大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
目录
一、说明
Voronoi 单元也称为泰森多边形。 Voronoi 图在许多领域都有实际和理论应用,主要是在科学和技术领域,但也在视觉艺术领域使用。Voronoi 图以数学家 Georgy Voronoy 的名字命名,也称为 Voronoi 镶嵌、Voronoi 分解、Voronoi 分区或 Dirichlet 镶嵌(以 Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet 命名)。
在数学中,Voronoi 图是将对平面(集合)划分为多个区域的算法。在最简单的情况下,这些对象只是平面上的有限多个点(称为种子、站点或生成器)。对于每个种子,都有一个对应的优先划分区域。这种区域称为 Voronoi 单元,由平面上离该种子比其他任何点更近的所有点组成。一组点的 Voronoi 图与该组的 Delaunay 三角剖分是对偶的。
注意:点、区域、边界线成为这个算法的关键要素。
二、帝国边界划分问题
我们用一个童话故事构成思想实验。
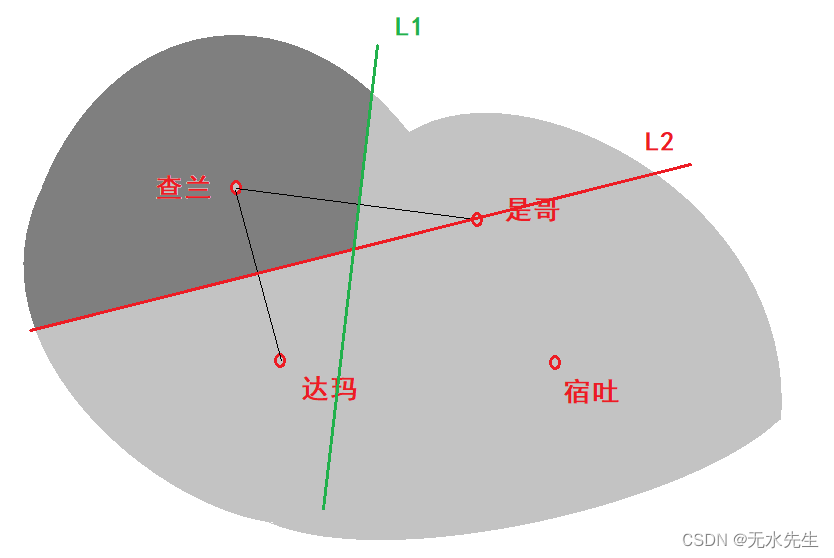
话说,哈里发国王年事已高,厌倦朝政,因而计划将他的王国分为四份,分别由四个王子管理。于是召来宰相易普拉辛,说到:“我亲爱的宰相,我打算将王国分成四个部落,分别交给王子们统辖,如今有四个城池,分别是查兰,是哥,达玛,宿吐作为它们的都城,可是如何划分疆土我毫无主张,是真主启发我召你商议此事。”宰相思索片刻,说到:“赞美安拉,我倒是有一个谋划,请借地图叙述”,国王当即请出地图如下:
且看宰相如何划分国土。首先,确定查兰的边疆,如下:
1)从查兰引出两个线段,分别连接(是哥,达玛)因为宿土与查兰不接壤,所以不必引进宿土。
2)分别作出两条线段的垂直中分线。
做出两条中分线L1,L2。中分线上的特征是:L1线上点到查兰的距离一定等于该点到是哥距离,L2上的任意点到查兰距离,一定等于它到达玛的距离。因此,站在平分线上看两国首都,谁也没“侵犯”谁。故绿线和红线都是“公平线”,就此,查兰的土地被公平线L1和L2包络,已经画出。
3)接着划分达玛:从达玛引出线段,连接宿土和是哥,作公平线S1,和S2,这样达玛土地在公平线L2,S1,S1包围下也能画出,如图粉色区域。
显然,图中新增出粉色区域中,任意一点到达玛距离比到其它三城距离更近,保证达玛没有“侵犯”其它邻国。至此,达玛的边界因L2,S1,S2包络而确定。
注意: 虽然有公平线L1横穿达玛,但此线是【查兰,是哥】的公平线,与达玛无关。
4)最后,从宿土到是哥引出线段,并做出中分线T ,如图:
至此,宿土的边疆也因T-S2-L1包络出是哥的领土,至此国土划分完成。
哈里发看了宰相的划分,依然不悦,对宰相说到:“依照爱卿的划分,国土面积不等,如何说服四位王子服从分配?”宰相说到:“安啦是唯一的主,不妨把命运交给安拉,让他们抓阄分配”,国王听后,大喜曰:“然”。
提示:有个三线交于一点的问题,如L1-L2-S2三线交于一点,T-S1-S2三线相交。这需要证明。
三条线共交于一点的说明:在相邻三城边界划分中,每三个中分线是共点的,如下证明:
先假定篮圈内三线不相交,从角的垂线定律说明,红蓝角+红黑角+黑绿角=180度,因此三线必然共点。
或者说,三个点组成三角形,其外接圆圆心引出三条到边的垂线,这三条垂线正好等分三边。
三、voronoi的正规定义
3.1 最简单的voronoi情况
在最简单的情况下,如第一张图片所示,我们在欧几里得平面中得到一组有限的点 {p1, …, pn}。在这种情况下,每个站点 pk 只是一个点,其对应的 Voronoi 单元 Rk 由欧几里得平面中的每个点组成,这些点到 pk 的距离小于或等于它到任何其他 pk 的距离。每个这样的单元都是从半空间的交集获得的,因此它是一个(凸)多面体。 [6] Voronoi 图的线段是平面上与最近的两个站点等距的所有点。 Voronoi 顶点(节点)是与三个(或更多)站点等距的点。
3.2 在距离空间的数学描述
下文中:生成点==站点
设X是一个距离函数的度量空间,K是一组索引,











Voronoi 图只是单元格的元组
在空间是有限维欧几里德空间的特殊情况下,每个站点都是一个点,有有限多个点并且所有点都不同,那么 Voronoi 单元是凸多边形,它们可以用组合方式表示它们的顶点、边、二维面等。有时,导出的组合结构被称为 Voronoi 图。然而,一般而言,Voronoi 单元可能不是凸的,甚至可能不是连接的。在通常的欧几里德空间中,我们可以用通常的术语重写形式定义。每个 Voronoi 多边形








3.3 不同距离空间所得 Voronoi 单元不同
如图,下面是基于欧氏空间和曼哈顿空间的划分:

以上就是欧氏空间和曼哈顿空间的划分细节。
四、代码和库
4.1 算法库
以下给出算法库Voronoi,是通过python写的代码
from PIL import Image, ImageColor, ImageDraw from random import randint, choice, random, seed as randomseed from typing import * from math import hypot, sqrt from queue import Queue from dataclasses import dataclass from enum import Enum import os import sys class ColorAlgorithm(Enum): random = 1 no_adjacent_same = 2 least_possible = 3 class RegionAlgorithm: def randomized(width: int, height: int, regions: int, mask_function) -> List[Tuple[int, int]]: """Return regions that are entirely random.""" points = [] while len(points) != regions: p = (randint(0, width - 1), randint(0, height - 1)) if p in points: continue if not mask_function(p): continue points.append(p) return points def uniform(width: int, height: int, regions: int, mask_function) -> List[Tuple[int, int]]: """Return regions that attempt to be somewhat uniform.""" k = 10 points = [] while len(points) != regions: best_p = None d_max = 0 i = 0 while i < k * len(points) + 1: p = (randint(0, width - 1), randint(0, height - 1)) if p in points: continue if not mask_function(p): continue if len(points) == 0: best_p = p break d_min = float('inf') for x, y in points: d = hypot(p[0]-x, p[1]-y) if d < d_min: d_min = d if d_min > d_max: d_max = d_min best_p = p i += 1 points.append(best_p) return points class DistanceAlgorithm: def euclidean(x, y, xn, yn): """Calculate the image regions (up to a distance) using euclidean distance.""" return hypot(xn-x, yn-y) def manhattan(x, y, xn, yn): """Calculate the image regions using manhattan distance.""" return abs(xn-x) + abs(yn-y) def euclidean45degrees(x, y, xn, yn): """Calculate the image regions using euclidean, but allow only lines in 45 degree increments.""" return sqrt(2 * min(abs(xn-x), abs(yn-y)) 2) + abs(abs(xn-x) - abs(yn-y)) def chebyshev(x, y, xn, yn): """Calculate the image regions using chebyshev distance.""" return min(abs(xn-x), abs(yn-y)) + abs(abs(xn-x) - abs(yn-y)) def set_each_point(seed: int, width: int, height: int, region_centers: List[Tuple[int, int]], image: List[List[int]], d_limit: int, f: List[Callable[[int, int, int, int], float]], mask_function): """Calculate the image regions (up to a distance) using the provided metric.""" randomseed(seed) region_distance_functions = [f if not isinstance(f, list) else choice(f) for _ in range(len(region_centers))] for x in range(width): for y in range(height): if not mask_function((x, y)): continue d_min = float('inf') for i, region in enumerate(region_centers): xn, yn = region d = region_distance_functions[i](x, y, xn, yn) if d < d_min: d_min = d if d <= d_limit: image[x][y] = id(region) class Utilities: def error(message, q=True): print(f"\u001b[38;5;1mERROR:\u001b[0m {message}", flush=True) if q: sys.exit(1) def warning(message): print(f"\u001b[38;5;208mWARNING:\u001b[0m {message}", flush=True) def info(message): print(f"\u001b[38;5;11mINFO:\u001b[0m {message}", flush=True) def success(message): print(f"\u001b[38;5;2mSUCCESS:\u001b[0m {message}", flush=True) def hex_to_tuple(color: str): color = color.strip("#") return (int(color[0:2], 16), int(color[2:4], 16), int(color[4:6], 16)) def get_different_adjacent_colors(width, height, image, colors, color_algorithm): from pulp import LpProblem, LpVariable, LpMinimize, lpSum, PULP_CBC_CMD edges = set() mapping = {} n = 0 for x in range(width): for y in range(height): for xd, yd in ((0, 1), (1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, -1)): xn, yn = x + xd, y + yd if not 0 <= xn < width or not 0 <= yn < height: continue i1, i2 = image[x][y], image[xn][yn] if i1 is None or i2 is None: continue if i1 < i2: if i1 not in mapping: n += 1 mapping[n] = i1 mapping[i1] = n if i2 not in mapping: n += 1 mapping[n] = i2 mapping[i2] = n edges.add((mapping[i1], mapping[i2])) edges = list(edges) model = LpProblem(sense=LpMinimize) chromatic_number = LpVariable(name="chromatic number", cat='Integer') variables = [[LpVariable(name=f"x_{i}_{j}", cat='Binary') \ for i in range(n)] for j in range(n)] for i in range(n): model += lpSum(variables[i]) == 1 for u, v in edges: for color in range(n): model += variables[u - 1][color] + variables[v - 1][color] <= 1 for i in range(n): for j in range(n): model += chromatic_number >= (j + 1) * variables[i][j] if color_algorithm == ColorAlgorithm.least_possible: model += chromatic_number else: model += chromatic_number == len(colors) status = model.solve(PULP_CBC_CMD(msg=False)) if chromatic_number.value() > len(colors): Utilities.error("Not enough colors to color without