大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
一、为什么需要无锁队列
1.多线程环境下锁的开销:
(1).线程切换:上下文切换、cache损坏;
(2).由于多线程情况下,当一个线程拿到锁以后,其它线程需要经过自旋等待、阻塞态、就绪态,时间浪费在保护队列时的锁争夺上面,而不是用在执行任务上。
2.不能基于锁的情况:
信号处理程序(打断运行)、硬实时系统 (执行时间有限,当一个线程持有锁工作时,时间结束强制切换到其它线程,会造成锁丢失)。
二、无锁消息队列结构:
1.无锁实现
(1).blocking:较弱保证系统向前移动。比如自旋锁
(2).lock free:较强保证系统向前移动,确保有一个线程往前移动。比如:cas(compare_exchange_weak, compare_exchane_strong),允许有限循环。
(3).wait free:强保证系统向前移动, 所有的线程都往前移动。比如exchange,fetch_add.
只能基于原子操作,内存屏障等实现
2.队列实现
–
消费者队列是并发系统中最基本的组件之一,没有
“
放之
”
的并发队列。
1.MPMC:多生产者/多消费者队列。
2.SPSC:单生产者/多消费者队列。
3.MPSC:多生产者/单消费者队列。
4.SPMC:单生产者/单消费者队列。
如果只有1个生产者和1个消费者线程,可以使用SPSC队列而不 是更一般的MPMC队列,它将明显更快。 根据底层数据结构,可以划分为:
Array-based:基于数组;
–
list
–
based
:基于链表;
:混合的;
链表:优点:简单, 动态扩容(无边界),缺点:频繁分配空间,降低了进程性能。
数组:优点:不会频繁的分配空间;缺点:固定队列数量(有边界),可能造成空间浪费。
使用链表+数组以混合的形式实现。
影响队列性能的因素:频繁在堆上分配空间,可以通过内存池解决。
三、无锁消息队列实现:
1.衡量多线程环境队列的性能高低:单位时间内插入元素的个数,单位事件内去除元素的个数;核心是单位时间内处理任务的个数。
2.设计队列原则:
(1).任务的耗时;
(2).生产者和消费者数量
问题:无锁队列是不是一定必有锁队列性能高呢?
答:如果是从操作队列的角度出发,无所队列性能高,如果是从队列所属系统角度出发,不一定,还需要看任务耗时。
3.开源框架
(1).locked_queue
应用场景:队列为空时不阻塞消费者线程,适合任务耗时的情况。
不区分生产者和消费者数量,性能不一定是最佳的。
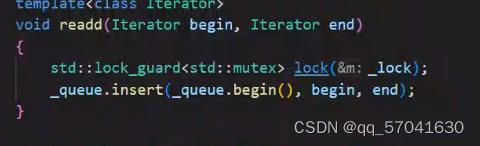
//lockedQueue.h #ifndef MARK_LOCKEDQUEUE_H #define MARK_LOCKEDQUEUE_H #include <deque> #include <mutex> template <class T, typename StorageType = std::deque<T> > class LockedQueue { //! Lock access to the queue. std::mutex _lock; //! Storage backing the queue. StorageType _queue; //! Cancellation flag. volatile bool _canceled; public: //! Create a LockedQueue. LockedQueue() : _canceled(false) { } //! Destroy a LockedQueue. virtual ~LockedQueue() { } //! Adds an item to the queue. void add(const T& item) { lock(); _queue.push_back(item); unlock(); } //! Adds