大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
多 表 联 查
多表联查
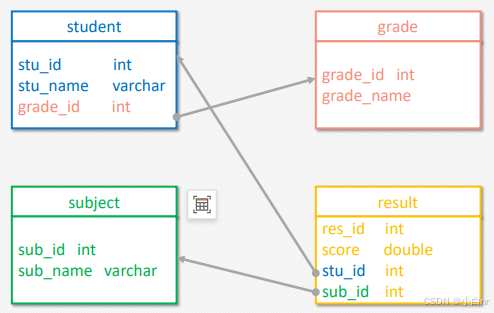
多表联查可以通过连接运算实现,即将多张表通过主外键关系关联在一起进行查询。下图提供了多表联查 时用到的数据库表之间的关系。
# 多表联查 -- 内联查询 -- 只有完全满足条件(主外键关系)的数据才能出现的结果 -- 非等值联查 -- 笛卡尔积 逻辑上有问题 select * from student,class; 等值查询和非等值查询
非等值查询:SELECT * FROM 表1,表2
等值查询:SELECT * FROM 表1,表2 WHERE 表1.字段1 = 表2.字段2…
其中:
• 与单表查询类似,都是SELECT语句;
• 把多个表放到FROM后,并用逗号隔开;
• 可使用AS关键字取别名,便于引用;
• 如无重名查询字段则可省略数据表的指定
-- 等值联查 -- 查询出学生和班级信息 student class select * from student,class where student.classid=class.classid; -- 五张表联查 select * from student,class,teacher,course,sc where student.classid=class.classid and student.sid=sc.sid AND sc.cid =course.cid and teacher.Tid=course.tid; -- 查询出学过张三老师课程的学生信息(面试!!!) select * from student,class,teacher,course,sc where student.classid=class.classid and student.sid=sc.sid AND sc.cid =course.cid and teacher.Tid=course.tid and teacher.Tname='张三'; -- 查询出每个学生的平均成绩 学生姓名 班级名称 平均成绩 select student.Sname,class.classname,avg(score) from student,class,sc where student.sid=sc.sid and student.classid=class.classid group by student.Sid; 连接查询
SELECT * FROM 表1 LEFT|right|INNER JOIN 表2 ON 条件
LEFT JOIN:从左表(表1)中返回所有的记录,即便在右 (表2)中没有匹配的行。
RIGHT JOIN:从右表(table_2)中返回所有的记录,即便 在左(table_1)中没有匹配的行。
INNER JOIN:在表中至少一个匹配时,则返回记录。
左表独有的数据:
select* fromt1 left joint2 ont1.id = t2.id wheret2.id isnull;
右表独有的数据 :
select* fromt1 right joint2 ont1.id = t2.id wheret1.id isnull;
-- inner ... join ... on -- 表个数多,每个表的数据量不大 吃内存 IO小 -- 笛卡尔积 -- 先拿出所有的结果在筛选 select * from student inner join class on student.classid=class.classid where ssex ='男'; -- 通过第一张表的结果进行on条件匹配 -- 表少,每张表的数据大 内存占用小 IO高 select * from student,class where student.classid=class.classid and ssex='男'; -- 5表联查 select * from student inner join class on student.classid=class.classid inner join sc on student.Sid=sc.Sid inner join course on student.classid=course.Cid inner join teacher on course.Tid=teacher.Tid -- 每门课程的平均成绩 课程名称 代课老师姓名 平均成绩 select avg(score),course.Cname,teacher.Tname from sc join course on sc.Cid=course.Cid join teacher on course.Tid=teacher.Tid group by course.Cname,teacher.Tname -- 外联查询 -- 找到主查表 -- 所有学生的数据对应的班级信息 -- left join on 左外联 select * from student left join class on student.classid=class.classid -- right join on 右外联 select *from class right join student on student.classid=class.classid -- 查询出所有的学生学过多少门课程 学生姓名 课程数 select Sname,count(cid) from student left join sc on student.Sid=sc.Sid group by student.Sid -- mysql 不支持检查约束 -- 查询没有班级的学生 select * from student left join class on student.classid=class.classid -- class表中classid为主键 where class.classid is null -- 查询没有学生的班级 select * from class left join student on class.classid=student.classid where student.sid is null UNION:
union是求两个查询的并集。
union合并的是结果集,不区分来自于哪一张表,所以可以合并多张表查询出来的数 据。
语法:
select A.field1 as f1, A.field2 as f2 from A union
(select B.field3 as f1, field4 as f2 from B)order by 字段 desc/asc
注意:
1列名不一致时,会以第一张表的表头为准,并对其栏目。
2会将重复的行过滤掉。
3如果查询的表的列数量不相等时,会报错。
4在每个子句中的排序是没有意义的,mysql在进行合并的时候会忽略掉。5如果子句中的排序和limit进行结合是有意义的。
6可以对合并后的整表进行排序
