大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
1.什么是mxgraph
1.1mxGraph 架构分析
mxGraph中有三个主要的组件:mxGraph、mxGraphModel、mxCell(含edge和vertex)。
mxGraph是用户直接操作的图,图的所有状态都保存;在mxGraphModel中,而图中的顶点和边都是用mxCell定义。三者层次关系如图所示:
当用户对mxGraph进行操作时,所有操作都映射到对mxGraphModel中保存的状态进行修改,而mxGraphModel中保存的状态也就是mxCell的状态。
围绕着这三个组件,mxGraph定义了很多属性,比如图的功能、mxGraphModel的持久化、mxCell的外观等等。此外mxGraph还具有非常强大的事务管理机制和事件监听器。
| 主要组件 | 描述 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| mxClient | mxClient.js是客户端的引导机制,此文件include了运行mxGraph所需的所有源文件,并加载了其依赖的资源文件,以及配置了客户端的语言。 | 设置加载相关文件的全局变量,设置相关路径,设置客户端语言,加载css文件和js文件 |
| mxGraph | mxGraph继承自mxEventSource以实现基于Web的图形组件的功能性方面。要激活平移和连接,使用setPanning和setConnectable,对于框线选择,必须创建一个新的mxRubberband实例。默认情况下,以下监听器添加到mouseListeners:tooltipHandler:显示工具提示的mxTooltipHandler,panningHandler:用于平移和弹出菜单的mxPanningHandler,connectionHandler:用于创建连接的mxConnectionHandler,graphHandler:用于移动和克隆cell的mxGraphHandler 如果启用了这些监听器,则将按上述顺序调用它们。 | |
| mxGraphModel | mxGraphModel 是描述了图形结构的核心的模型,被称为mxGraphModel,可以在model包中发现。 另外,对图形结构的添加,更改和清除是通过图模型API来完成的。该模型还提供了方法来确定图形 的结构,以及提供方法来设置,如能见度、分组和样式的视觉状态。mxGraphModel是基本的对象,它存储着图形的数据结构。 | |
| mxCell | mxCell是节点和连线的图元对象。mxCell从模型那里复制了许多的方法。它们的主要差别在于,使用模型的方法会创建相关的事件通知以及撤销方法 |
其中 API 提供如下能力: | 包 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| editor | 提供了实现图编辑器所需的类,主要的类是mxEditor |
| handler, layout, shape | 分别包含事件监听器,布局算法和形状。图形事件监听器包括用于框线选择的mxRubberband,用于工具提示的mxTooltipHandler和用于基本单元修改的mxGraphHandler。mxCompactTreeLayout实现树形布局算法,shape包提供各种形状,这些形状是mxShape的子类。 |
| view, model | view和model实现了图形组件,由mxGraph表示。它指的是包含了mxCells并缓存mxGraphView中单元格的状态的mxGraphModel。根据mxStylesheet中定义的外观,使用mxCellRenderer绘制单元格。撤消历史记录在mxUndoManager中实现。要在图表上显示图标,可以使用mxCellOverlay。验证规则使用mxMultiplicity定义。 |
| util | 提供了实用程序类,包括用于复制粘贴的mxClipboard,用于键和样式表值的mxConstants,用于跨浏览器事件处理和通用功能的mxEvent和mxUtils,用于国际化的mxResource和mxLog用于控制台输出。 |
| io | 实现了一个通用的mxObjectCodec,用于将JavaScript对象转换为XML。主要类是mxCodec。mxCodecRegistry是自定义编解码器的全局注册表。 |
2.mxgraph初体验:
npm install mxgraph-js --save 第二步.导入(在你需要用到的组件文件中导入):
import {
mxGraph } from 'mxgraph-js' 第三步:开始使用:
<template> <div ref="graph_container" class="graph_container"></div> </template> <script> import {
mxGraph } from 'mxgraph-js' export default {
name: 'HelloWorld', mounted () {
// 创建画布 var graph = new mxGraph(this.$refs.graph_container); var parent = graph.getDefaultParent(); // 开始更新画布 graph.getModel().beginUpdate(); try {
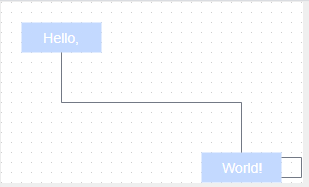
// 插入节点 let v1 = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, 'Hello,', 20, 20, 80, 30); let v2 = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, 'World!', 200, 150, 80, 30); // 插入连线 graph.insertEdge(parent, null, '', v1, v2); } finally {