items back to front of the queue template<class Iterator> void readd(Iterator begin, Iterator end) { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(_lock); _queue.insert(_queue.begin(), begin, end); } //! Gets the next result in the queue, if any. bool next(T& result) { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(_lock); if (_queue.empty()) return false; result = _queue.front(); _queue.pop_front(); return true; } template<class Checker> bool next(T& result, Checker& check) { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(_lock); if (_queue.empty()) return false; result = _queue.front(); if (!check.Process(result)) return false; _queue.pop_front(); return true; } //! Peeks at the top of the queue. Check if the queue is empty before calling! Remember to unlock after use if autoUnlock == false. T& peek(bool autoUnlock = false) { lock(); T& result = _queue.front(); if (autoUnlock) unlock(); return result; } //! Cancels the queue. void cancel() { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(_lock); _canceled = true; } //! Checks if the queue is cancelled. bool cancelled() { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(_lock); return _canceled; } //! Locks the queue for access. void lock() { this->_lock.lock(); } //! Unlocks the queue. void unlock() { this->_lock.unlock(); } ///! Calls pop_front of the queue void pop_front() { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(_lock); _queue.pop_front(); } ///! Checks if we're empty or not with locks held bool empty() { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(_lock); return _queue.empty(); } }; #endif每次添加都会使用锁,在lock的构造函数中使用lock,当这个函数体结束有会调用析构函数,析构函数中有unlock
(2).msgqueue
场景:多生产者多消费者
