大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
目录
1.物品识别
该项目使用Python,OpenCV进行图像捕捉,进行物品识别。我们将使用YOLO(You Only Look Once)模型进行物品识别,YOLO是一个高效的实时物体检测系统。
2.模型介绍
YOLO(You Only Look Once)是一种目标检测算法,它在实时性和精确度上取得了很好的平衡。它的核心思想是在一张图片上同时预测出所有物体的位置和类别,而无需像传统的区域提议网络(R-CNN)那样分步骤进行。
3.文件框架
models中的定义标签文件可以搜索yolo模型来找,下面的四个代码文件是主文件,camera是调用电脑摄像头,interaction是调用opencv绘制图像框,object_detection是定义物品检测函数,main是主函数。
运行main函数即可实现物品检测。
4.代码示例
4.1 camera.py
import cv2 # 导入OpenCV库 def get_camera_frame(): cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # 打开摄像头 if not cap.isOpened(): raise Exception("无法打开摄像头。") # 如果无法打开摄像头,抛出异常 ret, frame = cap.read() # 读取帧 cap.release() # 释放摄像头 if not ret: raise Exception("读取照片信息失败。") # 如果读取失败,抛出异常 return frame # 返回捕捉到的帧4.2 interaction.py
import cv2 # 导入OpenCV库 def draw_boxes(frame, detections): for (class_name, confidence, box) in detections: x, y, w, h = box label = f"{class_name} {confidence:.2f}" # 创建标签 cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2) # 绘制矩形框 cv2.putText(frame, label, (x, y - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 0), 2) # 绘制标签 return frame # 返回绘制后的帧4.3 object_detection.py
import cv2 # 导入OpenCV库,用于计算机视觉任务 import numpy as np # 导入NumPy库,用于处理数组 class ObjectDetector: def __init__(self, config_path, weights_path, names_path): # 初始化YOLO模型 self.net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet(config_path, weights_path) self.layer_names = self.net.getLayerNames() # 获取YOLO模型的输出层 self.output_layers = [self.layer_names[i - 1] for i in self.net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()] # 读入类别名称 with open(names_path, 'r') as f: self.classes = [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()] def detect_objects(self, frame): height, width = frame.shape[:2] # 获取图像的高度和宽度 # 将图像转换为YOLO模型输入所需的blob格式 blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 0.00392, (416, 416), (0, 0, 0), True, crop=False) self.net.setInput(blob) # 设置YOLO模型的输入 outs = self.net.forward(self.output_layers) # 前向传播,获取检测结果 class_ids = [] # 存储检测到的类别ID confidences = [] # 存储检测到的置信度 boxes = [] # 存储检测到的边框 # 处理每个输出层的检测结果 for out in outs: for detection in out: scores = detection[5:] # 获取每个类别的置信度分数 class_id = np.argmax(scores) # 获取置信度最高的类别ID confidence = scores[class_id] # 获取最高置信度 if confidence > 0.5: # 过滤低置信度的检测结果 center_x = int(detection[0] * width) center_y = int(detection[1] * height) w = int(detection[2] * width) h = int(detection[3] * height) x = int(center_x - w / 2) y = int(center_y - h / 2) boxes.append([x, y, w, h]) confidences.append(float(confidence)) class_ids.append(class_id) # 非极大值抑制,去除冗余的边框 indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.5, 0.4) result = [] if len(indices) > 0: for i in indices.flatten(): # 确保indices是一个可迭代的列表 box = boxes[i] result.append((self.classes[class_ids[i]], confidences[i], box)) return result4.4 main.py
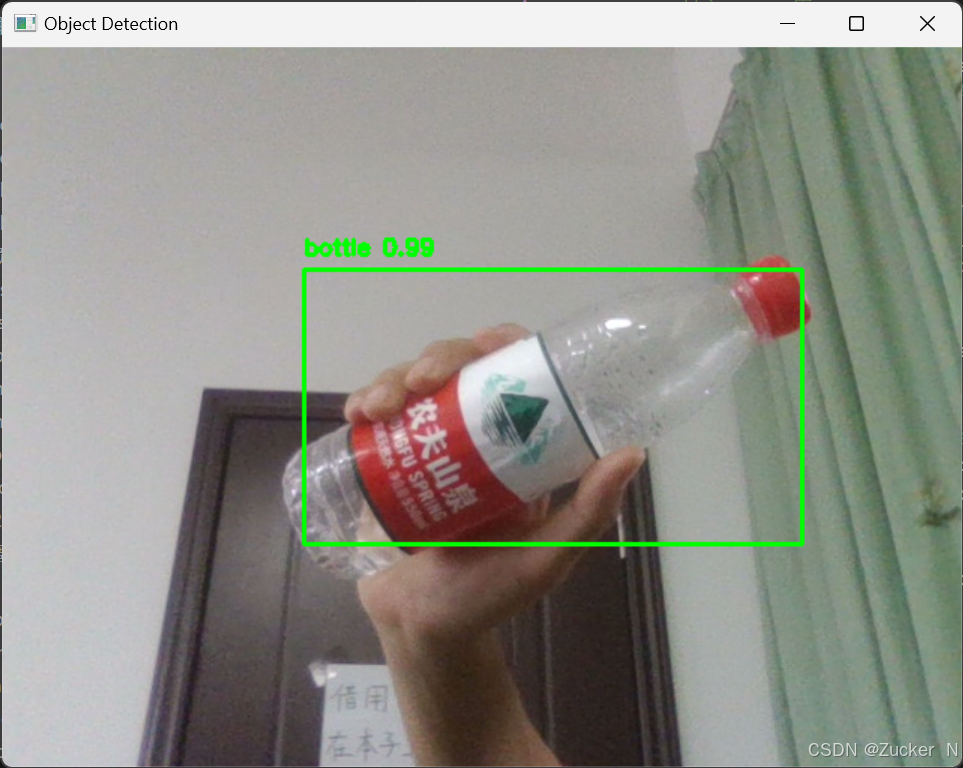
import sys import os import cv2 # 导入OpenCV库 from camera import get_camera_frame # 导入相机捕捉函数 from object_detection import ObjectDetector # 导入物体检测类 from interaction import draw_boxes # 导入绘制边框函数 def main(): # 配置文件路径 config_path = "./pythonProject/ai_modle_win/wupin/models/yolov3.cfg" weights_path = "./pythonProject/ai_modle_win/wupin/models/yolov3.weights" names_path = "./pythonProject/ai_modle_win/wupin/models/coco.names" # 初始化物体检测器 detector = ObjectDetector(config_path, weights_path, names_path) while True: frame = get_camera_frame() # 获取摄像头帧 detections = detector.detect_objects(frame) # 检测物体 frame = draw_boxes(frame, detections) # 绘制检测结果 cv2.imshow("Object Detection", frame) # 显示结果 if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): # 按下 'q' 键退出 break cv2.destroyAllWindows() # 关闭所有窗口 if __name__ == "__main__": main()4.5 运行结果
5.总结
YOLO的主要用途是计算机视觉中的目标检测任务,例如自动驾驶中的行人和车辆识别、安防监控、无人机拍摄分析等场景,它能够实现实时检测,并且对于小目标和大目标都具备较好的性能。你也快来试一试吧!
转载或使用代码记得备注来源呀!
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/131174.html