// 画布更新结束 graph.getModel().endUpdate(); } } }; </script> <style> </style> 方法的参数:
parent – 组结构中此图元的直接父图元。我们会很快谈论到组结构,但现在我们直接使用graph.getDefaultParent();作为默认的父图元,就像在 HelloWorld 这个例子一样。
id – 描述此单元的全局唯一身份号码,总是一个字符串。主要用于外部对这单元的引用。如果你不想自己维护这些号码,只需要传入一个空参数并确保mxGraphModel.isCreateIds()返回真即可。这样,模型就会管理这些号码,并保证它们的唯一性。
value – 此单元的用户对象。用户对象只是一些对象,可以让您把应用程序的商务逻辑与mxGraph的可视化呈现相关联。在手册的后面有详细地描述,这里我们就只用字符 串就好,并把它们显示成节点和边的标签。
x, y, width, height – 就像名字提到的,这是节点的左上角的 x 和 y 的位置以及它的宽度和高度。
style – 将被应用到节点的样式描述。关于样式,很快会有更详细的描述,简单来讲,就是一个特定格式的字符串。这个字符串有零个或多个样式名字和一些键/值配对,用来覆盖全局设置或者创立新的样式。除非我们要创建自己的样式,我们可以直接使用这些现有的设置。
source和target –参数定义了节点要连接的节点;注意,源节点 和目标节点需要已经被加入到模型中。
注意:
1.mxGraph事物的更新(插入新元素时)一定要放在 beginUpdate 和 endUpdate 里面。一次 beginUpdate 必须对应一次 endUpdate
2.由于mxGraph配置了默认的样式(节点字体、连线等元素样式)和默认的配置所以样式看起来比较单一;我们可以在绘制图形前修改mxGraph默认配置好的配置项,来达到我们想要的效果;
<template> <div ref="graph_container" class="graph_container"></div> </template> <script> import {
mxGraph, mxRubberband, mxConstants, mxEvent, mxGraphHandler, mxEdgeStyle } from 'mxgraph-js' export default {
name: 'HelloWorld', mounted () {
var graph = new mxGraph(this.$refs.graph_container); //创建视图 graph.setHtmlLabels(true); // Label 将显示 Html 格式的 Value graph.setTolerance(20); graph.setEnabled(true); //设置启用,就是允不允许你改变CELL的形状内容。 graph.setVertexLabelsMovable(true); // 允许移动 Vertex 的 Label graph.setConnectable(true); // 是否允许Cells通过其中部的连接点新建连接,false则通过连接线连接 graph.setDropEnabled(true); // 从工具栏拖动到目标细胞时细胞边界是否产生光圈 graph.setTooltips(true); // 是否显示提示,默认显示Cell的名称 graph.setResizeContainer(true); // 容器大小自适应 graph.setMultigraph(false); // 重复连接 graph.setAllowLoops(true); // 允许连线的目标和源是同一元素 new mxRubberband(graph); // 左键框选(编辑状态下生效) // 节点样式 var style = graph.getStylesheet().getDefaultVertexStyle(); // style[mxConstants.STYLE_VERTICAL_ALIGN] = mxConstants.ALIGN_BOTTOM;//文字对齐方式 // style[mxConstants.STYLE_FILLCOLOR] = 'rgb(251, 148, 79)'; //填充色 style[mxConstants.STYLE_FONTSIZE] = 14; //文字大小 style[mxConstants.STYLE_FONTCOLOR] = "#fff"; //文字颜色 style[mxConstants.STYLE_WHITE_SPACE] = "wrap"; //自动换行 delete style[mxConstants.STYLE_STROKECOLOR]; //去掉边框 graph.getView().updateStyle = true; // 动态改变样式 graph.setAutoSizeCells(true); // 鼠标拖动 graph.setPanning(true); // 移动镜头(移动容器坐标轴) graph.panningHandler.useLeftButtonForPanning = true; // 设置左键可移动容器坐标轴 graph.setCellsResizable(false); // 禁止改变元素大小 mxEvent.disableContextMenu(this.$refs.graph_container); // 禁用浏览器默认的右键菜单栏 graph.connectionHandler.setCreateTarget(true); // 是否创建目标 mxGraphHandler.prototype.setMoveEnabled(false);//是否可以移动 mxGraphHandler.prototype.guidesEnabled = true;//显示细胞位置标尺 /*禁用节点双击,防止改变数据 */ graph.dblClick = function (evt, cell) {
