大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
一、binwalk介绍
二、安装binwalk
git clone https://github.com/ReFirmLabs/binwalk.git cd binwalk sudo python ./setup.py uninstall # 如果您有以前安装的 Binwalk 版本,建议您在升级之前将其卸载 sudo ./deps.sh # 安装依赖项 sudo python ./setup.py install sudo -H pip install git+https://github.com/ahupp/python-magic sudo -H pip install git+https://github.com/sviehb/jeffersonhzy@ubuntu:~$ binwalk Binwalk v2.1.2-c036535 Craig Heffner, ReFirmLabs https://github.com/ReFirmLabs/binwalk Usage: binwalk [OPTIONS] [FILE1] [FILE2] [FILE3] ... Disassembly Scan Options: -Y, --disasm Identify the CPU architecture of a file using the capstone disassembler ... ... -s, --status=<int> Enable the status server on the specified port hzy@ubuntu:~$三、binwalk工具的使用帮助
root@node1:/home/binwalk# binwalk -h Binwalk v2.2.1+e0f9bf7 # 版本号 Craig Heffner, ReFirmLabs https://github.com/ReFirmLabs/binwalk Usage: binwalk [OPTIONS] [FILE1] [FILE2] [FILE3] ... Disassembly Scan Options: -Y, --disasm Identify the CPU architecture of a file using the capstone disassembler -T, --minsn=<int> Minimum number of consecutive instructions to be considered valid (default: 500) -k, --continue Don't stop at the first match Signature Scan Options: -B, --signature Scan target file(s) for common file signatures 扫描目标文件以获取常见文件签名 -R, --raw=<str> Scan target file(s) for the specified sequence of bytes 扫描目标文件的指定字符序列 -A, --opcodes Scan target file(s) for common executable opcode signatures 扫描目标文件中常见可执行代码 -m, --magic=<file> Specify a custom magic file to use 指定要使用的自定义签名文件 -b, --dumb Disable smart signature keywords 禁用智能签名关键字 -I, --invalid Show results marked as invalid 显示完整的扫描结果 -x, --exclude=<str> Exclude results that match <str> 排除与<str>匹配的结果 -y, --include=<str> Only show results that match <str> 只显示与<str>匹配的结果 Extraction Options: -e, --extract Automatically extract known file types 自动提取已知的文件类型 -D, --dd=<type[:ext[:cmd]]> Extract <type> signatures (regular expression), give the files an extension of <ext>, and execute <cmd> 提取<type>签名,为文件扩展名为<ext>,然后执行<cmd>,比如:binwalk -D 'png image:png' firmware.bin -M, --matryoshka Recursively scan extracted files 递归扫描提取的文件 -d, --depth=<int> Limit matryoshka recursion depth (default: 8 levels deep) 递归深度 -C, --directory=<str> Extract files/folders to a custom directory (default: current working directory) 将文件/文件夹提取到自定义目录(默认:当前工作目录) -j, --size=<int> Limit the size of each extracted file 限制每个提取文件的大小 -n, --count=<int> Limit the number of extracted files 限制提取文件的数量 -r, --rm Delete carved files after extraction 清理零大小文件和提取工具在提取期间无法处理的文件。