adjacent areas having the same one!") return {mapping[variable + 1]: colors[color] for variable in range(n) for color in range(n) if variables[variable][color].value() == 1} def add_border(background, border_size, read_image, write_image, width, height, mask_function): r = border_size // 2 for x in range(width): for y in range(height): if not mask_function((x, y)): continue for dx, dy in ((0, 1), (1, 0)): xn, yn = x + dx, y + dy if not 0 <= xn < width or not 0 <= yn < height: continue if not mask_function((xn, yn)): continue if read_image[x][y] != read_image[xn][yn]: draw = ImageDraw.Draw(write_image) draw.ellipse((x-r, y-r, x+r, y+r), fill=(*background,0)) def generate( path: str, regions: int, colors: List[Union[Tuple[int], str]], width: int = 1920, height: int = 1080, region_algorithm = RegionAlgorithm.uniform, distance_algorithm = DistanceAlgorithm.euclidean, color_algorithm = ColorAlgorithm.random, seed: Optional[int] = None, border_size: int = 0, mask: Optional[str] = None, mask_color = "#000000", animate = False, background = "#FFFFFF", ): # possibly seed the random algorithm if seed is None: seed = random() # possibly convert string colors to tuples i = 0 while i < len(colors): if type(colors[i]) == str: colors[i] = Utilities.hex_to_tuple(colors[i]) i += 1 if type(mask_color) == str: mask_color = Utilities.hex_to_tuple(mask_color) elif type(mask_color) == list: mask_color = tuple(mask_color) if type(background) == str: background = Utilities.hex_to_tuple(background) elif type(background) == list: background = tuple(background) randomseed(seed) mask_function = lambda p: True if mask is not None: try: mask_img = Image.open(mask) Utilities.info("Mask provided.") w, h = mask_img.size mask_function = lambda p: mask_img.getpixel(p) == mask_color if w != width: Utilities.warning("Specified width doesn't match mask width, using mask width.") width = w if h != height: Utilities.warning("Specified height doesn't match mask height, using mask width.") height = h except Exception as e: Utilities.error(f"Error loading mask from '{mask}'.") if type(regions) == list: Utilities.info("Region centers provided, skipping generation.") # flip vertically! region_centers = [(int(center[0] * width), int(height - center[1] * height)) for center in regions] else: Utilities.info("Calculating region centers.") region_centers = region_algorithm(width, height, regions, mask_function) image = [[None] * height for _ in range(width)] Utilities.info("Calculating region areas.") DistanceAlgorithm.set_each_point(seed, width, height, region_centers, image, float("inf"), distance_algorithm, mask_function) # either assign colors randomly, or calculate the chromatic number and assign them then if color_algorithm == ColorAlgorithm.random: Utilities.info("Assigning region colors.") region_colors = {id(region): choice(colors) for region in region_centers} else: Utilities.info("Assigning region colors such that no two adjacent regions have the same color.") region_colors = Utilities.get_different_adjacent_colors(width, height, image, colors, color_algorithm) # if we're masking, some regions won't be assigned region_colors[None] = background # the original, full image (without borders) pil_image = Image.new("RGB", (width, height)) for x in range(width): for y in