大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
文章目录
基本知识
- 代码不区分大小写
- 两个减号为单行注释
- 电路功能分为顺序语句和并行语句两种
库Library
- 存放已编译程序包和数据集合的地方,可以被调用
- 代码格式
library 库名; use 库名中的逻辑体名; - 代码实例
library ieee; --打开ieee库 use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; --加载ieee中std_logic_1164包内的所有内容 - 库的种类
- STD库 – VHDL标准库
- IEEE库 – VHDL标准库的扩展
- WORK库 – 用户自己的库
- 3个常用的库
library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; --包含std_logic、std_vector等类型定义及其相关逻辑类子程序定义 use ieee.std_logic_arith.all; --包括std_logic类型数据的算术运算子程序定义。(如+、-、*、移位、比较等) use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all; --std_logic_vector类型的无符号数算术运算子程序定义 use work.PCK_CRC32_D8.all;--用户自己的库
自定义库(程序包的使用)
VHDL中默认一个work库作为用户的project的设计库,用户可以通过定义PACKAGE(程序包)来定义work库中的内容。
程序号(PACKAGE)的定义分为两部分内容:包首部分和包体部分
- 包首部分
package <程序包名称> is --包首说明 :定义数据类型、元件和子程序等 end <程序包名称>; - 包体部分
package body <程序包名称> is --包体说明语句 :描述元件和子程序内容 end <程序包名称>; - 举例
library IEEE; use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all; package PCK_bk_serdes is constant FRM_VID : std_logic_vector(8-1 downto 0):= X"00"; constant FRM_VSYNC : std_logic_vector(8-1 downto 0):= X"01"; end PCK_bk_serdes; ---------------------------------------------------------------- ---------------------------------------------------------------- package body PCK_bk_serdes is end PCK_bk_serdes;
实体Entity
- 实体用于描述所设计系统的外部接口信号
- 格式
entity entity_name is generic( parameter_name : 数据类型 := default_value; parameter_name : 数据类型 := default_value ); port( port_name : 方向 数据类型; port_name : 方向 数据类型 ); end entity entity_name; - 端口方向
in - 输入端口,此类型的信号不能被赋值 out - 输出端口 inout - 双向端口 buffer - 缓冲端口 - 举例
entity entity_name is port( sysclk : in std_logic; nRST : in std_logic; led : out std_logic ); end entity;
结构体Architecture
- 构造体用于描述实体所代表的系统内部结构和行为
- 代码格式
architecture 结构体名 of 实体名 is [说明语句] begin [功能描述语句] end 结构体名; - 说明语句包括了内部信号、常数、元件、数据类型、函数定义
数据对象
常量Constant
- 常量声明格式
constant 常量名 : 数据类型 [:= 初始值]; - 可以在library/entity/architecture/process中定义
变量Variable
- 变量声明格式
variable 变量名 : 数据类型 [取值范围] [:= 初始值]; - 变量是局部量,只能在进程process和子程序中使用
- 变量的赋值是理想的,没有延时(即使用组合逻辑实现而不是时序逻辑)
- 变量赋值符号为
:= - 有些变量类型需要声明范围,比如integer类型就需要。而std_logic类型就不需要(std_logic取值范围比较小,而integer取值范围很大,手动声明范围可以减少元件的使用)
- 带取值范围的变量声明举例
variable x, y : integer range 15 downto 0 := 1;
信号Signal
- 在architecture中定义
- 信号赋值符号为
<=,但是初始化符号是:= - 信号声明格式
signal 信号名 : 数据类型 [:= 初始值];
数据类型
- 常用数据类型
- 标准逻辑 std_logic
- 标准逻辑序列 std_logic_vector
- 整数 integer
constant CLK_NUM : integer := 3; constant CLK_NUM : std_logic_vector(3 downto 0) := X"3"; signal clk_en : std_logic; signal clk_cnt : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0); signal num : integer range 0 to 15;--信号num的取值范围是0-15,可用4位二进制表示 - 数组
