大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
原文 PDF:https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/aemDocuments/documents/FTD/tekron/tekronwhitepapers/-A-guide-to-IRIG-B.pdf
IRIG-B3
概论
其中 IRIG-B 格式是最值得关注的。IRIG-B 是电力、工业自动化和控制行业中最常用的版本。
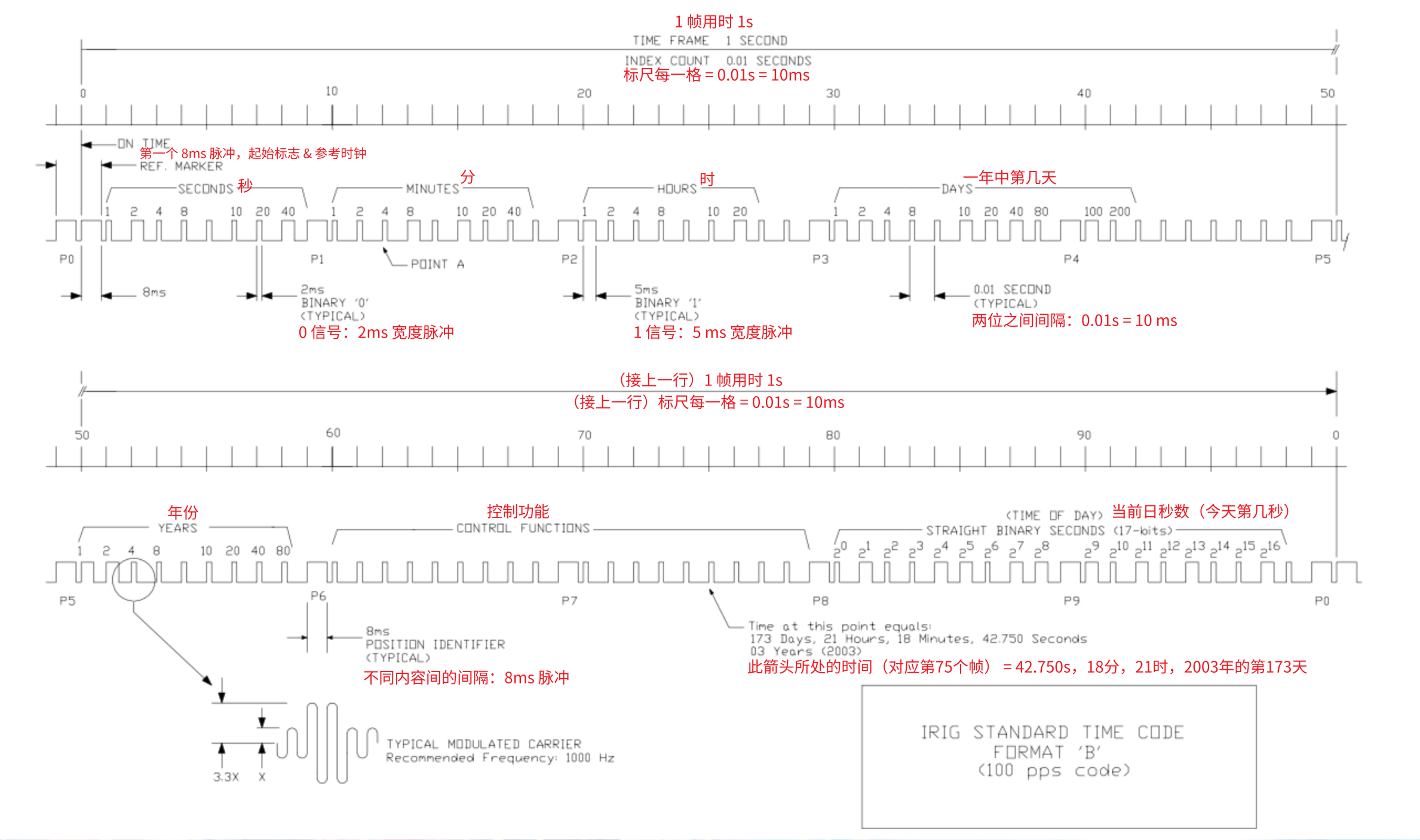
如图 1 所示:IRIG-B 是一个 100 Hz 的信号,每一帧包含 100 位数据,每个数据在 10 ms 的时间帧内传输,完成一帧传输的总时间为 1 秒(下表是信号相关参数表)
The time code that is worth focusing on is the IRIG-B format. IRIG-B is the most common version used within the Power, industrial automation and control industries. Referring to figure 1, IRIG-B is a 1 kHz signal which contains 100 bits of data, each transmitted over a 10 ms time frame, taking a total time of 1 second for a complete transmission (what amouthful…refer to table 1 for a summary)
| 编码 Code |
比特率 Bit Rate |
每比特时间 Bit Time |
每帧的比特数 Bits per Frame |
帧时间 Frame Time |
帧速率 Frame Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRIG-B | 100 Hz | 10 ms | 100 | 1000 ms(1s) | 1 Hz |
IRIG-B 信号格式
IRIG-B 调制类型
调制方式决定了实际输出信号的波形、表示 0/1信号的样式。IRIG-B具有三种不同的调制类型:
- 直流(DCLS):通常这是 0-5 V 直流脉宽调制信号,其中不同的脉宽表示编码数据。由于其高精度(时钟输出精度可 < 100 ns),这是当今最常用的调制方法。DCLS IRIG-B 信号的如图 2 中黄色的轨迹所示。