分为put队列和get队列,put队列用于生产者、get队列用于消费者,当put队列和get队列为空时阻塞消费者线程,当get队列为空时,尝试与put队列进行交换,此时生产者和消费者发生碰撞,其他情况,生产者不与消费者发生碰撞(争夺锁)。
msgqueue.h
/* Copyright (c) 2020 Sogou, Inc. Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. Author: Xie Han () */ #ifndef _MSGQUEUE_H_ #define _MSGQUEUE_H_ #include <stddef.h> typedef struct __msgqueue msgqueue_t; #ifdef __cplusplus extern "C" { #endif /* A simple implementation of message queue. The max pending messages may * reach two times 'maxlen' when the queue is in blocking mode, and infinite * in nonblocking mode. 'linkoff' is the offset from the head of each message, * where spaces of one pointer size should be available for internal usage. * 'linkoff' can be positive or negative or zero. */ msgqueue_t *msgqueue_create(size_t maxlen, int linkoff); void msgqueue_put(void *msg, msgqueue_t *queue); void *msgqueue_get(msgqueue_t *queue); void msgqueue_set_nonblock(msgqueue_t *queue); void msgqueue_set_block(msgqueue_t *queue); void msgqueue_destroy(msgqueue_t *queue); #ifdef __cplusplus } #endif #endif msgqueue.c
/* Copyright (c) 2020 Sogou, Inc. Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. Author: Xie Han () */ /* * This message queue originates from the project of Sogou C++ Workflow: * https://github.com/sogou/workflow * * The idea of this implementation is quite simple and obvious. When the * get_list is not empty, the consumer takes a message. Otherwise the consumer * waits till put_list is not empty, and swap two lists. This method performs * well when the queue is very busy, and the number of consumers is big. */ #include <errno.