源的函数库,参考手册通过File,Data Struction,Module三个方面列出了uIP的内容。我这里的理解在调用uIP的函数前首先要自己编写网络驱动部分,将驱动函数的返回数据提交给uIP,就可以实现ISO7层协议中2层以上的协议,当然对于特殊的协议还需要在uIP的基础上开发。
uIP 协议栈主要提供了三个函数供系统底层调用。即uip_init(), uip_input()和uip_periodic()。其与应用程序的主要接口是UIP_APPCALL( )。
uip_init()是系统初始化时调用的,主要用于初始化协议栈的侦听端口和默认所有连接是关闭的。当网卡驱动收到一个输入包时,将其放入全局缓冲区 uip_buf 中,包的大小由全局变量uip_len 约束。同时将调用uip_input()函数,这个函数将会根据包首部的协议处理这个包并在需要时调用应用程序。当uip_input()返回时,一个输出包同样放在全局缓冲区uip_buf 里,并把大小赋给uip_len。若uip_len 是0,则说明没有包要发送;否则调用底层系统的发包函数就会将包发送到网络上。uIP周期计时用于驱动所有的uIP内部时钟事件:当周期计时激发,每一个TCP连接都会调用uIP函数uip_periodic()。类似于uip_input()函数,uip_periodic()函数返回时,输出的IP 包要放到uip_buf 中,供底层系统查询uip_len 的大小并发送。由于TCP/IP 的应用场景很多,所以应用程序作为单独的模块由用户实现。uIP 协议栈提供一系列接口函数供用户程序调用,其中大部分函数是作为C的宏命令实现的,主要是为了速度、代码大小、堆栈和效率的使用。用户需要将应用层入口程序作为接口提供给uIP协议栈,并将这个函数定义为UIP_APPCALL()。这样以来,uIP在接受到底层传来的数据包后,在需要送到上层应用程序处理的地方,调用UIP_APPCALL(),在不用修改协议栈的情况下可以适配不同的应用程序。
现在我们来动手将uIP移植到U-Boot中并实现一个简单的网络发送和接收的功能。
在uIP参考手册的1.7节提供了一些示例程序,我们就使用1.7.2的示例程序,下面讲述移植过程,这里有个捷径,如果您想跳过复杂的修改过程,可以直接使用我提供的Patch文件,在SDK文件Code/Patch目录下的uip_demo.patch文件,使用方法为: 进入SDK的Code/Uboot目录下 然后执行 patch -p1 < ../Patch/uip_demo.patch
具体的移植过程为:
在U-Boot根目录下建立uip文件夹,将uip0.9中的这些文件复制进去。
uip
├── Makefile
├── uip_arch.c
├── uip_arch.h
├── uip_arp.c
├── uip_arp.h
├── uip.c
├── uipdemo.c
├── uipdemo.h
├── uip.h
└── uipopt.h
红色标注部分为新建文件:
新建uipdemo.h,内容为:
//The configuration for the application: #define UIP_APPCALL example2_app #define UIP_APPSTATE_SIZE sizeof(struct example2_state) struct example2_state { enum {WELCOME_SENT, WELCOME_ACKED} state; }; void example2_init(void); void example2_app(void); 新建uipdemo.c,内容为:
#include "uip.h" void example2_init(void) { uip_listen(HTONS(2345)); } void example2_app(void) { struct example2_state *s; s = (struct example2_state *)uip_conn->appstate; if(uip_connected()) { s->state = WELCOME_SENT; uip_send("Welcome!\n", 9); return; } if(uip_acked() && s->state == WELCOME_SENT) { s->state = WELCOME_ACKED; } if(uip_newdata()) { uip_send("ok\n", 3); } if(uip_rexmit()) { switch(s->state) { case WELCOME_SENT: uip_send("Welcome!\n", 9); break; case WELCOME_ACKED: uip_send("ok\n", 3); break; } } } 其中uipopt.h为uip的参数配置文件,这里需要修改一项配置:
将117行 #define UIP_FIXEDADDR 1
改为: #define UIP_FIXEDADDR 0
否则下一步将uIP的IP地址修改为U-Boot配置地址时会出错。
到这里uIP的移植已经基本完成,下面的操作就是修改U-Boot来调用uIP,下面修改net/net.c文件:
在头部定义部分添加:
int uipdemo_is_running = 0; int arptimer = 0; void NetSendDemo(void); void NetReceiveDemo(volatile uchar * inpkt, int len); void DemoHandler(void); int NetLoopDemo(void);在文件尾部添加函数实体:
/ * * UIPDEMO section */ #define BUF ((struct uip_eth_hdr *)&uip_buf[0]) void NetSendDemo( void ){ volatile uchar *tmpbuf = NetTxPacket; int i; for ( i = 0; i < 40 + UIP_LLH_LEN; i++ ) { tmpbuf[i] = uip_buf[i]; } for( ; i < uip_len; i++ ) { tmpbuf[i] = uip_appdata[ i - 40 - UIP_LLH_LEN ]; } eth_send( NetTxPacket, uip_len ); } void NetReceiveDemo( volatile uchar * inpkt, int len ) { memcpy( uip_buf, ( const void * )inpkt, len ); uip_len = len; if ( BUF->type == htons( UIP_ETHTYPE_IP ) ) { uip_arp_ipin(); uip_input(); if ( uip_len > 0 ) { uip_arp_out(); NetSendDemo(); } } else if( BUF->type == htons( UIP_ETHTYPE_ARP ) ) { uip_arp_arpin(); if ( uip_len > 0 ) { NetSendDemo(); } } } void DemoHandler(void) { // int i; for (i = 0; i < UIP_CONNS; i++) { uip_periodic(i); if (uip_len > 0) { uip_arp_out(); NetSendDemo(); } } // TODO: check this if (++arptimer == 20) { uip_arp_timer(); arptimer = 0; } } /* * * * UIPDEMO for UIP TEST * */ int NetLoopDemo(void){ DECLARE_GLOBAL_DATA_PTR; bd_t *bd = gd->bd; unsigned short int ip[2]; unsigned char ethinit_attempt = 0; struct uip_eth_addr eaddr; #ifdef CONFIG_NET_MULTI NetRestarted = 0; NetDevExists = 0; #endif /* XXX problem with bss workaround */ NetArpWaitPacketMAC = NULL; NetArpWaitTxPacket = NULL; NetArpWaitPacketIP = 0; NetArpWaitReplyIP = 0; NetArpWaitTxPacket = NULL; #ifdef DEBUG printf("File: %s, Func: %s, Line: %d\n", __FILE__,__FUNCTION__ , __LINE__); #endif // if ( !NetTxPacket ) { int i; BUFFER_ELEM *buf; /* * Setup packet buffers, aligned correctly. */ buf = rt2880_free_buf_entry_dequeue( &rt2880_free_buf_list ); NetTxPacket = buf->pbuf; debug( "\n NetTxPacket = 0x%08X \n", NetTxPacket ); for ( i = 0; i < NUM_RX_DESC; i++ ) { buf = rt2880_free_buf_entry_dequeue( &rt2880_free_buf_list ); if ( buf == NULL ) { printf("\n Packet Buffer is empty ! \n"); return ( -1 ); } NetRxPackets[i] = buf->pbuf; printf( "\n NetRxPackets[%d] = 0x%08X\n",i,NetRxPackets[i] ); } } NetTxPacket = KSEG1ADDR( NetTxPacket ); printf("\n KSEG1ADDR(NetTxPacket) = 0x%08X \n",NetTxPacket); if ( !NetArpWaitTxPacket ) { NetArpWaitTxPacket = &NetArpWaitPacketBuf[0] + ( PKTALIGN - 1 ); NetArpWaitTxPacket -= ( ulong )NetArpWaitTxPacket % PKTALIGN; NetArpWaitTxPacketSize = 0; } printf("\n NetLoopHttpd,call eth_halt ! \n"); eth_halt(); #ifdef CONFIG_NET_MULTI eth_set_current(); #endif while( ethinit_attempt < 10 ) { if ( eth_init( bd ) ) { ethinit_attempt = 0; break; } else { ethinit_attempt++; eth_halt(); udelay( ); } } if ( ethinit_attempt > 0 ) { eth_halt(); printf( " Error: couldn't initialize eth (cable disconnected?)