Direct Current Level Shift (DCLS) – typically this is a 0-5 Vdc pulse width modulated signal, where the different pulse widths represent coded data. This is the most common modulation method used today due to its high accuracy (< 100 ns at the port). An example of a DCLS signal is shown by the yellow trace in figure 2. - 载波调制–调幅(AM):用1 kHz 的正弦波载波信号以 3:1 的比例调制。此信号无直流成分,适合远距离传输,这使得AM 在过去很受欢迎。但由于信号精度较低(时钟输出精度 < 2μs),现在 AM 不再是首选。AM IRIG-B 信号的一个示例可以在图2中的绿色轨迹上看到。
Amplitude Modulated (AM) – modulated with a 1 kHz sine wave carrier signal with a 3:1 ratio, this signal has no DC content. This made AM popular in the past as it allowed the signal to be transmitted over long distances. Due to the low signal accuracy (< 2 microseconds at the port) AM is no longer the signal of choice. An example of an AM IRIG-B signal can be seen on the green trace in figure 2. - AM 调制 + 曼彻斯特编码:使用1 kHz 的方波作为载波;使用相位调制而不是 DCLS(曼彻斯特编码),该信号不包含直流偏置。这种调制方法可长距离传输,并时保持高精度(时钟精度 <100 ns)。这种调制方法是 IRIG-B最不常见的调制类型。
Modified Manchester Modulation – Modified Manchester modulation is the least common modulation type for IRIG-B. Using a 1 kHz square wave with phase modulation rather than DC level shift, this signal contains no DC bias. This allows for transmission over long distances, while maintaining a high accuracy (<100 ns)
每种调制方式的精度和传输特性总结在下表中
The accuracy and transmission characteristics of each modulation type are summarised in table 2.