仅当与--extract或--dd一起使用时有效。有助于清除提取期间从目标文件中复制的误报文件 -z, --carve Carve data from files, but don't execute extraction utilities 从文件中读取数据,但不执行提取实用程序 -V, --subdirs Extract into sub-directories named by the offset Entropy Options: -E, --entropy Calculate file entropy 计算文件熵,熵分析可以帮助识别固件映像中有趣的数据部分 -F, --fast Use faster, but less detailed, entropy analysis -J, --save Save plot as a PNG 自动将 --entropy 生成的熵图保存到 PNG 文件中,而不是显示它 -Q, --nlegend Omit the legend from the entropy plot graph 从熵图中省略图例 -N, --nplot Do not generate an entropy plot graph 不生成熵图 -H, --high=<float> Set the rising edge entropy trigger threshold (default: 0.95) 设置上升沿熵触发阈值 -L, --low=<float> Set the falling edge entropy trigger threshold (default: 0.85) 设置下升沿熵触发阈值 Binary Diffing Options: -W, --hexdump Perform a hexdump / diff of a file or files 比较文件 -G, --green Only show lines containing bytes that are the same among all files -i, --red Only show lines containing bytes that are different among all files -U, --blue Only show lines containing bytes that are different among some files -u, --similar Only display lines that are the same between all files -w, --terse Diff all files, but only display a hex dump of the first file Raw Compression Options: -X, --deflate Scan for raw deflate compression streams -Z, --lzma Scan for raw LZMA compression streams 通过暴力激活成功教程识别可能的原始 LZMA 压缩数据流 -P, --partial Perform a superficial, but faster, scan -S, --stop Stop after the first result General Options: -l, --length=<int> Number of bytes to scan -o, --offset=<int> Start scan at this file offset -O, --base=<int> Add a base address to all printed offsets -K, --block=<int> Set file block size -g, --swap=<int> Reverse every n bytes before scanning -f, --log=<file> Log results to file 将结果记录到文件 -c, --csv Log results to file in CSV format -t, --term Format output to fit the terminal window -q, --quiet Suppress output to stdout 禁止输出到标准输出 -v, --verbose Enable verbose output 详细输出 -h, --help Show help output -a, --finclude=<str> Only scan files whose names match this regex -p, --fexclude=<str> Do not scan files whose names match this regex -s, --status=<int> Enable the status server on the specified port 启用指定端口上的状态服务器四、binwalk工具的基本用法介绍


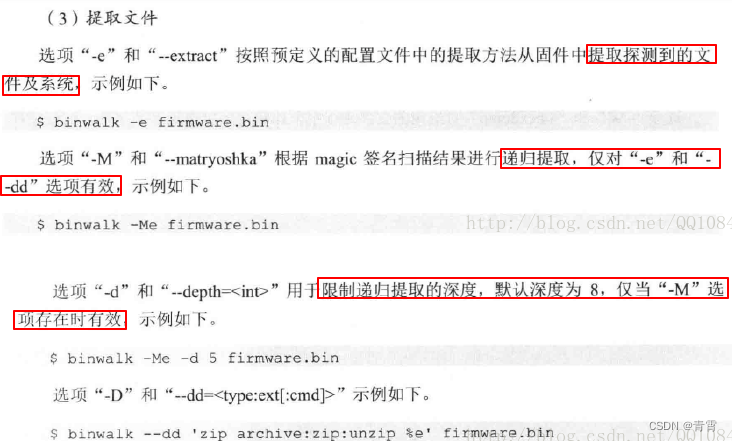












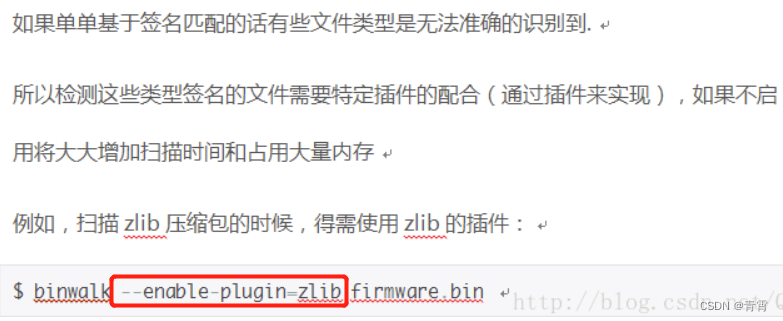
-
type:是包含在签名描述中的*小写*字符串(支持正则表达式)
-
ext:是保存数据磁盘时要使用的文件扩展名(默认为none)
-
cmd:是在数据保存到磁盘后执行的可选命令