-- union 两个结果的集的并集 -- 去除重复 与distinct 一样 -- 不同类型的字段是可以合并的 -- 不同列数的数量集不允许合并 -- 起别名给第一个结果集才有用 -- 库中的所有人的名字 select sname from student union select tname from teacher select sname,ssex,classid from student -- 不同列数的数量集不允许合并 union select tname,tsex from teacher -- 错误 SELECT Sname,ssex,classid FROM student UNION SELECT Tname,Tsex,temail FROM teacher SELECT Sname 姓名,ssex,classid FROM student -- 起别名给第一个结果集才有用 UNION SELECT Tname,Tsex 性别,temail FROM teacher -- 查询没有班级的学生和没有学生的班级 select * from student left join class on student.classid=class.classid -- class表中classid为主键 where class.classid is null union select * from class left join student on class.classid=student.classid where student.sid is null UNION ALL:
语法:
select A.field1 as f1, A.field2 as f2 from A union all
(select B.field3 as f1, field4 as f2 from B)order by 字段 desc/asc
union all 是求两个查询的并集,但是不会把重复的过滤掉,而是全部显示出来
-- 获取没有班级的学生和有班级有学生和没有学生的班级 -- union all -- 全连接 -- 不去重的并集 select * from student left join class on student.classid=class.classid union ALL select * from student right join class on student.classid=class.classid 子 查 询
子查询,又叫内部查询
1. where 型子查询:
查询id最大的一个学生(使用排序+分页实现
查询id最大的一个学生(使用where子查询实现)
查询每个班下id最大的学生(使用where子查询实现)
# 子查询(面试) -- 所有的子查询必须用括号包起来 -- 去查询id最大的一个学生 -- 效率极低 select * from student order by sid desc limit 1 -- 去查询id最大的一个学生(子查询) select max(sid) from student select * from student where sid=10 -- 魔数 select * from student where sid=(select max(sid) from student) -- 查询每个班下id最大的学生(子查询) select * from student where sid in(select max(sid) from student group by classid) and student.classid=class.classid select * from student left join class on student.classid=class.classid where sid IN(select max(sid) from student group by classid) -- 查询学过张三老师的课程的学生 select * from student where sid in( select sid from sc where cid= (select cid from course where tid= (select tid from teacher where tname='张三') ) ) -- 查询没有学过张三老师的课程的学生 select * from student where sid not in( select sid from sc where cid= ( select cid from course where tid= (select tid from teacher where tname='张三') ) )2.from型子查询:
把内层的查询结果当成临时表,供外层sql再次查询。查询结果集可以当成表看待。临时表要使用一个别名。
查询大于5人的班级名称和人数(不使用子查询)
查询大于5人的班级名称和人数(使用from型子查询)
-- from 子查询 查询结果将作为一张表使用 (重要) -- 查询大于5人的班级名称和人数(不适用子查询) select classname,count(*) from class left join student on class.classid=student.classid group by class.classid having count(*)>5 -- 查询大于5人的班级名称和人数(子查询) select classname,人数 from class left join (select classid,count(*)人数 from student group by classid)t1 on class.classid=t1.classid where 人数>53.exists型子查询:
把外层sql的结果,拿到内层sql去测试,如果内层的sql成立,则该行取出。内层查询是exists后的查询。
从学生表中取出学生的信息,(如果该性别下没有男学生则不显示)
select * from student where exists (select * from student where ssex=’男’)
-- exists 子查询 子句有结果,父句执行 子句没结果,父句不执行 select * from teacher where exists (select * from student where classid=2) select * from teacher where exists (select * from student where classid=10)4. any, some, all子查询:
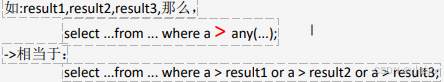
(1) any 子查询
表示满足其中任意一个条件
假设any内部的查询语句返回的结果个数是三个,
some 是 any的别名,所以用法是一样的,可以替代使用
查询出一班成绩比二班最低成绩高的学生