type ARRAY_3xVID_NUM is array (0 to VID_NUM-1) of std_logic_vector(2 downto 0); signal vsync_meta : ARRAY_3xVID_NUM; ------------------------------------------------------------------------ for i in 0 to VID_NUM-1 loop vsync_meta(i) <= vsync_meta(i)(1 downto 0)&vsync_in(i); if vsync_meta(i)(2 downto 1) = "10" then vsync_neg(i) <= '1'; else vsync_neg(i) <= '0'; end if; end loop;
类型转换
- use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all
| 转换函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| to_std_logic_vector | 将 bit_vector 转换为 std_logic_vector |
| to_bit_vector | 将 std_logic_vector 转换为 bit_vector |
| to_std_logic | 将 bit 转换为 std_logic |
| to_bit | 将 std_logic 转换为 bit |
- use IEEE.std_logic_arith.all
| 转换函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| conv_std_logic_vector | 将 integer、unsigned、signed 转换为 std_logic_vector |
| to_bit_vector | 将 std_logic_vector 转换为 bit_vector |
- use IEEE.std_logic_unsigned.all
| 转换函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| conv_integer | 将 std_logic_vector 转换为 integer |
信号运算
- 信号赋值:
<=例: x <= ‘1’ - 逻辑运算符:
and、or、not、xor异或、xnor同或、nand与非、nor或非- 例: x <= not y; x <= y and z; …
- 算术运算符:
+加、-减、*乘、/除、乘方、mod取模、rem取余、sll逻辑左移、srl逻辑右移、sla算数左移、sra算数右移、rol逻辑循环左移、ror逻辑循环右移、abs取绝对值 - 关系运算符:
=、/=、>、<、>=、<= - 位拼接运算:
&
并行语句
- 在结构体语句中,并行语句的位置为
architecture 结构体名 of 实体名 is [说明语句] begin [并行语句] end 结构体名;
进程语句-process
- 进程描述格式
process (sensitivity list) begin --功能代码 end process - 进程由敏感信号变化启动
- 进程内语句为顺序语句,但结构体内的不同进程是并行的,各个进程根据敏感信号独立运行
参数传递语句-generic
- 参数传递语句(GENERIC)主要用来传递信息给设计实体的某个具体元件,如用来定义端口宽度、器件延迟时间等参数后,并将这些参数传递给设计实体
- 使用参数传递语句易于使设计具有通用性
- 格式
generic(常数名 数据类型 := 设定值); - 应用场景
- 定义实体的端口大小
- 设计实体的物理特征;传输延迟,上升和下降延迟等
- 结构体的总线宽度
- 设计实体中底层中同种原件的例化数量
元件例化语句-component
元件声明格式
component 元件名 generic( NUM1 : integer:= 1; --参数说明1; NUM2 : integer:= 2 --参数说明2 ); port( port1 :in std_logic;--端口说明1; port2 :out std_logic_vector(NUM2-1 downto 0)--端口说明2 );end component; 注意分号的位置;端口说明中的参数为该元件参数
元件例化格式
module1_inst:元件名 generic map( NUM1 => NUM3, --参数映射 NUM2 => NUM4 ) port map( port3 =>port1,--端口映射 port4 =>port2 ); 生成语句-generate
- GENERATE 语句用来产生多个相同的结构和描述规则结构,如阵列、元件例化和进程
- for…generate语句设计规则体,不规则体可用if…generate语句
for…generate
- 该生成语句用于描述多重模式,结构中所列举的是并发处理语句。这些语句并发执行而不是顺序执行,因此结构中不能用EXIT和NEXT语句
- 格式:
标号:for 变量 in 不连续区间 generate <并发处理的生成语句> end generate [标号名];
if…generate
- 该语句用于描述结构的例外情况,如边界处发生的特殊情况
- 格式:
标号:if 条件 generate <并发处理的生成语句> end generate [标号名];
块语句-block
- 块(BLOCK)语句可以看作是结构体中的子模块,块语句把许多并行语句组合在一起形成一个子模块,而它本身也是一个并行语句
- 格式
块结构名: BLOCK 端口说明 类属说明 BEGIN 并行语句 END BLOCK 块结构名;
信号赋值语句
简单信号赋值 <=