var model = graph.getModel(); if (model.isVertex(cell)) {
return false; } }; //重写方法不允许那条线(edge)可以编辑 graph.isCellEditable = function (cell) {
return !this.getModel().isEdge(cell) && !this.getModel().isVertex(cell); }; // 鼠标滚轮缩放 mxEvent.addMouseWheelListener(function (evt, up) {
if (up) {
graph.zoomIn(); } else {
graph.zoomOut(); } mxEvent.consume(evt); }); style = graph.getStylesheet().getDefaultEdgeStyle(); style[mxConstants.STYLE_EDGE] = mxEdgeStyle.TopToBottom; style[mxConstants.STYLE_STROKECOLOR] = "rgb(115, 121, 133)"; //连接线颜色 delete graph.getStylesheet().getDefaultEdgeStyle()["endArrow"]; //去掉箭头 //绑定双击事件 graph.addListener(mxEvent.DOUBLE_CLICK, function (sender, evt) {
var cell = evt.getProperty("cell"); console.log(cell) }); var parent = graph.getDefaultParent(); graph.getModel().beginUpdate(); // 开始画图 try {
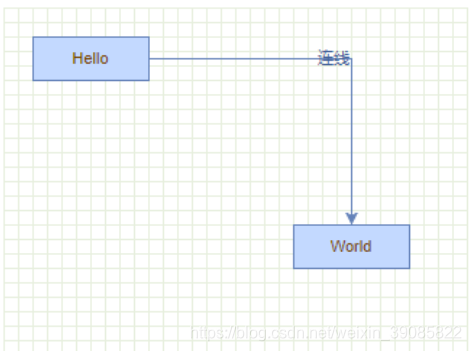
// 插入节点 var v1 = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, "Hello,", 20, 20, 80, 30); // 插入节点 var v2 = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, "World!", 200, 150, 80, 30); graph.insertEdge(parent, null, " ", v2, v1); graph.insertEdge(parent, null, " ", v2, v2); } finally {
graph.getModel().endUpdate(); } } }; </script> <style > </style> <template> <div ref="graph_container" class="graph_container"></div> </template> <script> import {
mxHierarchicalLayout, mxGraph, mxUtils } from 'mxgraph-js' export default {
name: 'HelloWorld', mounted () {
this.init() }, methods: {
init () {
// 创建一个mxGraph 实例 var graph = new mxGraph(this.$refs.graph_container); var model = graph.getModel(); var parent = graph.getDefaultParent(); var doc = mxUtils.createXmlDocument(); // 创建userObject var uo1 = doc.createElement('person'); uo1.setAttribute("firstName", 'Sponge'); uo1.setAttribute("lastName", 'Bob') var uo2 = doc.createElement('person'); uo2.setAttribute("firstName", "Super"); uo2.setAttribute("lastName", 'Man'); var uo3 = doc.createElement('person'); uo3.setAttribute("firstName", "Good"); uo3.setAttribute("lastName", 'Boy'); var uo4 = doc.createElement('person'); uo4.setAttribute("firstName", "Bad"); uo4.setAttribute("lastName", 'Girl'); // 定义convertValueSTotring方法 graph.convertValueToString = function (cell) {
if (mxUtils.isNode(cell.value)) {
// 判断节点类型是否为'person' if (cell.value.nodeName == "person") {
var firstName = cell.getAttribute("firstName", ''); var lastName = cell.getAttribute("lastName", ''); if (lastName != null && lastName.length > 0) {
return lastName + '---' + firstName; } return firstName } } return ''; }; // 创建一个布局实例 var layout = new mxHierarchicalLayout(graph) // var layout = new mxCircleLayout(graph,20) model.beginUpdate(); try {