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <pthread.h> #include "msgqueue.h" struct __msgqueue { size_t msg_max; size_t msg_cnt; int linkoff; int nonblock; void *head1; void *head2; void get_head; void put_head; void put_tail; pthread_mutex_t get_mutex; pthread_mutex_t put_mutex; pthread_cond_t get_cond; pthread_cond_t put_cond; }; void msgqueue_set_nonblock(msgqueue_t *queue) { queue->nonblock = 1; pthread_mutex_lock(&queue->put_mutex); pthread_cond_signal(&queue->get_cond); pthread_cond_broadcast(&queue->put_cond); pthread_mutex_unlock(&queue->put_mutex); } void msgqueue_set_block(msgqueue_t *queue) { queue->nonblock = 0; } static size_t __msgqueue_swap(msgqueue_t *queue) { void get_head = queue->get_head; size_t cnt; queue->get_head = queue->put_head; pthread_mutex_lock(&queue->put_mutex); while (queue->msg_cnt == 0 && !queue->nonblock) pthread_cond_wait(&queue->get_cond, &queue->put_mutex); cnt = queue->msg_cnt; if (cnt > queue->msg_max - 1) pthread_cond_broadcast(&queue->put_cond); queue->put_head = get_head; queue->put_tail = get_head; queue->msg_cnt = 0; pthread_mutex_unlock(&queue->put_mutex); return cnt; } void msgqueue_put(void *msg, msgqueue_t *queue) { void link = (void )((char *)msg + queue->linkoff); *link = NULL; pthread_mutex_lock(&queue->put_mutex); while (queue->msg_cnt > queue->msg_max - 1 && !queue->nonblock) pthread_cond_wait(&queue->put_cond, &queue->put_mutex); *queue->put_tail = link; queue->put_tail = link; queue->msg_cnt++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&queue->put_mutex); pthread_cond_signal(&queue->get_cond); } void *msgqueue_get(msgqueue_t *queue) { void *msg; pthread_mutex_lock(&queue->get_mutex); if (*queue->get_head || __msgqueue_swap(queue) > 0) { msg = (char *)*queue->get_head - queue->linkoff; *queue->get_head = *(void )*queue->get_head; } else msg = NULL; pthread_mutex_unlock(&queue->get_mutex); return msg; } msgqueue_t *msgqueue_create(size_t maxlen, int linkoff) { msgqueue_t *queue = (msgqueue_t *)malloc(sizeof (msgqueue_t)); int ret; if (!queue) return NULL; ret = pthread_mutex_init(&queue->get_mutex, NULL); if (ret == 0) { ret = pthread_mutex_init(&queue->put_mutex, NULL); if (ret == 0) { ret = pthread_cond_init(&queue->get_cond, NULL); if (ret == 0) { ret = pthread_cond_init(&queue->put_cond, NULL); if (ret == 0) { queue->msg_max = maxlen; queue->linkoff = linkoff; queue->head1 = NULL; queue->head2 = NULL; queue->get_head = &queue->head1; queue->put_head = &queue->head2; queue->put_tail = &queue->head2; queue->msg_cnt = 0; queue->nonblock = 0; return queue; } pthread_cond_destroy(&queue->get_cond); } pthread_mutex_destroy(&queue->put_mutex); } pthread_mutex_destroy(&queue->get_mutex); } errno = ret; free(queue); return NULL; } void msgqueue_destroy(msgqueue_t *queue) { pthread_cond_destroy(&queue->put_cond); pthread_cond_destroy(&queue->get_cond); pthread_mutex_destroy(&queue->put_mutex); pthread_mutex_destroy(&queue->get_mutex); free(queue); } 队列结构体:
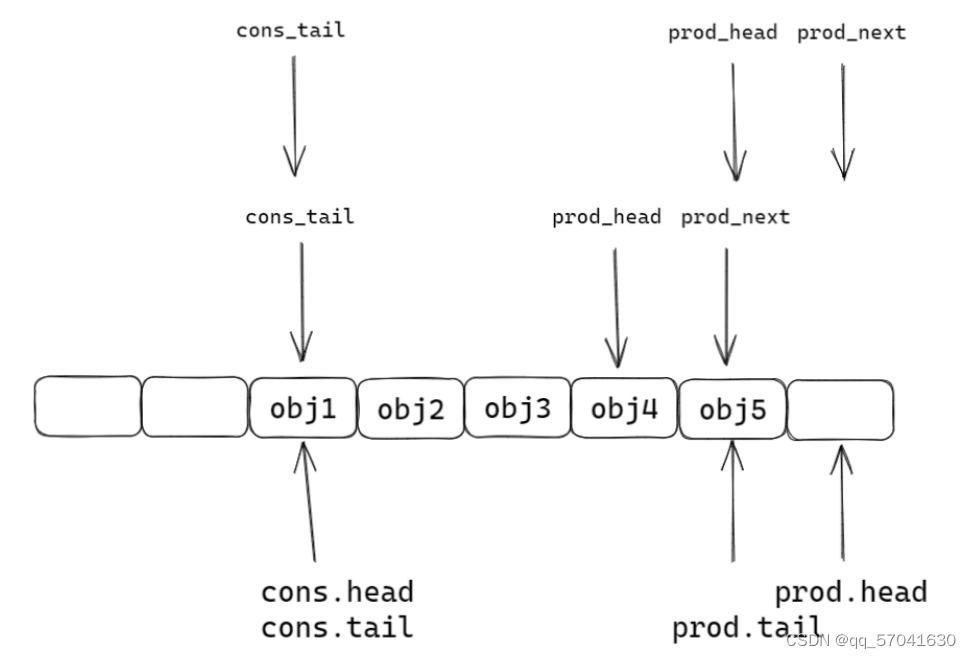
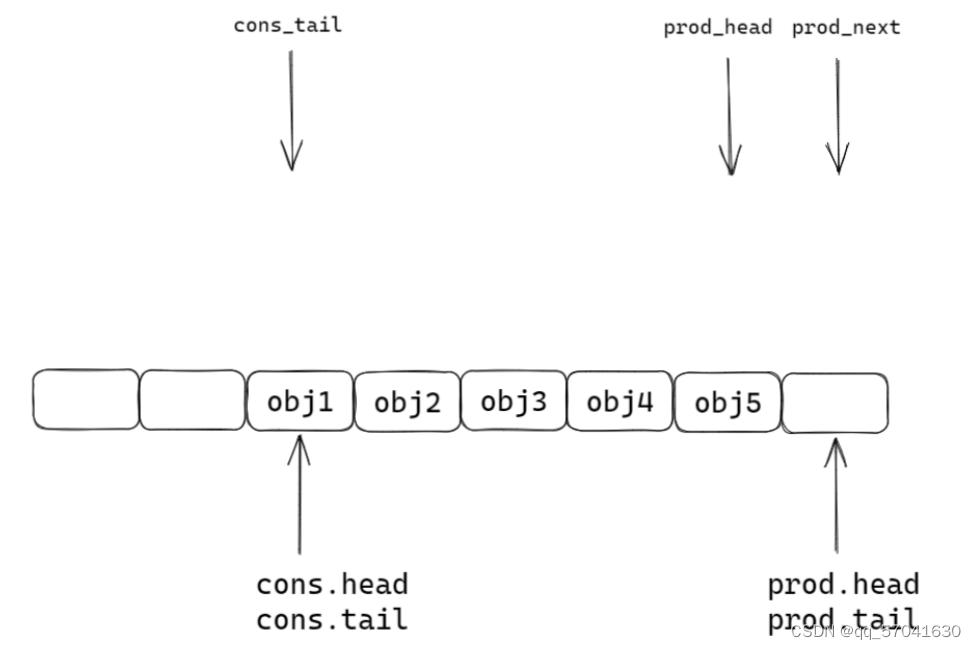
struct __msgqueue { size_t msg_max; size_t msg_cnt; int linkoff; int nonblock; void *head1; void *head2; void get_head; void put_head; void put_tail; pthread_mutex_t get_mutex; pthread_mutex_t put_mutex; pthread_cond_t get_cond; pthread_cond_t put_cond; };(3).rte_ring:dpdk中的消息队列
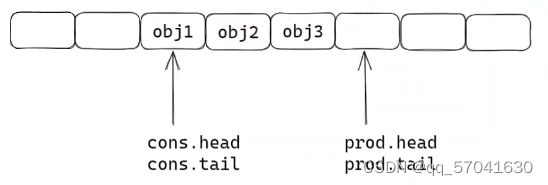
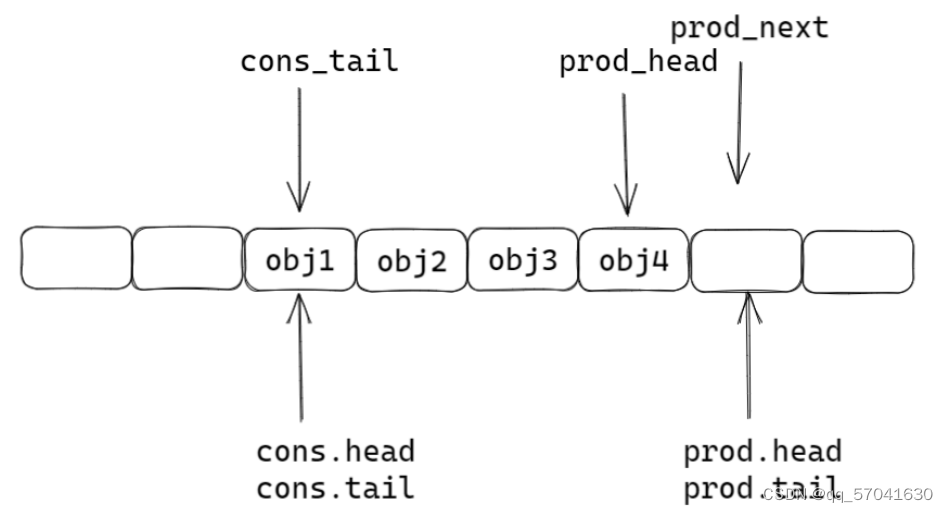