| 调制方式 Modulation Type |
最大传输距离 Maximum Transmission Distance |
精准度(时钟端口处的输出) Accuracy (at clock port) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 直流 DCLS | < 100 m | < 100 ns |
| 1 | 载波调制–调幅 AM | < 300 m | < 2 μs |
| 2 | AM + 曼彻斯特编码 | < 300 m | < 100 ns |
载波频率
- 无载波 – 直流(DCLS IRIG-B)不需要载波调制,因此没有载波频率
No carrier – DCLS requires no carrier frequency - 1 kHz载波 –【AM 调制】和【AM + 曼彻斯特编码】通常使用 1 kHz载波
1 kHz carrier – AM and Modified Manchester both commonly use a 1 kHz carrier
综上,有三种 IRIG-B 格式代码:
- IRIG-B00z – 没有载波 –> 直流 IRIG-B 信号(DCLS IRIG-B)
IRIG-B00z – This is a DCLS IRIG-B signal with no carrier. - IRIG-B12z – 调幅(AM)信号,载波为1 kHz正弦波(AM IRIG-B)
IRIG-B12z – This is an amplitude modulated (AM) signal with a 1 kHz carrier sine wave - IRIG-B22z – AM + 曼彻斯特编码的 IRIG-B 信号
IRIG-B22x – This is the modified Manchester modulation type with a 1 kHz square wave carrie
IRIG-B 编码表达式
这里在下表 3 中定义 IRIG-B 中不同编码内容使用的缩略词。编码内容的组合形成了编码表达式
| 缩写 Acronym |
全称 Name |
定义 Definition |
|---|---|---|
| BCD_TOY | BCD编码的时间(一年中的第几天) Binary coded Decimal – Time of Year |
使用 BCD 编码,包含以下信息:秒、分、时、一年中的第几天 BCDTOY contains the following information: seconds, minutes, hours, day of year |
| BCD_YEAR | BCD编码的年份 Binary Coded Decimal – Year |
使用 BCD 编码,显示年份(范围 0-99) BCDYEAR contains the year value (0-99) |
| CF | 控制功能 Control Function |
控制功能是IRIG-B代码的空白部分,可以用用户定义的控制字段填充。更多内容请见《控制功能》小节 Control functions are a blank section of the IRIG-B code that can be filled with user defined control fields. More about this in the extensions section |
| SBS | 二进制秒数 Straight Binary Seconds |
直接显示一天到现在到当前时间经过的秒数。范围 0-86399。可用来获取一天中的具体时间,也可用作检查 SBS counts from 0 to 86,399. This is the number of seconds that have passed during the day. This can be used to get time of day also, and is sometimes used as a check |
| 编号 z = Code |
表达式 Expression |
详情 Details |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | BCD_TOY , CF, SBS | 秒,分,时,一年中的第几天,控制指令,二进制秒数 |
| 1 | BCD_TOY , CF | 秒,分,时,一年中的第几天,控制指令 |
| 2 | BCD_TOY | 秒,分,时,一年中的第几天 |
| 3 | BCD_TOY , SBS | 秒,分,时,一年中的第几天,二进制秒数 |
| 4 | BCD_TOY , BCD_YEAR , CF, SBS | 秒,分,时,一年中的第几天,年份,控制指令,二进制秒数 |
| 5 | BCD_TOY , BCD_YEAR , CF | 秒,分,时,一年中的第几天,年份,控制指令 |
| 6 | BCD_TOY , BCD_YEAR | 秒,分,时,一年中的第几天,年份 |
| 7 | BCD_TOY , BCD_YEAR , SBS | 秒,分,时,一年中的第几天,年份,二进制秒数 |
- IRIG-B004 – 没有载波、传送完整信息的 IRIG-B 信号(DCLS IRIG-B 信号,传送 4 号数据)
IRIG-B004 – This is a DCLS IRIG-B signal with no carrier - IRIG-B124 – 使用载波调幅(AM)、载波为1 kHz正弦波、传送 4 号数据的 AM IRIG-B 信号
IRIG-B124 – This is an amplitude modulated (AM) signal with a 1 kHz carrier sine wave - IRIG-B224 – 使用曼彻斯特编码、载波为 1 kHz方波、传送 4 号数据的 IRIG-B 信号
IRIG-B224 – This is the modified Manchester modulation type with a 1 kHz square wave carrier
总结:IRIG-B 格式代码
IRIG-B 信号报文
物理IRIG-B信号由几个关键属性组成。了解这些属性并不重要,有助于全面了解 IRIG-B 信号的工作原理。也有助于在示波器上查看、分析 IRIG-B 信号。
起始标志
信号报文
- 时间信息的 BCD 码数被分成 10 个字节
From the reference marker come the binary coded decimals which are split into ten 8-bit groups. - 每个字节间被 8 ms 的位置标识符(P1 至 P0)分隔
Each divided by 8 ms position identifiers (P1 to P0). - 数据使用不同的脉冲宽度(脉宽调制)来编码
The data contained in these blocks are coded using different pulse widths to represent either a binary 0 or a binary 1- 二进制 0 = 2 ms 宽度的脉冲
A binary “0” is represented by a 2 ms pulse. - 二进制 1 = 5 ms 宽度的脉冲
A binary “1” is represented by a 5 ms pulse.