Sginal_name <= expression; 条件信号赋值 when…else…
Sginal_name <= value_a when condition1 else value_b when condition2 else value_c; --Example Rd_en <= '1' when (Rd_empty = '0') else '0'; 选择信号赋值 with…select…when
with selection_signal select Select_name <= value_a when value_1_of_selection_signal, value_b when value_2_of_selection_signal, value_c when others; --Example with S select X <= A when "00"|"10", B when "01", C when others; 选择信号赋值语句不允许条件重叠或条件涵盖不全,注意区分逗号和分号
顺序语句
顺序语句 – 进程语句
进程描述格式:
[进程标签 :] process (敏感信号参数表) [进程说明] begin [顺序描述语句] end process - 进程由敏感信号变化启动
- 进程内语句为顺序语句,但构造体内的不同进程是并行的,各个进程根据敏感信号独立运行
- 时序电路中CLK信号常为敏感信号
常见顺序语句
赋值语句
变量赋值与信号赋值
if-else语句
- 分支少、具有优先级时候使用
- if 必须有一个 else 对应(除下面情况可不写 else 语句),当没有 else 语句,将产生不希望的存储器
process(Clk,Rst) begin if(Rst = '1')then Q <= '0'; elsif rising_edge(Clk) then Q <= D; end if; end process;
case – when 语句
- 在多条分支的时候使用
- case-when 语句必须有 when others 支项
- 这里的
=>不是操作符,相当于thencase Selection_signal is when value1_of_selction sigal => Statements1; when value2_of_selction sigal => Statements2; ... when others => NULL; end case;
for…loop语句
- 在重复操作时使用
process(signal1,signal2) beign for i in 开始值 to 结束值 loop --功能代码 end loop; end process;
时序逻辑相关
- 上升沿的描述:
rising_edge(clk) - 状态机定义
type state is( INIT, REC_DATA, SEND_DATA, TAIL ); signal pstate : state := INIT; - 时钟:一定频率的方波
- 组合逻辑:输出只由输入决定,与时钟无关
- 无时钟边沿敏感
process (A,B) begin if(A = '1' and B = '0') then C <= X"1"; elsif (A = '1' and B = '1') then C <= X"2"; else C <= X"3"; end if; end process; - 时序逻辑:输出不仅由输入决定,还与时钟相关
- 异步复位逻辑
- 时钟单边沿敏感
process (sysclk, nRST) begin if (nRST = '0') then C <= X"0"; elsif (rising_edge(sysclk)) then if(A = '1' and B = '0') then C <= X"1"; elsif (A = '1' and B = '1') then C <= X"2"; else C <= X"3"; end if; end if; end process;
状态机
type state is( IDLE, CONFIG, DATA, DONE ); signal C_S,N_S: state:= IDLE; FSM_ONE: process(clk)begin if (rst = '1') then C_S <= IDLE; else C_S <= N_S; end if; end process; FSM_TWO: process(C_S) begin when IDLE => if () then N_S = ; else N_S = IDLE; when others => N_S = IDLE; end case; end process; FSM_THREE: process(clk)begin if (rst = '1') then else end if; end process; TEXTIO
TEXTIO 是VHDL 标准库STD 中的一个程序包(Package)。在该包中定义了三个类型:LINE 类型、TEXT类型以及SIDE 类型。另外,还有一个子类型(subtype)WIDTH。此外,在该程序包中还定义了一些访问文件所必须的过程(Procedure)。
详细见链接:
VHDL学习之TEXTIO在仿真中的应用 – 蓝旭伯 – 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
VHDL读写txt文件