struct rte_ring { char name[RTE_RING_NAMESIZE]; /< Name of the ring. */ int flags; /< Flags supplied at creation. */ / Ring producer status. */ struct prod { uint32_t watermark; /< Maximum items before EDQUOT. */ //预设的数组长度 uint32_t sp_enqueue; /< True, if single producer. */ uint32_t size; /< Size of ring. */ uint32_t mask; /< Mask (size-1) of ring. */ volatile uint32_t head; /< Producer head. */ volatile uint32_t tail; /< Producer tail. */ } prod __rte_cache_aligned; / Ring consumer status. */ struct cons { uint32_t sc_dequeue; /< True, if single consumer. */ uint32_t size; /< Size of the ring. */ uint32_t mask; /< Mask (size-1) of ring. */ volatile uint32_t head; /< Consumer head. */ volatile uint32_t tail; /< Consumer tail. */ #ifdef RTE_RING_SPLIT_PROD_CONS } cons __rte_cache_aligned; #else } cons; #endif 单生产者入队
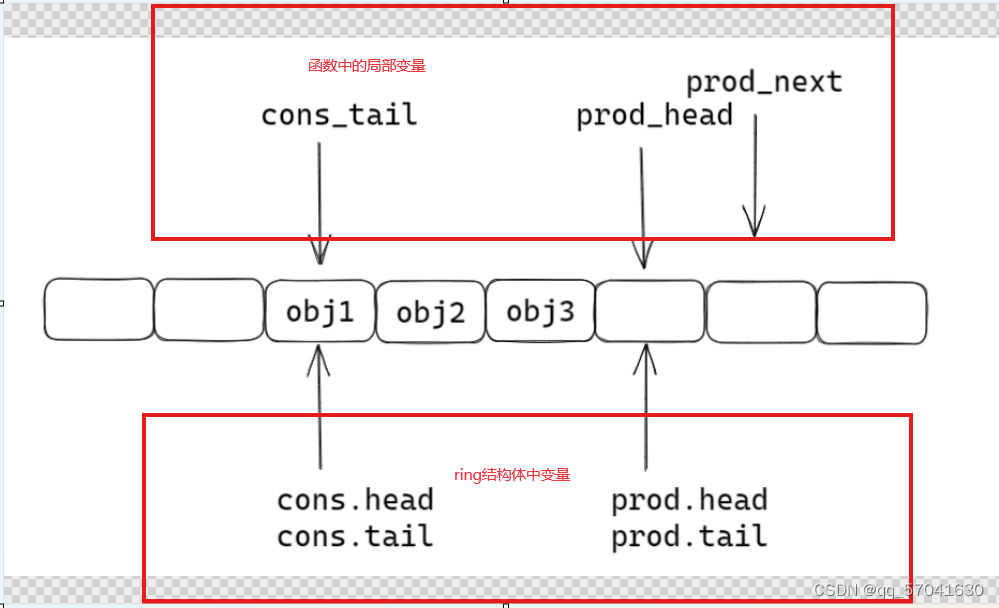
static inline int __attribute__((always_inline)) __rte_ring_sp_do_enqueue(struct rte_ring *r, void * const *obj_table, unsigned n, enum rte_ring_queue_behavior behavior) { uint32_t prod_head, cons_tail; uint32_t prod_next, free_entries; unsigned i; uint32_t mask = r->prod.mask; int ret; prod_head = r->prod.head; cons_tail = r->cons.tail; /* The subtraction is done between two unsigned 32bits value * (the result is always modulo 32 bits even if we have * prod_head > cons_tail). So 'free_entries' is always between 0 * and size(ring)-1. */ free_entries = mask + cons_tail - prod_head; //队列空余位置 /* check that we have enough room in ring */ if (unlikely(n > free_entries)) { //不用在意unlikely这个是编译器需要处理的,只需要看n>free_entries if (behavior == RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED) { //检测队列大小是否固定,固定的话返回false __RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_fail, n); return -ENOBUFS; } else { //队列长度可以扩容 /* No free entry