- 二进制 0 = 2 ms 宽度的脉冲
- 获取位置标识符(Px)之间的所有位,可将 BCD 格式的二进制转换为十进制值,获得正确的时间和日期
Taking all the bits between the position identifiers, you can convert binary to a decimal value to get the correct time and date. - 秒、分、小时和年字段被分成两个 4 位部分。
The seconds, minutes, hours and year field are broken into two 4-bit sections.- 前四位表示小数 0-9
The first four bits represent decimals 0-9. - 后四位表示该数字整 10 倍,即 10、20、30、40、50
The next four bits representing the 10’ s of that number – 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50.
- 前四位表示小数 0-9
具体每一位表示的内容如下
Please refer to table 5 for the full details.
控制功能
法国扩展标准 AFNOR NFS 87-500
- 控制功能部分添加了额外的两个字段:【月 Month (0-12)】、【每月第几天 Day of Month (0-31)】
- IRIG-B 中本年第几天最后一个字节未使用的位(42-48)用于显示星期(Day of Week 1-7)
IEEE C37.118.1(取代 IEEE-1344 和 C37.118)扩展标准
| 位 Bit |
=1值含义 Value |
定义 Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 60 | 0 | 闰秒补偿发生 LSP:在插入/删除跳跃之前,该位在 59 秒内变为 1,事件发生后清0。 Leap Second Pending – This field becomes a 1 up to 59 seconds BEFORE a leap is inserted/ deleted. Returns to 0 after the event. |
| 61 | 0 | 闰秒补偿模式 LS:0 = 加一秒(最常见),1 = 减一秒 Leap Second (LS) – 0 = Add a Second (most common) and 1 = Subtract a Second |
| 62 | 0 | 夏令时切换发生 DSP:此位在进入夏令时前一分钟变为 1。进入夏令时后清 0。 Daylight Saving Pending (DSP) – This field becomes a 1 up to 59 seconds BEFORE a DST event. Returns to 0 after the event. |
| 63 | 0 | 夏令时 DST:1= 夏令时期间,0 = 不是夏令时 Daylight Savings Time (DST) – Becomes 1 during DST |
| 64 | 0 | 时间偏移的符号:0 = 正偏移(+),1 = 负偏移(-) Time Offset sign – 0 = + and 1 = – |
| 65 | 1 | 时间偏移:IRIG-B 时间相对 UTC 时间的偏移,即本地时区偏移。如北京在 UTC +8 时区,则 IRIG 时间 – 8 小时= UTC 时间 Time Offset – This is the offset from the IRIG-B time to UTC time i.e. the local time offset (+12 hr for NZ). Taking this offset, and the IRIG time you can get the UTC time. i.e IRIG time – 12 h = UTC time |
| 66 | 2 | |
| 67 | 4 | |
| 68 | 8 | |
| 69 | P7 – 位置标识符 Position ID | |
| 70 | 0 | 时间偏移 0.5 小时(用于精确补偿时区):0 = 不偏移,1 = 启用偏移 Time offset 0.5 hours – 0 = No offset and 1 = 0.5-hour offset |
| 71 | 1 | 时间质量 TQ:时钟源与 UTC 时钟源时间误差信息,4位数值表示。数值的具体含义,参见 TQ 章节。 Time Quality bit – this is a 4-bit code representation of the approximate clock time error from UTC. Refer to table 7 for the full range of values. |
| 72 | 2 | |
| 73 | 4 | |
| 74 | 8 | |
| 75 | 0 | 奇偶校验位:对报文 75 位及之前数据进行偶校验,以确保前面的数据不出错 Parity – this is the parity for preceding bits. Acts as a check to ensure the preceding data make sense. The parity bit will ensure EVEN parity is generated. |
| 76 | 1 | 连续时间质量 CTQ:表示传输消息中的估计时间误差信息,3位数值表示。数值的具体含义,参见 CTQ 章节。Continuous Time Quality – This is a 3-bit code representation of the estimated time error in the transmitted message. Refer to table 8 for the full range of values. |
| 77 | 2 | |
| 78 | 4 | |
| 79 | P8 – 位置标识符 Position ID | |
时间质量(TQ)
| 值 Value |
含义 Definition |
|---|---|