range(height): pil_image.putpixel((x, y), region_colors[image[x][y]]) if border_size != 0: Utilities.add_border(background, border_size, image, pil_image, width, height, mask_function) if animate: if not os.path.exists(path): os.makedirs(path) d = 1 while True: animation_image = [[None] * height for _ in range(width)] DistanceAlgorithm.set_each_point(seed, width, height, region_centers, animation_image, d, distance_algorithm, mask_function) animation_pil_image = Image.new("RGB", (width, height)) for x in range(width): for y in range(height): animation_pil_image.putpixel((x, y), background if animation_image[x][y] is None else region_colors[image[x][y]]) if border_size != 0: Utilities.add_border(background, border_size, animation_image, animation_pil_image, width, height) animation_path = os.path.join(path, f"{d}.png") animation_pil_image.save(animation_path, "PNG") Utilities.success(f"Animation image saved to {animation_path}") d += 1 if image == animation_image: Utilities.success(f"Done!") break else: pil_image.save(path, resolution=300) Utilities.success(f"Image saved to {path}!")4.2 参数说明
generate function arguments
path: the path (including an extension) to save the resulting file toregions: the number of distinct regions in the diagramcolors: a list of tuples denoting the RGB of the color, or strings denoting the color in hexwidth: the width of the image; defaults to 1920height: the height of the image; defaults to 1080region_algorithm: the algorithm that determines the centers of the regions:RegionAlgorithm.uniformattempts to make the centers equidistant to one another; defaultRegionAlgorithm.randomizedmakes the center positions entirely random
distance_algorithm: the algorithm that determines the way the distance is measured; if a list of the algorithms is provided, a random one is picked for each pointDistanceAlgorithm.euclidean: standard euclidean distance (hypotenuse); defaultDistanceAlgorithm.manhattan: Manhattan (taxicab) distance (4 directions)DistanceAlgorithm.chebyshev: Chebyshev distance (8 directions)DistanceAlgorithm.euclidean45degrees: euclidean distance, but lines can only point in 45 degree increments
color_algorithm: the algorithm that determines the colors of the regionsDistanceAlgorithm.random: pick the colors randomlyDistanceAlgorithm.no_adjacent_same: pick the colors such that no two adjacent regions have the same colorDistanceAlgorithm.least_possible: same asno_adjacent_same, but attempt to do so in the least number of colors
seed: the seed for the random number generator; no seed by defaultborder_size: the thickness of the border (in pixels); defaults to 0 (no border)mask: a path to an image mask so only specific areas are usedmask_color: the color of the mask to fill, ignoring everything else; defaults to#000000animate: creates images in the folderpathof the regions filling in; defaults to Falsebackground: background of the animation/masking/borders; defaults to#FFFFFF
4.3 调用模块的方法
from voronoi import * generate( path = "1.png", width = 3840, height = 2160, regions = 70, colors = [(0, 0, 0), (15, 15, 15), (23, 23, 23), (30, 30, 30)], color_algorithm = ColorAlgorithm.no_adjacent_same, )结果图:
五、后记
值得注意的是,本文专注于说明Voronoi图是个啥,有两个问题需要进一步阐述:1)特殊情况分析。2)算法和原理没有说明。鉴于时间和精力有限,本文先就此告一段落,后续文章我们继续讨论更多的相关内容。
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/125264.html