大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
目录
1. try-catch处理异常
使用 try-catch 处理异常
try:表示将有可能出现异常的代码书写在 try 代码块中
catch:用于捕获 try 代码块中有可能出现的异常
try不能单独使用必须结合 catch 或者 finally 或者 catch-finally
catch不能单独使用 必须结合try
情况1:出现异常 并且能够被捕获到
public class TestTryCatch1 { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入被除数:"); int num1 = in.nextInt(); System.out.print("请输入除数:"); int num2 = in.nextInt(); System.out.println(num1+"/"+ num2 +"="+ num1/ num2); } catch(InputMismatchException exception){ exception.printStackTrace(); // 打印异常堆栈信息 具体为 哪个类 哪一行 什么原因出错了 } System.out.println("感谢使用本程序!"); } }情况2:出现异常 但是捕获的异常和出现的异常类型不匹配依然会中断程序
public class TestTryCatch2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入被除数:"); int num1 = in.nextInt(); System.out.print("请输入除数:"); int num2 = in.nextInt(); System.out.println(num1+"/"+ num2 +"="+ num1/ num2); } catch(InputMismatchException exception){ exception.printStackTrace(); // 打印异常堆栈信息 具体为 哪个类 哪一行 什么原因出错了 } System.out.println("感谢使用本程序!"); } }情况3:处理多种异常
可以书写多个catch块,注意:写多个catch处理异常 先写子类后写父类,否则编译报错
也可以使用 | 或运算符 分割 书写多个异常
public class TestTryCatch3 { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入被除数:"); int num1 = in.nextInt(); System.out.print("请输入除数:"); int num2 = in.nextInt(); System.out.println(num1+"/"+ num2 +"="+ num1/ num2); } catch(InputMismatchException | ArithmeticException | NullPointerException exception){ exception.printStackTrace(); // 打印异常堆栈信息 具体为 哪个类 哪一行 什么原因出错了 } System.out.println("感谢使用本程序!"); } }2. finally
finally:表示最终都会执行的代码,书写在 finally 代码块中
finally不能单独使用 必须结合 try 或者 try-catch
不执行finally 的唯一情况:在执行finally之前退出JVM虚拟机
System.exit(int status):表示退出JVM虚拟机 0表示正常退出,非0表示不正常退出
public class TestFinally1 { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入被除数:"); int num1 = in.nextInt(); System.out.print("请输入除数:"); int num2 = in.nextInt(); System.out.println(num1+"/"+ num2 +"="+ num1/ num2); // System.exit(12345); } catch(InputMismatchException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } finally{ System.out.println("感谢使用本程序!"); } } }值传递和引用传递:
finally面试题:
在 try 中return值,如果为基本数据类型,则在finally中对返回值的修改 不会改变原返回值
在 try 中return值,如果为引用数据类型,则在finally中对返回值的修改,会改变原返回值,比如数组类型
public class TestFinally2 { public static int getNum(){ int num = 10; try{ num++; return num; }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ num++; } return num; } public static int[] getNums(){ int [] nums = {1,2,3,4,5}; try{ return nums; }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ for(int i =0;i< nums.length;i++){ nums[i]++; } } return nums; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(getNum()); // 11 int[] nums = getNums(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums)); } }3. throw 和 throws
RuntimeException 运行时异常:RuntimeException 及其子类属于运行时异常,即程序运行期间出现异常
CheckedException 检查异常(受检异常):除运行时异常外,其余异常都属于检查异常
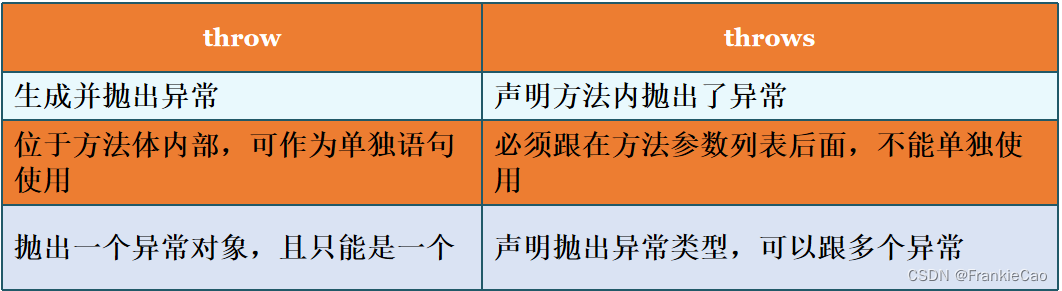
throw:
用于方法体内抛出异常,书写在方法体内,一句话只能抛出一个异常
针对抛出的异常类型不同 决定书是否需要立即处理
如果抛出的是运行时异常 则不必处理
如果抛出的是检查异常 则必须处理 使用try-catch处理,或者用 throws 声明
throws:
用于定义方法的时候声明当前方法出现了哪些异常
针对声明的异常 根据不同的类型有两种处理方案:
1.如果声明的运行时异常 则不必处理
2.如果声明的是检查异常 则必须处理 使用try-catch处理 或者 继续声明给JVM虚拟机
public class TestThrows { public static void m1() { throw new ArithmeticException("除数不能为0"); } public static void m2(){ throw new RuntimeException(); } public static void m3() throws NullPointerException{ throw new NullPointerException(); } public static void m4() throws ClassNotFoundException,IOException, SQLException { throw new ClassNotFoundException(); } public static void m5() throws IOException { throw new IOException(); } public static void m6(){ try { throw new IllegalAccessException(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { m1(); m2(); m3(); try { m4(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } m5(); m6(); } }3. 自定义异常
实际开发中,JDK提供异常不能满足我们的开发需求时,需要自定义异常
步骤:
1.继承Exception 或者 RuntimeException 二者其中之一
2.编写构造方法 调用父类的构造实现异常信息初始化
public class Student { private String name; private int age; private int score; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) throws InputAgeOutOfBoundsException { if(age >= 0 && age <= 130){ this.age = age; }else{ throw new InputAgeOutOfBoundsException("年龄不合法" + age); } } public int getScore() { return score; } public void setScore(int score) { if(score >= 0 && score <= 100 ){ this.score = score; }else{ throw new InputScoreException("分数不合法" + score); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InputAgeOutOfBoundsException { Student stu1 = new Student(); stu1.setAge(999); stu1.setScore(888); } }public class InputAgeOutOfBoundsException extends Exception{ public InputAgeOutOfBoundsException(String message){ super(message); } } public class InputScoreException extends RuntimeException{ public InputScoreException(String message){ super(message); } }4. 总结
异常处理与性能
异常只能用于非正常情况
不要将过于庞大的代码块放在try中
在catch中指定具体的异常类型
需要对捕获的异常做处理
6. 内部类
内部类:即一个类中 再书写其他的类
普通内部类
静态内部类
局部内部类
匿名内部类
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/112818.html