| 0 | 时钟锁定到 UTC 可追踪源(时钟与卫星实时同步) Clock is locked to a UTC traceable source |
| 1 | 与 UTC 的时间误差 < 1ns Time is within <1ns of UTC |
| 2 | 与 UTC 的时间误差 < 10ns Time is within <10ns of UTC |
| 3 | 与 UTC 的时间误差 < 100ns Time is within <100ns of UTC |
| 4 | 与 UTC 的时间误差 < 1μs Time is within <1μs of UTC |
| 5 | 与 UTC 的时间误差 < 10μs Time is within <10μs of UTC |
| 6 | 与 UTC 的时间误差 < 100μs Time is within <100μs of UTC |
| 7 | 与 UTC 的时间误差 < 1ms Time is within <1ms of UTC |
| 8 | 与 UTC 的时间误差 < 10ms Time is within <10ms of UTC |
| 9 | 与 UTC 的时间误差 < 100ms Time is within <100ms of UTC |
| 10 | 与 UTC 的时间误差 < 1s Time is within <1s of UTC |
| 11 | 与 UTC 的时间误差 < 10s Time is within <10s of UTC |
| 15 | 时钟故障,时间不可靠 Fault – Clock failure, time is not reliable |
连续时间质量(CTQ)
| 值 Value |
含义 Definition |
|---|---|
| 0 | 未使用(用于兼容旧版 IEEE 标准的位) Not used (indicates code from previous version of standard) |
| 1 | 时钟源时间误差 < 100ns Estimated maximum time error <100ns |
| 2 | 时钟源时间误差 < 1μs Estimated maximum time error <1μs |
| 3 | 时钟源时间误差 < 10μs Estimated maximum time error <10μs |
| 4 | 时钟源时间误差 < 100μs Estimated maximum time error <100μs |
| 5 | 时钟源时间误差 < 1ms Estimated maximum time error <1ms |
| 6 | 时钟源时间误差 < 10ms Estimated maximum time error <10ms |
| 7 | 时钟源时间误差 > 10ms 或时间误差位置 Estimated maximum time error > 10mS or time error unknown |
设计和安装建议
传输介质:屏蔽双绞线(STP) / 同轴电缆
IRIG-B 最常使用同轴电缆作为传输介质。通常,RG58 电缆用于传输直流或载波 IFIG-B 信号,因为它易于布线,易于串接终端电阻,且具有良好的屏蔽特性。
The most common implementations of IRIG-B throughout the world use coaxial cable as the transmission medium. Generally, RG58 cabling is used to carry both AM and DCLS signals, as it is easy to wire, easy to clip on termination resistors and has good shielding characteristics.
其次最常见的是使用屏蔽双绞线(STP)电缆,比如标准以太网电缆。 屏蔽双绞线有几个优点,包括电缆屏蔽层、高传输速率、良好的屏蔽特性(特别是平衡对)、低电容特性。
The next most common is to use shielded twisted pair (STP) cabling like that found in a standard Ethernet cable – except with a braided shield around the outside of the cable. Shielded twisted pair has several benefits including high transmission rates, good shielding characteristics (especially with balanced pairs) and low capacitance characteristics.
如果只用于传输 IRIG-B 信号,哪种介质更好? STP,因为 STP 有较低的电缆电容。
In the case of the transmission of IRIG-B, which one is better? The answer is STP. The key reason as to why STP is better than coax, is the lower cable capacitance.
- 对于 RG58 同轴电缆,建议在距离大于 50 m时安装信号中继器
- 对于 STP 屏蔽双绞线,建议在距离大于 100 m时安装信号中继器
终端电阻
对于直流 IRIG-B(DCLS IRIG-B)
- 对于屏蔽双绞线电缆 STP ,电缆阻抗通常为120 Ω(如 Belden 9841)。
For a shielded twisted pair cabling, the cable impedance is usually 120 Ω (e.g. Belden 9841) - 对于同轴电缆,电缆阻抗取决于你使用的电缆类型。
For coaxial cable it will depend on what type of cable you use, as to the terminating resistor.- 对于RG 58,建议端接 50 Ω 电阻。
For RG58 you would expect to use a 50 Ω terminating resistor. - 对于RG 59,建议端接 75 Ω 电阻。
For RG59 a 75 Ω resistor.