-- any -- 查询出一班成绩比二班最低成绩高的学生 select DISTINCT student.* from sc left join student on sc.Sid=student.Sid where student.classid=1 and score > any( select score from sc left join student on sc.sid=student.Sid where student.classid=2)(2)all 子查询
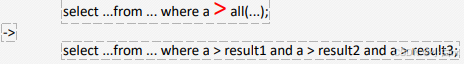
表示满足其中所有条件条件,ALL关键字与any关键字类似,只不过上面的or改成and。假设any内部的查询语句返回的结果个数是三个,
查询出一班成绩比二班最高成绩高的学生
-- ALL -- 查询出一班成绩比二班最高成绩高的学生 select DISTINCT student.* from sc left join student on sc.Sid=student.Sid where student.classid=1 and score > ALL( select score from sc left join student on sc.sid=student.Sid where student.classid=2)case when then end语句
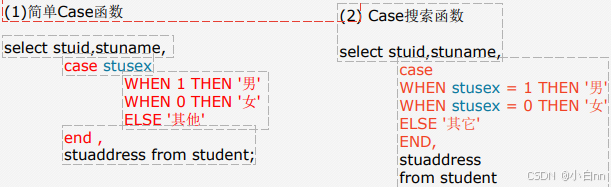
Case具有两种格式。简单Case函数和Case搜索函数。
-- case when then end 必须同时出现 缺一不可(可以无缩进无符号) -- 写法1 select tid,tname,tsex,tbirthday from teacher select tid,tname, case tsex when 0 then '男' -- 类型必须是常量 when 1 then '女' end tsex,tbirthday from teacher select tid,tname, case tsex when 0 then '男' -- 选项中没有的为null when 1 then '女' else '不明生物' end tsex,tbirthday from teacher -- 写法2 select tid,tname, case when tsex > 1 then '男' when tsex = 1 then '女' when tsex < 1 then '未知' end tsex,tbirthday from teacher -- 查询学生的成绩, -- 并将大于90分的用A显示, -- 大于80分的用B显示, -- 大于70分的用C显示, -- 大于60分的用D显示, -- 小于60分的显示不及格 select score, case when score>=90 then 'A' when score>=80 then 'B' when score>=70 then 'C' when score>=60 then 'D' when score<60 then '不及格' end from sc 流程控制函数,语句
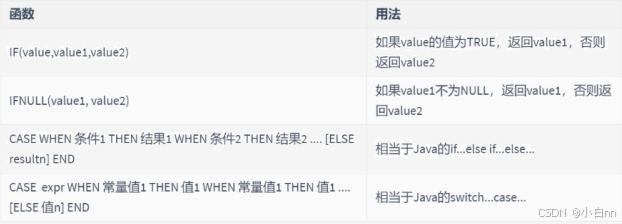
# 结果集的控制 -- if(expr1,expr2,expr3) -- expr1 条件 -- expr2 条件成立 显示数据 -- expr3 条件不成立 select * from teacher -- 1女 0男 select tid,tname, if(tsex=1,'女','男')tsex,tbirthday,taddress from teacher -- IFNULL(expr1,expr2) -- expr1 字段 -- expr2 当字段为null 默认值 select sid,sname,IFNULL(birthday,"可怜宝宝") bir,ssex from student -- 虚拟表 -- 写法1 select tid,tname,tsex,tbirthday from teacher select tid,tname, case tsex when 0 then '男' -- 类型必须是常量 when 1 then '女' end tsex,tbirthday from teacher select tid,tname, case tsex when 0 then '男' -- 选项中没有的为null when 1 then '女' else '不明生物' end tsex,tbirthday from teacher -- 写法2 select tid,tname, case when tsex > 1 then '男' when tsex = 1 then '女' when tsex < 1 then '未知' end tsex,tbirthday from teacher -- 查询学生的成绩, -- 并将大于90分的用A显示, -- 大于80分的用B显示, -- 大于70分的用C显示, -- 大于60分的用D显示, -- 小于60分的显示不及格 select score, case when score>=90 then 'A' when score>=80 then 'B' when score>=70 then 'C' when score>=60 then 'D' when score<60 then '不及格' end from scS q l 执 行 顺 序
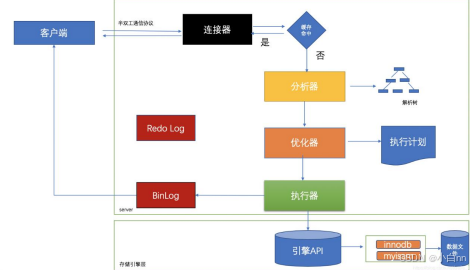
Sql语句在数据库中的执行流程
1.系统(客户端)访问 MySQL 服务器前,做的第一件事就是建立 TCP 连接。
2. Caches & Buffers: 查询缓存组件
3. SQL Interface: SQL接口 接收用户的SQL命令,并且返回用户需要查询的结果。比如
SELECT … FROM就是调用SQL Interface
MySQL支持DML(数据操作语言)、DDL
(数据定义语言)、存储过程、视图、触发器、自定 义函数等多种SQL语言接口
4. Parser: 解析器:在解析器中对 SQL 语句进行语法分析、语义分析。
5. Optimizer: 查询优化器
6.存储引擎
7.文件系统
8.日志系统
Sql查询语句的执行顺序
本章总结
•连接查询的分类
•1、右连接:从右表(table_2)中返回所有的记录,即便在左(table_1)中没有匹配的行;•2、左连接: 从左表(表1)中返回所有的记录,即便在右(表2)中没有匹配的行;
•3、内连接:在表中至少一个匹配时,则返回记录。
•子查询等特殊查询
•where子查询
•from子查询
•exists子查询
•any,some(or),all(and)子查询•特殊查询
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/129328.html