library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; use ieee.std_logic_arith.all; use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all; --//TXT相关的Library库 use std.textio.all; use ieee.std_logic_textio.all; --//实体 entity wr_txt_tb is --generic(); --port(); end entity; --//实体 architecture beha of wr_txt_tb is --//定义元件及其端口 --//定义常量(时间) constant PERIOD : time := 5ns; constant INPUT_FILE : string:= "data_input.txt"; constant OUTPUT_FILE : string:= "data_output.txt"; --//定义其他信号 signal dv_i : std_logic:= '0'; signal da_i0 : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0):=(others =>'0'); signal da_i1 : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0):=(others =>'0'); signal da_i2 : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0):=(others =>'0'); signal da_i3 : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0):=(others =>'0'); signal sim_end : std_logic:= '0'; signal dv_o : std_logic:= '0'; signal da_o : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0):=(others =>'0'); signal clk : std_logic := '0'; signal nRST : std_logic := '0'; signal RST : std_logic := '1'; signal cnt : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0):=(others =>'0'); ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- begin ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- clk <= not clk after (PERIOD/2); nRST <= '1' after 2*PERIOD; RST <= not nRST; -----------------------------读数据------------------------------ process_read_file : process(clk,nRST) constant NUM_COL : integer := 4; --number fo column of file type data_array is array(integer range<>) of std_logic_vector(7 downto 0); file file_in : text open read_mode is INPUT_FILE; variable line_in: line; variable data_in : data_array(1 to NUM_COL); --文件里一行只有多个数(用空格隔开) -- variable data_in : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);--文件里一行只有一个数 begin if nRST = '0' then elsif(rising_edge(clk)) then if not(endfile(file_in)) then dv_i <= '1'; readline(file_in, line_in); for j in 1 to NUM_COL loop --一行有多个数,同时读出 read(line_in, data_in(j)); end loop; da_i0 <= data_in(1); da_i1 <= data_in(2); da_i2 <= data_in(3); da_i3 <= data_in(4); else dv_i <= '0'; da_i0 <= (others => '0'); da_i1 <= (others => '0'); da_i2 <= (others => '0'); da_i3 <= (others => '0'); end if; end if; end process; ---------------------------写数据----------------------------- process(clk,nRST)begin if nRST = '0' then cnt <= (others => '0'); elsif rising_edge(clk) then if cnt(7) = '0' then cnt <= cnt + '1'; end if; if cnt(7) = '0' then dv_o <= '1'; else dv_o <= '0'; sim_end <= '1'; end if; end if; end process; da_o <= cnt; process_write_file : process(clk,nRST) file file_out : text open write_mode is OUTPUT_FILE; variable line_out:LINE; begin if(nRST = '0') then elsif(rising_edge(clk))then if(sim_end = '1') then --利用sim_end来控制关闭文件 file_close(file_out); elsif(dv_o='1') then write(line_out, da_o, left, 15); --以二进制存储;left表示左对齐,相反,right表示右对齐;15表示字符长度(可用来插入空格) -- write(line_out, conv_integer(da_o), left, 15); --以整数存储 -- hwrite(line_out, da_o, left, 15); --以十六进制存储 -- hwrite(line_out, x"00"&da_o, left, 15); --以4位十六进制存储 writeline(file_out,line_out); end if; end if; end process; end beha; 其他知识点