// 绘制节点 var child1 = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, uo1, 300, 100, 80, 30, 'fillColor=#3CAEA3;strokeColor = white;rounded=1;fontStyle=1'); var child2 = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, uo2, 20, 20, 80, 30, 'fillColor=#3CAEA3;strokeColor = white;rounded=1;fontStyle=1'); var child3 = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, uo3, 200, 150, 80, 30, 'fillColor=#3CAEA3;strokeColor = white;rounded=1;fontStyle=1'); var child4 = graph.insertVertex(parent, null, uo4, 300, 150, 80, 30, 'fillColor=#3CAEA3;strokeColor = white;rounded=1;fontStyle=1'); // 绘制连线 graph.insertEdge(parent, null, '', child1, child2, 'strokeColor=#F6D55C'); graph.insertEdge(parent, null, '', child1, child3, 'strokeColor=#F6D55C'); graph.insertEdge(parent, null, '', child1, child4, 'strokeColor=#F6D55C'); graph.insertEdge(parent, null, '', child2, child4, 'strokeColor=#F6D55C'); layout.execute(parent) } finally {
model.endUpdate() } } } }; </script> <style> </style> var rubberBand = new mxRubberband(graph); 注意:我们可以通过css来修改选择框的填充颜色;如: .mxRubberband {
background-color: rgb(58, 58, 207); position: absolute; } 5.3修改连线样式 mxEdgeStyle 中定义了线的各种样式:Loop、ElbowConnector、SideToSide等等,可以通过以下方式自定义连线样式: mxEdgeStyle.MyStyle = function(state, source, target, points, result){
if (source != null && target != null){
var pt = new mxPoint(target.getCenterX(), source.getCenterY()); if (mxUtils.contains(source, pt.x, pt.y)){
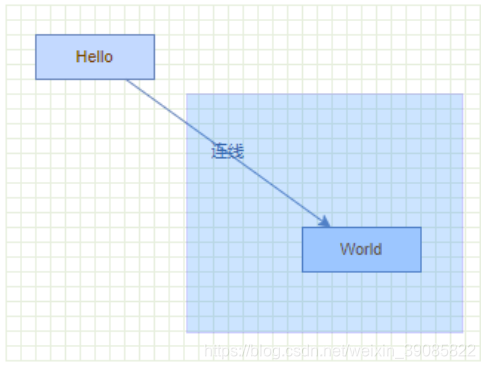
pt.y = source.y + source.height; } result.push(pt); } }; mxStyleRegistry.putValue('myEdgeStyle', mxEdgeStyle.MyStyle); var e1 = graph.insertEdge(parent, null, '连线', v1, v2); graph.getModel().setStyle(e1, 'edgeStyle=myEdgeStyle'); 也可以在定义好自定义样式后,直接修改连线的默认样式:
var style = graph.getStylesheet().getDefaultEdgeStyle(); style[mxConstants.STYLE_EDGE] = mxEdgeStyle.MyStyle; 5.4开起“指引”功能
mxGraphHandler.prototype.guidesEnabled = true; 可以通过以上代码开起“指引”功能,即在拖动节点时会有对齐线等提示效果
关于mxGraph,由于官方API文档是全英文的,而且介绍简单;,官网的Demo倒是不少,但是官方Demo在自己的环境下跑会报错,只有根据官方的demo不断地尝试和理解才能解决使用上的问题,目前只基本掌握基础使用,后续会着重补充针对API的使用总结。
5.5 鼠标划过节点或连线时;边框高亮显示
可以通过以上代码添加对线和节点在鼠标划过时的高亮效果。mxCellTracker(graph, color, funct) 的第三个参数是可选的,如果设置了funct则需要在此函数中重写getCell逻辑。 // 创建画布并进行初始化 createGraph () {
// 创建graph // 方式一:直接构建graph实例 // this.graph = new mxGraph(this.$refs.container) // eslint-disable-next-line new-cap this.editor = new mxEditor() this.graph = this.editor.graph this.editor.setGraphContainer(this.$refs.container) ......//其他配置项 } // 配置鼠标在画布中的事件 configMouseEvent () {
this.graph.addMouseListener( {