- 对于RG 58,建议端接 50 Ω 电阻。
在选择电阻器时,还需要考虑额定功率。 直流 IRIG-B 信号通常为 5 V,因此可以使用以下公式计算额定功率:
When selecting a resistor you will also need to consider the power rating. As DCLS is generally a 5 V DC signal, you can calculate the power rating easily using:
P = V 2 R P=\frac{V^{2}}{R} P=RV2
对于调幅载波 IRIG-B(AM IRIG-B)
在开始计算之前,需要收集以下信息(设终端电阻阻抗为 R t e r m R_{term} Rterm):
Before starting this calculation you will need to know the following information:
- 时钟输出的内部阻抗 R s R_s Rs。 可在时钟源的手册中找到相关参数,这里以 120 Ω 为例。
The internal impedance of the clock’s output. In the case of Tekron’s range this is 120 Ω - 连接到 IRIG-B 总线上的每个从设备的输入阻抗 R 1 , R 2 , … , R n R_1, R_2, \dots, R_n R1,R2,…,Rn。 可在从设备手册中找到相关参数,通常为 kΩ 级。这里设每个从设备的输入阻抗为 6 kΩ,连接 5 个从设备(n = 5)。
The input impedance of each IED that is connected to the IRIG-B bus. For most relays this will be in the range of kΩ’s. For this example we are assuming all the relays have a 6 kΩ input impedance. This can be found on most relay manufacturers datasheets. - 从设备接口允许的最大输入电压 V r e q V_{req} Vreq(峰-峰值), 可在从设备手册中找到相关参数,范围通常为 5V 到 10V。
The input voltage requirements of the IED’s. This is where you need to determine the maximum voltage input that the relay allows. This can be anywhere from 5 Vdc to 10 Vdc. This can be found on most relay manufacturers datasheets. - 时钟源的输出电压 V o u t V_{out} Vout(峰-峰值), 可在时钟源手册中找到相关参数。这里设定为 8 V。
he output voltage of the clock. In the case of Tekron this is 8 V.
基于以上信息,首先可计算 IRIG-B 总线上的总负载 R L R_L RL。由于它们是并联的,可列出方程如下:
Now that you have this information, the first step is to calculate the total load on the IRIG-B bus. This can be done by adding together all the input impedances of the slave devices. As they are connected in parallel we would expect the equation to look like this:
1 R L = 1 R 1 + 1 R 2 + ⋯ + 1 R n \frac{1}{R_L}=\frac{1}{R_1}+\frac{1}{R_2}+\dots+\frac{1}{R_n} RL1=R11+R21+⋯+Rn1
1 R L = 1 R s + 1 R 1 + 1 R 2 + 1 R 3 = 1 6000 + 1 6000 + 1 6000 + 1 6000 + 1 6000 = 5 6000 \frac{1}{R_L}=\frac{1}{R_s}+\frac{1}{R_1}+\frac{1}{R_2}+\frac{1}{R_3}=\frac{1}{6000}+\frac{1}{6000}+\frac{1}{6000}+\frac{1}{6000}+\frac{1}{6000}=\frac{5}{6000} RL1=Rs1+R11+R21+R31=60001+60001+60001+60001+60001=60005
因此总负载 R L R_L RL为:
Solving for R_L:
R L = 1 5 / 6000 = 1200 Ω R_L=\frac{1}{5/6000}=1200 \Omega RL=5/60001=1200Ω
根据并联电路分压原理,可得到:
1 / R t e r m + 1 / R L R S = V r e q V o u t − V r e q ⇒ 1 R t e r m + 1 R L = V r e q ∗ R s V o u t − V r e q \frac{1/R_{term}+1/R_L}{R_S}=\frac{V_{req}}{V_{out}-V_{req}} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{R_{term}} + \frac{1}{R_L} = \frac{V_{req} * R_s}{V_{out}-V_{req}} RS1/Rterm+1/RL=Vout−VreqVreq⇒Rterm1+RL1=Vout−VreqVreq∗Rs
整理得到终端电阻 R t e r m R_{term} Rterm的计算表达式:
Now that we know what RL is, we can work out the required terminating resistor by using the following equation:
R t e r m = ( V o u t − V r e q R s ∗ V r e q − 1 R L ) − 1 R_{term}=(\frac{V_{out}-V_{req}}{R_s * V_{req}}-\frac{1}{R_L})^{-1} Rterm=(Rs∗VreqVout−Vreq−RL1)−1
其中:
- V o u t V_{out} Vout= 时钟源的输出电压(峰-峰值)。这里 V o u t = 8 V d c V_{out} = 8V dc Vout=8Vdc
The AM IRIG-B output voltage - V r e q V_{req} Vreq= 从设备接口允许的最大输入电压(峰-峰值)。这里 V r e q = 6 V d c V_{req} = 6V dc Vreq=6Vdc
The minimum required voltage for the slave device to operate - R s R_s Rs= 时钟输出的内部阻抗。这里 R s = 120 Ω R_s = 120 \Omega Rs=120Ω
The output Impedance of the AM IRIG-B output - R L R_L RL= 总负载。这里 R L = 1200 Ω R_L=1200\Omega RL=1200Ω
The total calculate load
带入公式后计算得到终端电阻 R t e r m R_{term} Rterm:
This gives us the following calculation:
R t e r m = ( V o u t − V r e q R s ∗ V r e q − 1 R L ) − 1 = ( 8 − 6 120 ∗ 6 − 1 1200 ) − 1 = 514.3 Ω R_{term}=(\frac{V_{out}-V_{req}}{R_s * V_{req}}-\frac{1}{R_L})^{-1}=(\frac{8-6}{120*6}-\frac{1}{1200})^{-1}=514.3\Omega Rterm=(Rs∗VreqVout−Vreq−RL1)−1=(120∗68−6−12001)−1=514.3Ω
使用直流 IRIG-B(DCLS IRIG-B)
- 时钟输出的驱动功率是多少? 这些参数应该在 IRIG-B 时钟源的说明书中提供
What is the drive power of the clocks output? For Tekron this is commonly 150 mA - 从设备的输入阻抗是多少?或者电流消耗是多少? 这些参数应在从设备的说明书中提供
What is the input impedance of the IED? Or what is the current drain of the IED? These parameters should be available in the vendors datasheets - 第一个从设备和最后一个从设备之间的距离
The distance between the 1st IED and the last IED that you want to synchronise.
这里通过一个示例进行说明。以下等式可计算总负载电流 I L I_L IL:
I L = I 1 + I 2 + I 3 + ⋯ + I n + V s R t e r m I_L=I_1+I_2+I_3+\dots+I_n+\frac{V_s}{R_{term}} IL=I1+I2+I3+⋯+In+RtermVs
其中:
- I L I_L IL= 总的电流负载
- I 1 I_1 I1到 I n I_n In= 总线上每一路从设备的电流消耗
- V s V_s Vs= 时钟的电源电压。通常为 5 V 直流。
- R t e r m R_{term} Rterm= 与电缆阻抗匹配的终端电阻值(屏蔽双绞线 = 120 Ω)
- 输入电压范围(5 Vdc)
- 阻抗(kΩ)/ 电流负载(mA)
如果手册中已经说明了电流负载,则电流负载即为 I n I_n In。如果手册中只有电压范围和阻抗,则可根据欧姆定律计算额定电流负载:
I n = V R I_n=\frac{V}{R} In=RV
这里:
- V V V= 输入电压 = 电源电压(对于直流 IRIG-B 信号,通常为 5V)
- R R R= 从设备的输入阻抗
I 1 = 5 5000 = 1 m A I_1=\frac{5}{5000}=1 mA I1=50005=1mA
I L = 25 × 5 5000 + 5 120 = 67 m A I_L=25\times\frac{5}{5000}+\frac{5}{120}=67mA IL=25×50005+1205=67mA
在知道当前线路电流负载后,检查此时 I L I_L IL是否大于信号源能提供的驱动电流。
ow we know the total loading of the relays on the IRIG-B output. The next point is to check that this I L is not larger than the clocks drive power.
实际上要考虑时钟和最后一个继电器之间的电缆总长度。如果电缆长度超过 50 米,建议将剩余的设备接到另一个输出上,或者使用信号中继器重新生成此信号。原因有以下两点:
If the cable length is getting greater than 50 m it’s recommended that you either split the remaining relays off onto another output, or use a signal repeater to regenerate this signal. There are several reasons for this suggestion.