- rising_edge(clk) 和 (clk’event and clk=‘1’)的区别
- rising_edg 是非常严格的上升沿,必须从0到1;
- (clk’event and clk=‘1’) 可以从 X 到1,只要当前状态为1,结果就为TRUE,不管前一个状态
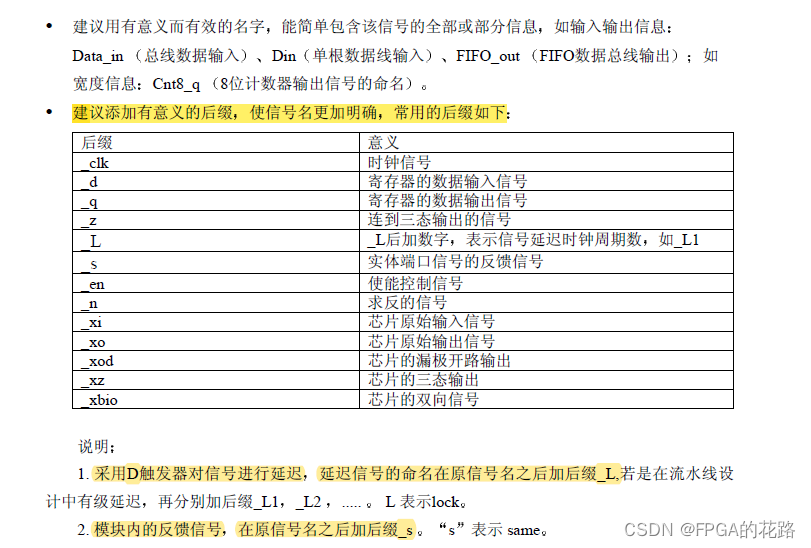
书写规范
标识符(Identifiers)命名习惯
标识符定义命名
- 标识符第一个字符必须是字母,最后一个字符不能是下划线,不许出现连续两个下划线;
- 基本标识符只能由字母、数字和下划线组成;
- 标识符两词之间需用下划线连接
如:Packet_addr , Data_in
- 标识符不得与保留字同名
标识符大小写
- 对常量、数据类型、实体名和结构体名采用全部大写;
- 对变量采用小写;
- 对信号采用第一个词首字符大写;
- 保留字一律小写
信号名连贯缩写
部分缩写的统一规定为:
Addr address; Clk clock; Clr clear; Cnt counter
En enable; Inc increase; Lch latch; Mem memory
Pntr pointer; Pst preset; Rst reset
Reg register; Rd reader; Wr write
常用多个单次的缩写
ROM RAM CPU FIFO ALU CS CE
自定义的缩写必须在文件头注释
信号名缩写的大小写
- 单次的缩写若是信号名的第一个单次则首字母大写,如:Addr_in 中的 Addr;若该代词缩写不是第一个单词则小写,如:Addr_en 中的 en
- 多个单次的首字母缩写都大写,不管该缩写在标识符的什么位置,如:RAM_addr,Rd_CPU_en
信号名一致性
同一信号在不同层次应保持一致性
信号命名建议
其它注意地方
- 只有三态电路才可以在多个process 中出现
- 使用 Latch 必须有所记录,不希望使用 Latch 时,应该将条件赋值语句写全,如在 if 语句最后加 else,case 语句后加 others
- TAB键的间隔,采用4个字符
- 若元件的类属在定义时已经指定默认值,在调用时,若不改变该参数值可以不用定义实参的映射,即map(实参)可不写
- 建议运算操作符两边都加上空格
- 向量比较时,比较的向量的位宽要相等
代码模块划分
设计模块的基本原则是:
- 有利于模块的可重用性
- 在组合电路设计中应当没有层次
- 每个模块输出尽量采用寄存器输出
- 模块按功能进行划分,划分要合理
- 模块大小应适中,一般为2000门左右
- 模块的层次应当至少有三级,可将一个设计划分为三个层次:TOP、MID、功能CORE
- TOP
包括实例化的MID和输入输出定义
- MID
由两部分组成:1)时钟产生电路;2)功能CORE的实例化
- 功能CORE
包括各种功能电路的设计。一个复杂的功能可以分成多个子功能来实现,即再划分子层
- TOP
VHDL保留字
函数书写实例
注意:
- 函数参数只能是输入类型,不能被赋值修改
- 只能有一个返回值
- 定义函数必须为顺序语句,且其中不能定义新的信号,但可在函数说明域中说明新的变量,并在定义域中对其进行赋值
-- Filename : FullAdd.vhd -- Author : xioaming -- Description : A example of function -- Called by : Top module -- Revision History : 2022-07-01 library IEEE; use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all; use IEEE.std_logic_arith.all; use IEEE.std_logic_unsigned.all; entity FULLADD is port( A :in STD_LOGIC; B :in STD_LOGIC; Carry_in :in STD_LOGIC; Sum :out STD_LOGIC; Carry_out :out STD_LOGIC ); end FULLADD; architecture BEHAVIOR of FULLADD is function Majority(A,B,C: STD_LOGIC) return STD_LOGIC is begin reture((A and B)or(A and C)or(B and C)) end Majority; begin Sum <= A xor B xor Carry_in; Carry_out <= Majority(A,B,Carry_in); end BEHAVIOR; 程序包书写实例