available */ if (unlikely(free_entries == 0)) { //队列没有空余位置 __RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_fail, n); return 0; } n = free_entries; } } prod_next = prod_head + n; r->prod.head = prod_next; /* write entries in ring */ ENQUEUE_PTRS(); // 插入操作 COMPILER_BARRIER(); //两个作用: 1.内存屏障 /*/ //以此为标记,在内存序上,上面的不能优化下来,下面的不能优化上去; // 2.将r刷入内存中,其它线程可以看到r /* if we exceed the watermark */ if (unlikely(((mask + 1) - free_entries + n) > r->prod.watermark)) { ret = (behavior == RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED) ? -EDQUOT : (int)(n | RTE_RING_QUOT_EXCEED); __RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_quota, n); } else { ret = (behavior == RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED) ? 0 : n; __RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_success, n); } r->prod.tail = prod_next; //任务入队 return ret; }第一步:由函数中的局部变量prod_next检测下一位置是否空闲
第二步:ring结构体中head下移,插入任务
第三步:ring结构体中tail指向prod_next
多生产者入队
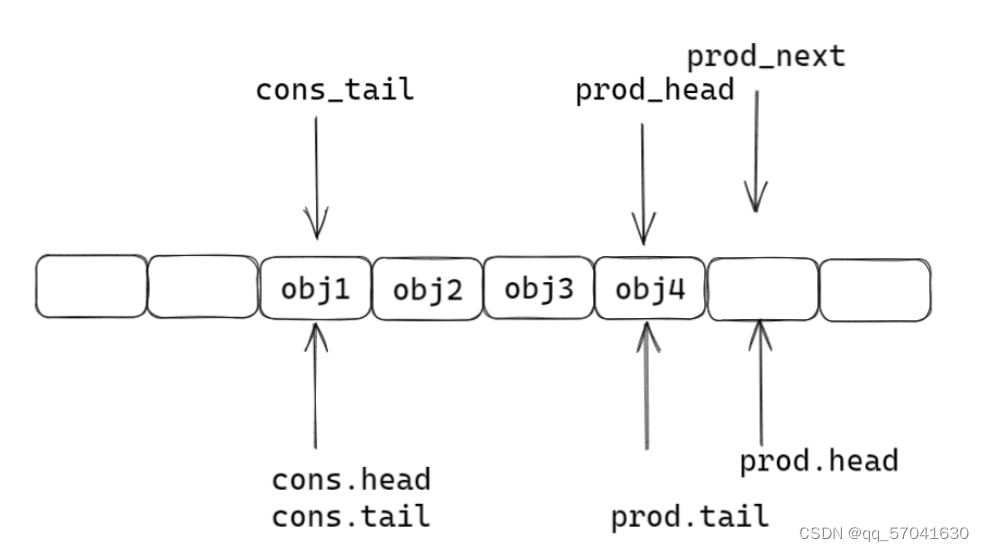
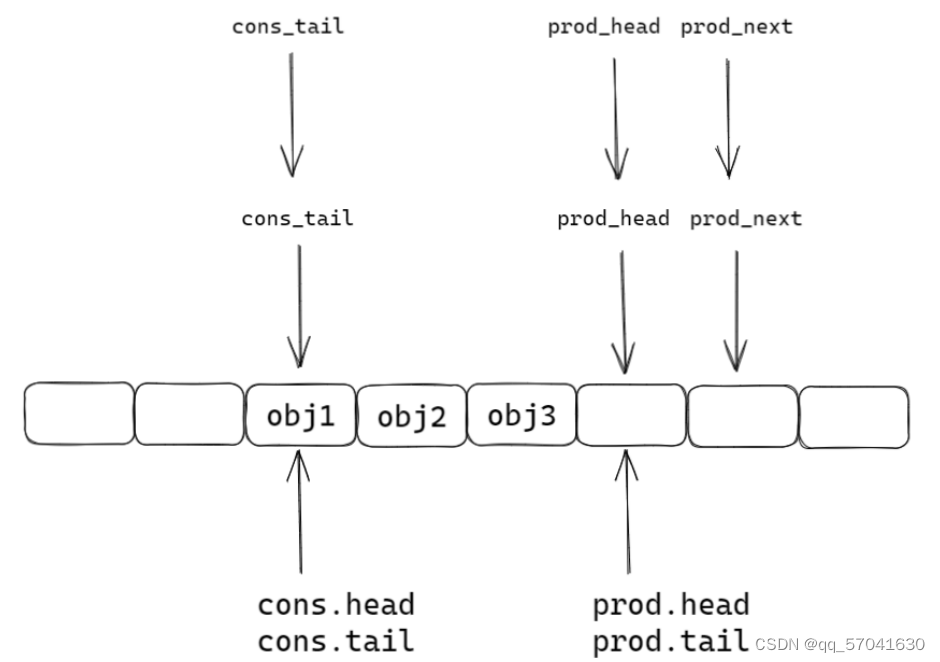
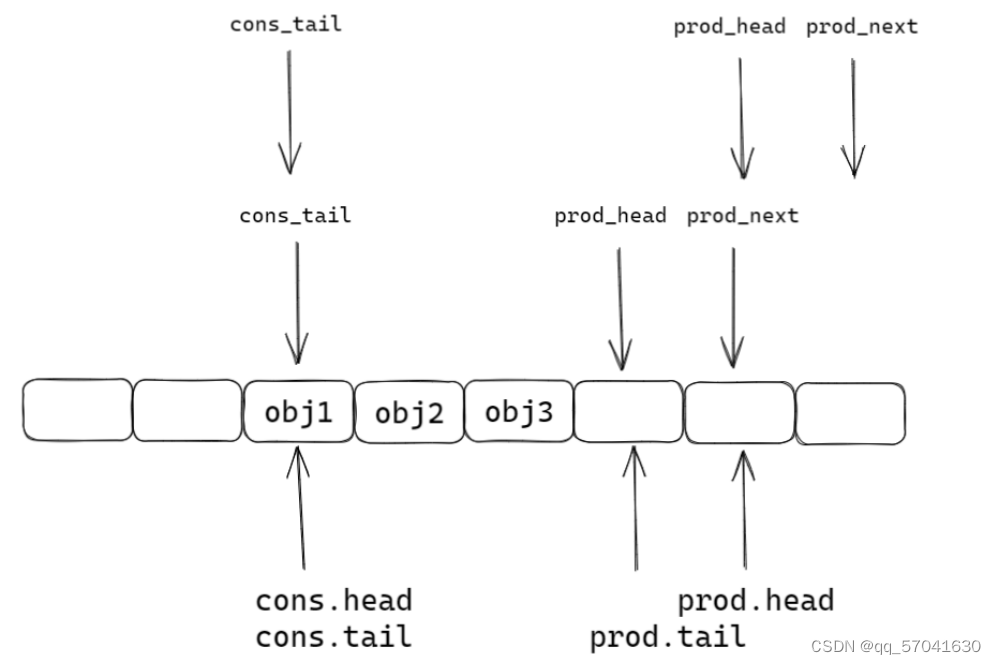
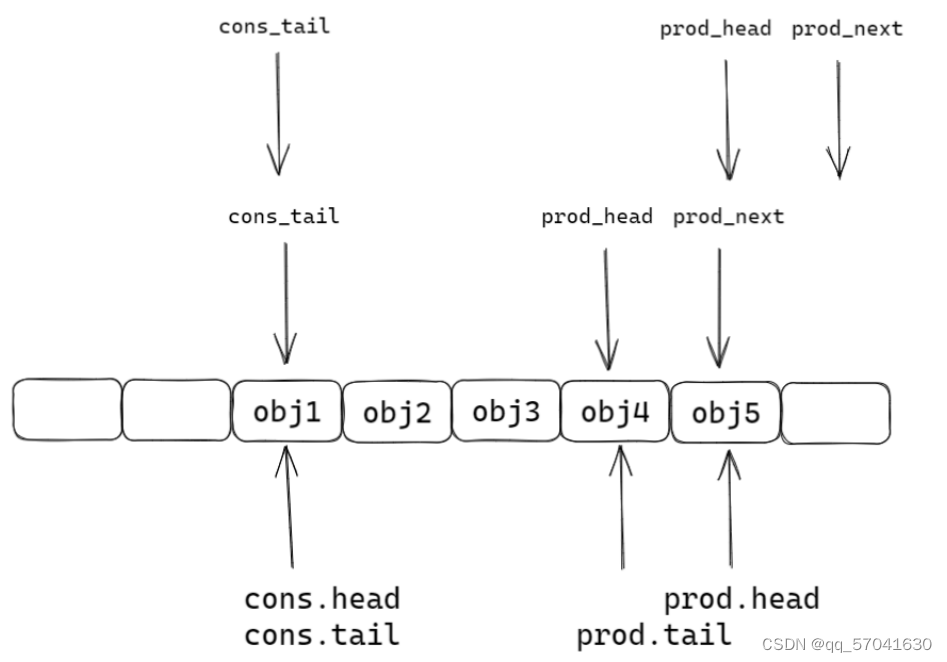
static inline int __attribute__((always_inline)) __rte_ring_mp_do_enqueue(struct rte_ring *r, void * const *obj_table, unsigned n, enum rte_ring_queue_behavior behavior) { uint32_t prod_head, prod_next; uint32_t cons_tail, free_entries; const unsigned max = n; int success; unsigned i; uint32_t mask = r->prod.mask; int ret; /* move prod.head atomically */ do { /* Reset n to the initial burst count */ n = max; prod_head = r->prod.head; cons_tail = r->cons.tail; /* The subtraction is done between two unsigned 32bits value * (the result is always modulo 32 bits even if we have * prod_head > cons_tail). So 'free_entries' is always between 0 * and size(ring)-1. */ free_entries = (mask + cons_tail - prod_head); /* check that we have enough room in ring */ if (unlikely(n > free_entries)) { if (behavior == RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED) { __RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_fail, n); return -ENOBUFS; } else { /* No free entry available */ if (unlikely(free_entries == 0)) { __RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_fail, n); return 0; } n = free_entries; } } prod_next = prod_head + n; success = rte_atomic32_cmpset(&r->prod.head, prod_head, prod_next); //原子操作,只允许一个线程操作 } while (unlikely(success == 0)); //一直循环到最后一个线程操作完成 /* write entries in ring */ ENQUEUE_PTRS(); COMPILER_BARRIER(); /* if we exceed the watermark */ if (unlikely(((mask + 1) - free_entries + n) > r->prod.watermark)) { ret = (behavior == RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED) ? -EDQUOT : (int)(n | RTE_RING_QUOT_EXCEED); __RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_quota, n); } else { ret = (behavior == RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED) ? 0 : n; __RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_success, n); } /* * If there are other enqueues in progress that preceeded us, * we need to wait for them to complete */ while (unlikely(r->prod.tail != prod_head)) rte_pause(); //不切换线程,空转cpu等待 r->prod.tail = prod_next; return ret; }第一步:函数中的局部变量prod_next检测队列中是否有空闲
第二步:使用cas锁住当前线程,ring中head前移
第三步:插入任务
第四步:
第五步:
资源链接:【免费】开源消息队列lockedqueue.h、msgqueue、rte-ring资源-CSDN文库
分享一个学习链接,有需要的同学可以看一下:
https://xxetb.xetslk.com/s/3yNycZ
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/113822.html