// currentState: null, // previousStyle: null, mouseDown: (sender, evt) => {
if (!evt.state) {
console.log('点击了画布') } else if (evt.state.cell.edge) {
console.log('点击了连线', evt.state.cell) } }, mouseMove: (sender, me) => {
// this.graphX = Math.ceil(me.graphX) // this.graphY = Math.ceil(me.graphY) }, mouseUp: (sender, evt) => {
if (evt.sourceState === undefined) {
return false } else {
var cell = evt.sourceState.cell if (cell) {
if (cell.edge && cell.edge === true) {
// 点击的是连线 localStorage.setItem('currOptEdgeId', cell.id) } else if (cell.vertex && cell.vertex === true) {
// 点击的是节点 localStorage.setItem('currOptInstId', cell.id) } else {
// 点击的是其他元素 console.log('点击了其他元素') } } else {
this.$message.error('请选择节点或者连线') } } } }) }, graph.popupMenuHandler.factoryMethod = (menu) => {
menu.addItem('菜单名称', null, () => {
}) } // 配置右键菜单栏 configMenu () {
// 禁用浏览器默认的右键菜单栏 mxEvent.disableContextMenu(this.$refs.container) this.graph.popupMenuHandler.factoryMethod = (menu) => {
menu.addItem('输出所有节点', null, () => {
Object.values(this.graph.getModel().cells).forEach((cell) => {
console.log(cell) }) }) menu.addSeparator() menu.addItem('全选', null, () => {
this.graph.selectAll() }) menu.addItem('选中所有节点', null, () => {
this.graph.selectCells(true, false) }) menu.addItem('选中所有连线', null, () => {
this.graph.selectCells(false, true) }) } // 初始化基础节点 initGeneralTool () {
var generalToolbarDomArray = this.$refs.generalToolItems // 判断是否为数组且数组是否为空 if (!(generalToolbarDomArray instanceof Array || generalToolbarDomArray.length <= 0)) {
return } generalToolbarDomArray.forEach((dom, domIndex) => {
var toolItem = this.generalToolbarItemsView[domIndex] var {
width, height } = toolItem var itemClass = (toolItem.class) // 新增基础节点 var generalDropHandler = (graph, evt, dropCell, x, y) => {
this.addByDrag = true const drop = !R.isNil(dropCell) const realX = drop ? x - dropCell.geometry.x : x const realY = drop ? y - dropCell.geometry.y : y const {
width, height } = toolItem const style = `shape=ellipse;fillColor=${
this.colorMapping[toolItem['entity_class']['entity_type']]};` const parent = drop ? dropCell : this.graph.getDefaultParent() this.graph.getModel().beginUpdate() try {
let vertex = this.graph.insertVertex(parent, null, null, realX - (width / 2), realY - (height / 2), width, height, style) vertex.value = toolItem['entity_class']['entity_name'] vertex.id = this.get_uuid() vertex.instanceClassInfo = toolItem localStorage.setItem('currOptInstId', vertex.id) } finally {
this.graph.getModel().endUpdate() } } // 设置节点被拖拽时的样式(预览) var generalcreateDragPreview = () => {
var elt = document.createElement('div') elt.style.width = `${
width}px` elt.style.height = `${