第一点,IRIG-B 信号在传输50 m之后,由于电缆电容的影响,直流方形 IRIG-B 信号边缘会变圆,信号质量下降将会比较严重。 可能导致从设备不能正常响应信号,或由于信号边缘不清晰导致数据的错误舍入,降低数据精度。
The first is that after 50 m of transmission, the square IRIG-B signal may start to show rounded edges as the cable capacitance starts to degrade the signal quality. It may even start to degrade to a point where IEDs will reject it as a valid signal, or the signal accuracy will decrease due to the rounded rising and falling signal edges.
第二点,要考虑的是信号在通过一段长导线时的累积传播延迟。 对于Belden 9841屏蔽双绞线电缆,传播延迟为 5.25 ns/m。超过 50 m 时 ,延迟增加到262.5 ns。对于大多数应用来说,若对时精度只要求 ms 级或更低,则这是可以接受的。但是在目标要求对时精度 < 1 μs 的应用中,这里的延迟将不可忽略,因为仅在电缆传输延迟上就可能损失 26% 的开销。
The second point to think about is the accumulated propagation delay of the signal as it passes down a long piece of wire. For Belden 9841 shielded twisted pair cabling the propagation delay is 5.25 ns/ m. Over 50 m this adds to 262.5 ns of delay. For most applications this is minimal, especially when your target accuracy is only 1 ms. But in an application where you are aiming for a < 1 μs accuracy, this is important as you could lose 26% of your overhead just in the cable transmission delay.
使用载波 IRIG-B(AM IRIG-B)
在 25 个从设备连接到总线的示例的情况下,关键问题变成:从设备的输入电压要求与从时钟供应的线电压之间的关系。
In the case of the example where 25 IEDs are connected to a bus, the key concern will now become the input voltage requirements for the IEDs compared to the line voltage supplied from the clock.
使用【终端电阻】章节的计算公式,确定对应从设备数量应使用的终端电阻,保证分压要求满足从设备需求。
Using the equation in the terminating resistor section, you will need to determine the voltage level which all the IEDs will accept, and then work through the equation to determine the best voltage divider to reach that.
同时还要根据精度要求,考虑电缆引起的传播延迟是否可以忽略。
You will need to take into consideration your accuracy targets, and factor in the propagation delay which is induced from the cable.
使用光纤传输
- 完美的介质隔离:在时钟输出和从设备之间,使用光纤收发器实现光纤链路,实现线路的物理隔离,如果其中一个进入故障状态,则故障电压、电流不会进入光纤介质,这可以保护设备。
Perfect isolation – using a fibre link between a clock and a IED or media converter gives an isolation barrier which protects both devices, should one enter a fault state. - 传输距离长:使用多模/单模光纤链路,可以传输长达 2km/25km 的信号,而无需中继器。
Long transmission distances – using a multi/singlemode fibre link you can transmit a signal up to 2/25 kilometer without the need for repeaters. - 抗辐电磁噪声:直流 IRIGB-B 信号是 5V 直流信号,对外部电磁噪声非常敏感。使用光纤链路可以消除这些问题,因为电磁噪声不会干扰光纤信号。
Immune to Radiated noise – DCLS is a 5 Vdc signal which is quite susceptible to external noise. Using a fibre link you remove these concerns as electrical noise will not affect it.
- 光纤传输是点对点连接: 如果您有数百个需要从设备需要连接,需要一系列的分配单元来将单个光纤输出分成多个输出。这提供了完美的隔离,但会增加成本。
Point to Point connection – If you have hundreds of IEDs that require IRIG-B, you now need a range of distribution units to split a single fibre output into many outputs. This gives perfect isolation, but my increase the cost of the installation. - 光纤传输的菊花链式连接:如果使用菊花链(串联连接)所有设备,若单个设备出现故障,所有下游设备都可能失去同步。
Daisy chained links – when using fibre across multiple IEDs, you need to daisy chain (series connection) all the devices. If a single device fails there is potential for all the downstream devices to lose sync
其他定时信号:定时脉冲信号
总结
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/132467.html