library IEEE; use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all; use IEEE.std_logic_unsigned.all; use IEEE.std_logic_arith.all; package time_pkg is constant XX : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0):= x"11"; type TP_DATA_12x5bit is array(0 downto 11) of std_logic_vector(4 downto 0); type TP_UTC_YMD is record yy :std_logic_vector(7 downto 0); mm :std_logic_vector(3 downto 0); dd :std_logic_vector(4 downto 0); end record; function MULT10( din : in std_logic_vector(3 downto 0) )return std_logic_vector; end time_pkg; package body time_pkg is function MULT10( din : in std_logic_vector(3 downto 0) )return std_logic_vector is variable result : std_logic_vector(6 downto 0); begin result := (din & "000") + ("00" & din & '0'); return result; end MULT10; end time_pkg; 调用程序包
library time_lib; use time_lib.time_pkg.all; 参数化元件实例
component REG_GROUP is generic( Size : INTEGER:= 2 );port( Clk : in STD_LOGIC; Rst : in STD_LOGIC; Load : in STD_LOGIC; D : in STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(Size-1 downto 0); Q : out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(Size-1 downto 0) ); end component; U_REG_GROUP:REG_GROUP generic map( Size => 2 )port map( Clk => Clk , Rst => Rst , Load => Load, D => D , Q => Q ); VHDL模板
-- Filename : Div5.vhd -- Author : xioaming -- Description : Five division -- Called by : Top module -- Revision History : 2022-07-01 library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; use ieee.std_logic_arith.all; use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all; entity module_name is generic( SIM : std_logic:= '0'; NUM1 : integer:= 1; NUM2 : integer:= 2 ); port( port1 :in std_logic; port2 :out std_logic_vector(NUM1-1 downto 0) ); end entity; architecture BEHAVIOR of module_name is --------------STATE-------------- type state is( ST_A, ST_B, ST_C ); signal pstate : state := ST_A; --------------COMPONENT-------------- component module1 is generic( NUM3 : integer:= 3; NUM4 : integer:= 4 ); port( port3 :in std_logic; port4 :out std_logic_vector(NUM3-1 downto 0) ); end component; --------------SIGNAL-------------- constant NUM5 : integer:= 5; signal signal1 : std_logic; signal signal2 : std_logic_vector(NUM5-1 downto 0); ---------------------------- begin ---------------------------- module1_inst:module1 generic map( NUM3 => NUM1, NUM4 => NUM2 ) port map( port3 => port1, port4 => port2(NUM2-1 downto 0) ); vid: for i in 0 to NUM1-1 generate module1_inst1: module1 port map( ); end generate vid; process(clk,nRST)begin if nRST = '0' then elsif rising_edge(clk) then end if; end process; process(list1,list2)begin for i in 0 to NUM5 loop if then else end if; end loop; end process; end architecture BEHAVIOR; begin
elsif rising_edge(clk) then end if; end process;
else end if; end loop; end process;
end architecture BEHAVIOR;
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/133082.html