$ binwalk -D 'zip archive:zip:unzip %e' -D 'png image:png' firmware.bin
五、binwalk提取原理
binwalk提取文件的原理:通过自带强大的magic特征集,扫描固件中文件系统初始地址的特征码,若匹配成功,则将该段数据dump下来。
这个magic特征集位于:
https://github.com/ReFirmLabs/binwalk/blob/62e9caaa18d7d1f037ab27d14ac933d3cf/src/binwalk/magic/filesystems
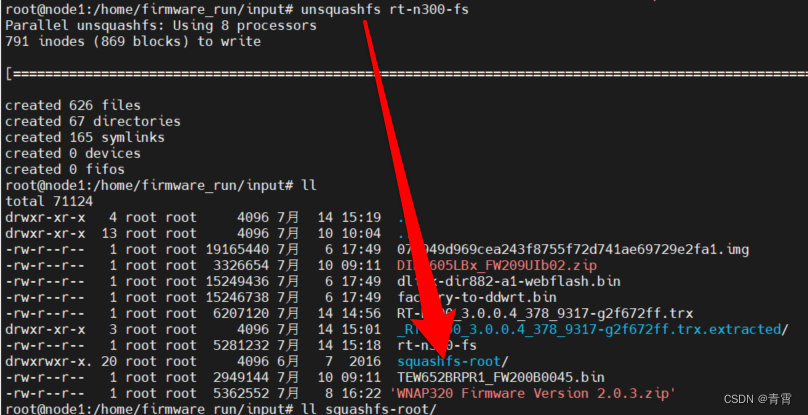
1、在GitHub – G4rb3n/IoT_Sec_Tutorial: IoT安全教程中下载固件RT-N300_3.0.0.4_378_9317-g2f672ff.trx
2、binwalk提取
binwalk -t -vv -e RT-N300_3.0.0.4_378_9317-g2f672ff.trx
通过输出信息,可以得知该固件系统没有加密压缩,且系统为Squashfs。
提取出来的文件夹为_RT-N300_3.0.0.4_378_9317-g2f672ff.trx.extracted,其中的squashfs-root就是我们想要的该固件的文件系统
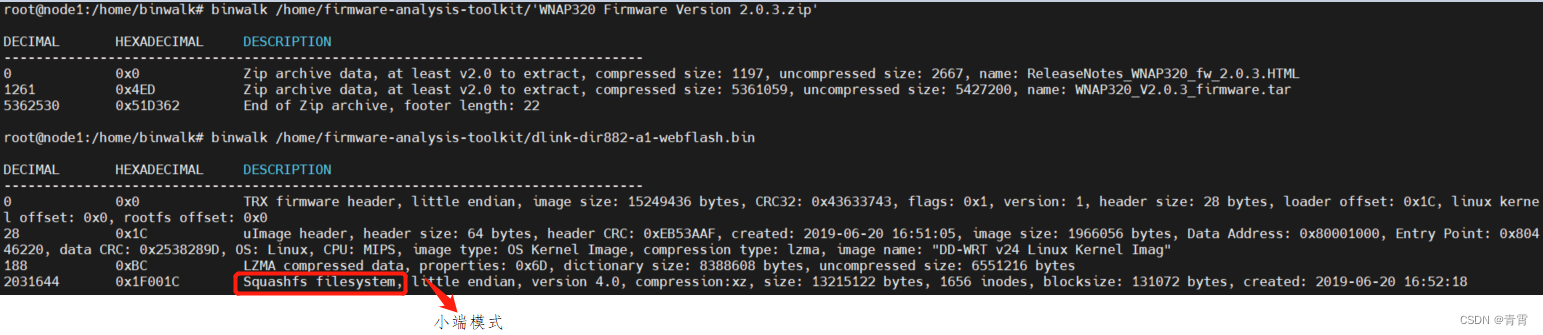
Squashfs, little endian文件系统,对应的扫描特征码为hsqs
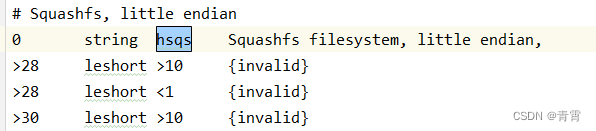
4、使用hexdump搜索hsqs的地址,为0xe20c0,这个就是文件系统的初始地址
hexdump -C RT-N300_3.0.0.4_378_9317-g2f672ff.trx | grep -i ‘hsqs’
5、使用dd命令截取地址(0xe20c0)之后的数据,保存到rt-n300-fs。
dd if=RT-N300_3.0.0.4_378_9317-g2f672ff.trx bs=1 skip= of=rt-n300-fs
6、最后,使用unsquashfs rt-n300-fs命令解析rt-n300-fs文件,得到的squashfs-root就是固件系统,这个跟上述binwalk提取的那个是一样的。
六、python使用binwalk
python3 -m pip install git+https://github.com/ReFirmLabs/binwalk
最感兴趣的两个属性是结果和错误对象
。每个都是 binwalk.core.module.Result 和 binwalk.core.module.Error的实例。每个Result或Error实例可能包含每个模块设置的自定义属性,但保证至少具有以下属性(尽管不需要模块来填充所有属性):
|
Attribute
|
Description
|
|
offset
|
The file offset of the result/error (usually unused for errors)
|
|
description
|
The result/error description, as displayed to the user
|
|
module
|
Name of the module that generated the result/error
|
|
file
|
The file object of the scanned file
|
|
valid
|
Set to True if the result is valid, False if invalid (usually unused for errors)
|
|
display
|
Set to True to display the result to the user, False to hide it (usually unused for errors)
|
|
extract
|
Set to True to flag this result for extraction (not used for errors)
|
|
plot
|
Set to False to exclude this result from entropy plots (not used for errors)
|
|
Attribute
|
Description
|
|
exception
|
Contains the Python exception object if the encountered error was an exception
|
import binwalk for module in binwalk.scan('firmware1.bin', 'firmware2.bin', signature=True, quiet=True): # --quiet选项,它阻止binwalk模块将其正常输出打印到屏幕 print ("%s Results:" % module.name) for result in module.results: print ("\t%s 0x%.8X %s" % (result.file.path, result.offset, result.description))try: binwalk.scan() except binwalk.ModuleException as e: print ("Critical failure:", e)七、参考
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/110337.html