!\n\n" ); return( -1 ); } // get MAC address #ifdef CONFIG_NET_MULTI memcpy( NetOurEther, eth_get_dev()->enetaddr, 6 ); #else memcpy( NetOurEther, bd->bi_enetaddr, 6 ); #endif eaddr.addr[0] = NetOurEther[0]; eaddr.addr[1] = NetOurEther[1]; eaddr.addr[2] = NetOurEther[2]; eaddr.addr[3] = NetOurEther[3]; eaddr.addr[4] = NetOurEther[4]; eaddr.addr[5] = NetOurEther[5]; // set MAC address uip_setethaddr( eaddr ); // set ip and other addresses // TODO: do we need this with uIP stack? NetCopyIP( &NetOurIP, &bd->bi_ip_addr ); NetOurGatewayIP = getenv_IPaddr( "gatewayip" ); NetOurSubnetMask = getenv_IPaddr( "netmask" ); #ifdef CONFIG_NET_VLAN NetOurVLAN = getenv_VLAN( "vlan" ); NetOurNativeVLAN = getenv_VLAN( "nvlan" ); #endif // start server... IPaddr_t tmp_ip_addr = ntohl( bd->bi_ip_addr ); printf( "server is starting at IP: %ld.%ld.%ld.%ld\n", ( tmp_ip_addr & 0xff000000 ) >> 24, ( tmp_ip_addr & 0x00ff0000 ) >> 16, ( tmp_ip_addr & 0x0000ff00 ) >> 8, ( tmp_ip_addr & 0x000000ff ) ); //uip init uip_init(); // set local host ip address ip[0] = htons( ( tmp_ip_addr & 0xFFFF0000 ) >> 16 ); ip[1] = htons( tmp_ip_addr & 0x0000FFFF ); uip_sethostaddr( ip ); // set network mask (255.255.255.0 -> local network) ip[0] = htons( ( ( 0xFFFFFF00 & 0xFFFF0000 ) >> 16 ) ); ip[1] = htons( ( 0xFFFFFF00 & 0x0000FFFF ) ); uip_setnetmask( ip ); // should we also set default router ip address? //uip_setdraddr(); //demo init example2_init(); //set uipdeom_is_running uipdemo_is_running = 1; // infinite loop for ( ; ; ) { /* * Check the ethernet for a new packet. * The ethernet receive routine will process it. */ if ( eth_rx() > 0 ) { DemoHandler(); } } return 0; } 修改NetReceive函数,在局部变量定义结束后添加: if ( uipdemo_is_running ) { NetReceiveDemo( inpkt, len ); return; }到这里net/net.c文件保存,修改完成。
然后修改lib_mips文件的board_init_f()函数,在switch(BootType)中添加
case '5': printf("System Enter UIPDEMO.\n"); eth_initialize(gd->bd); NetLoopDemo(); break;接下来修改两个Makefile文件:
根目录下的Makefile: LIBS变量增加 uip/uip.a
uip目录下的Makefile:
# # Makefile for uIP demo # include $(TOPDIR)/config.mk LIB = uip.a OBJS += uip.o uip_arch.o uip_arp.o uipdemo.o all: $(LIB) $(LIB): $(START) $(OBJS) $(AR) crv $@ $(OBJS) .depend: Makefile $(OBJS:.o=.c) $(CC) -M $(CFLAGS) $(OBJS:.o=.c) > $@ sinclude .depend 修改完成,保存退出。
经过上面的修改后就到了检验成果的时候了,将编译好的U-Boot载入到内存并运行,console的输出结果为:
Set info->start[0]=BF000000 flash_protect ON: from 0xBF030000 to 0xBF030FFF ============================================ Ralink UBoot Version: 3.6.0.0 -------------------------------------------- ASIC 3052_MP2 (Port5<->None) DRAM component: 128 Mbits SDR DRAM bus: 32 bit Total memory: 32 MBytes Flash component: NOR Flash Date:Oct 3 2016 Time:19:36:10 ============================================ icache: sets:256, ways:4, linesz:32 ,total:32768 dcache: sets:128, ways:4, linesz:32 ,total:16384 The CPU freq = 384 MHZ estimate memory size =16 Mbytes Please choose the operation: 1: Load system code to SDRAM via TFTP. 2: Load system code then write to Flash via TFTP. 3: Boot system code via Flash (default). 4: Entr boot command line interface. 5: Entr UIP_DEMO. 7: Load Boot Loader code then write to Flash via Serial. 9: Load Boot Loader code then write to Flash via TFTP. You choosed 5 0 System Enter UIPDEMO. NetTxPacket = 0x80FE5780 NetRxPackets[0] = 0x80FE5D80 NetRxPackets[1] = 0x80FE6380 NetRxPackets[2] = 0x80FE6980 NetRxPackets[3] = 0x80FE6F80 NetRxPackets[4] = 0x80FE7580 NetRxPackets[5] = 0x80FE7B80 NetRxPackets[6] = 0x80FE8180 NetRxPackets[7] = 0x80FE8780 NetRxPackets[8] = 0x80FE8D80 NetRxPackets[9] = 0x80FE9380 NetRxPackets[10] = 0x80FE9980 NetRxPackets[11] = 0x80FE9F80 NetRxPackets[12] = 0x80FEA580 NetRxPackets[13] = 0x80FEAB80 NetRxPackets[14] = 0x80FEB180 NetRxPackets[15] = 0x80FEB780 NetRxPackets[16] = 0x80FEBD80 NetRxPackets[17] = 0x80FEC380 NetRxPackets[18] = 0x80FEC980 NetRxPackets[19] = 0x80FECF80 NetRxPackets[20] = 0x80FED580 NetRxPackets[21] = 0x80FEDB80 NetRxPackets[22] = 0x80FEE180 NetRxPackets[23] = 0x80FEE780 KSEG1ADDR(NetTxPacket) = 0xA0FE5780 NetLoopHttpd,call eth_halt ! Trying Eth0 (10/100-M) Waitting for RX_DMA_BUSY status Start... done Header Payload scatter function is Disable !! ETH_STATE_ACTIVE!! server is starting at IP: 192.168.1.2 然后ping 192.168.1.2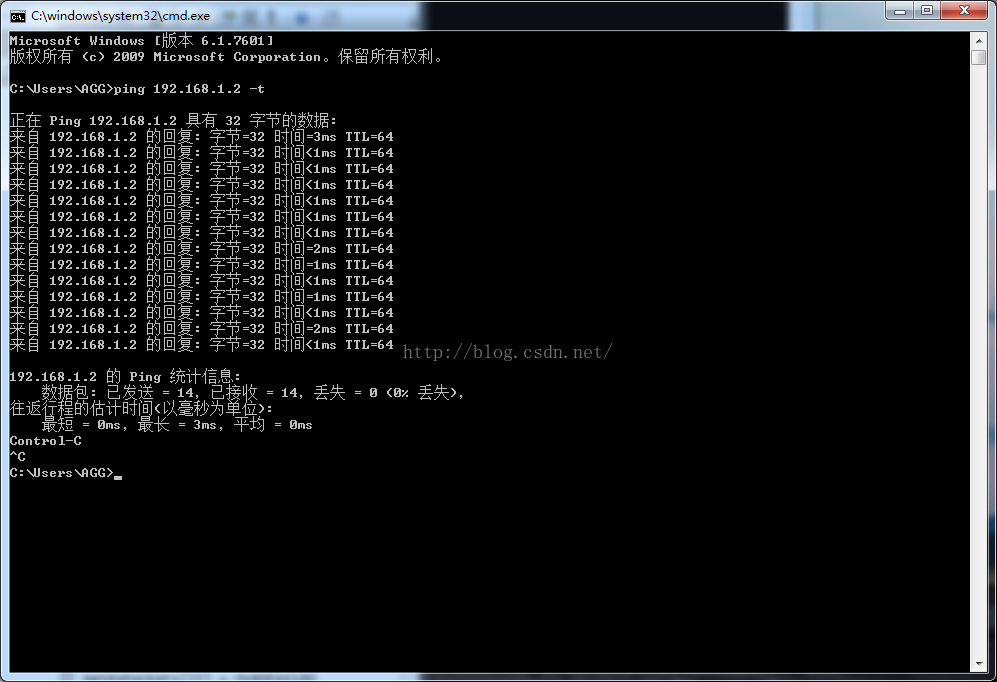
如果icmp包有回应,说明uIP已经正常工作,现在我们来检验example2程序是否正常,使用SDK中Tools文件夹下的SocketTool工具与开发板进行连接,端口为2345,连接后会收到”Welcome!”信息,然后发送任意内容都会收到”ok”信息。
可以使用wireshark分析具体的通信过程: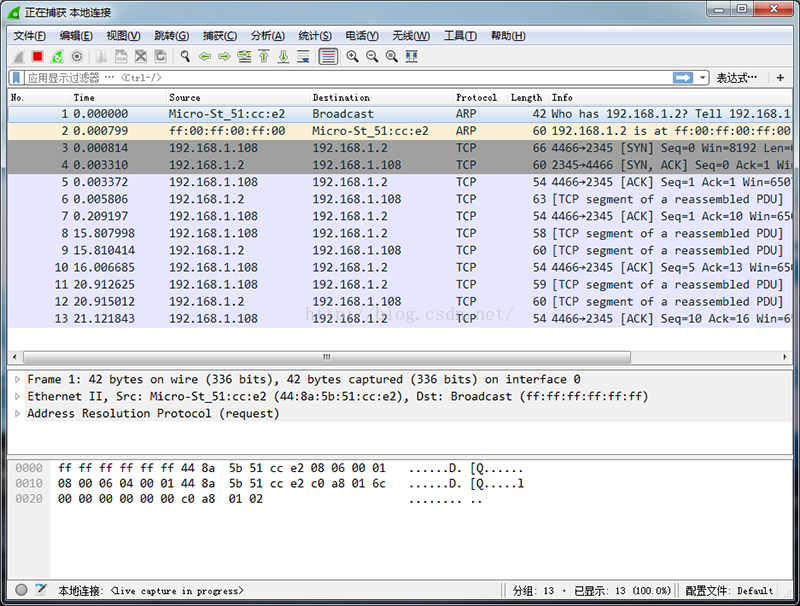
OK,到这里uIP在U-Boot上面的移植已经完成,基本验证了uIP在U-Boot上运行的可行性,下一步就是在这个基础上继续添加httpd功能,实现web failsafe功能,也就是打造传说中的”不死U-Boot”。
———————————-
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/152247.html