height}px` elt.style.transform = 'translate(-50%,-50%)' elt.style.backgroundColor = toolItem.instanceColor elt.style.lineHeight = `${
height}px` elt.style.color = `#ffff` elt.style.textAlign = `center` elt.className = itemClass elt.textContent = toolItem['entity_class']['entity_name'] return elt } // 允许拖拽 let ds = mxUtils.makeDraggable(dom, this.graph, generalDropHandler, generalcreateDragPreview(), 0, 0, true, true) ds.setGuidesEnabled(true) }) }, 6.1首先获取左侧所有节点的dom,generalToolbarDomArray 这里有所有节点的样式和节点信息,
获取后遍历所有节点绑定generalcreateDragPreview , generalDropHandler , makeDraggable函数
var generalToolbarDomArray = this.$refs.generalToolItems 6.2当每次将左侧的节点拖拽时就会自动执行generalcreateDragPreview,此函数实现左侧节点被拖拽时的样式预览;
6.3当节点拖拽至画布并松开后会执行generalDropHandler
6.4当节点新增到画布之后会自动触发 ADD_CELLS 事件
// 布局 graphLayout (animate, layoutType) {
this.graph.getModel().beginUpdate() try {
if (layoutType === 'randomLayout') {
// 随机布局 mxFastOrganicLayout.prototype.minDistanceLimit = 100 // eslint-disable-next-line new-cap var layout = new mxFastOrganicLayout(this.graph) layout.forceConstant = 500 layout.execute(this.graph.getDefaultParent()) } else if (layoutType === 'hierarchicalLayout') {
// 分层布局 mxHierarchicalLayout.prototype.intraCellSpacing = 300 mxHierarchicalLayout.prototype.fineTuning = false mxHierarchicalLayout.prototype.traverseAncestors = false mxHierarchicalLayout.prototype.resizeParent = true // 无关系实体之间的间距 mxHierarchicalLayout.prototype.interHierarchySpacing = 200 // 层级之间的距离 mxHierarchicalLayout.prototype.interRankCellSpacing = 800 // eslint-disable-next-line new-cap var hierarchicallayout = new mxHierarchicalLayout(this.graph, mxConstants.DIRECTION_NORTH) hierarchicallayout.execute(this.graph.getDefaultParent()) } else if (layoutType === 'compactTreeLayout') {
// 树形布局 // eslint-disable-next-line new-cap var compactTreelayout = new mxCompactTreeLayout(this.graph) compactTreelayout.execute(this.graph.getDefaultParent()) } else if (layoutType === 'circleLayout') {
// 圆形布局 // eslint-disable-next-line new-cap var circleLayout = new mxCircleLayout(this.graph, 400) circleLayout.execute(this.graph.getDefaultParent()) } } catch (e) {
throw e } finally {
// 是否开启布局动画 if (animate) {
// eslint-disable-next-line new-cap var morph = new mxMorphing(this.graph, 20, 7.7, 40) morph.addListener(mxEvent.DONE, () => {
this.graph.getModel().endUpdate() }) morph.startAnimation() } else {
this.graph.getModel().endUpdate() } } 项目源码欢迎star:
项目源码地址:https://github.com/Jason-chen-coder/Mxgraph-EasyFlowEditor
项目地址:https://github.com/Jason-chen-coder/Mxgraph-EasyFlowEditor
推荐文章:
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/110547.html