大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
一、UART简介
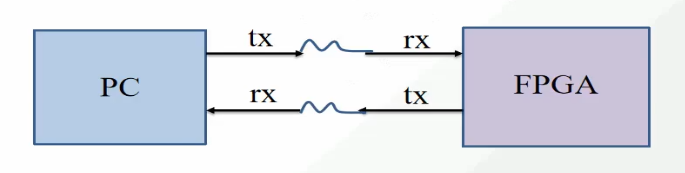
UART 通常是指通用异步串行收发传输器( Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter)。UART 是一种通用的数据通信总线,也是串行总线接口的总称。我们通常所说的 UART 只有两根信号线,一根是发送数据端口线(TX),一根是接收数据端口线(RX)。
发送数据:发送设备将数据转换成串行数据来传输(并转串)。
接收数据:接收设备将接收到的串行数据转换成并行数据(串转并)。
1)协议层:通信协议(包括数据格式,传输速率等);
2)物理层:接口类型,电平标准等。
二、UART原理
2.1协议层
2.1.1 数据格式
一帧数据由4 部分组成,
• 起始位(1bit)
• 数据位(6\7\8 bit)
• 奇偶校验位(1bit)
• 停止位(1bit\1.5bit\2bit)
数据帧格式:
空闲位:
UART协议规定,当总线处于空闲状态时信号线的状态为‘1’即高电平,表示当前线路上没有数据传输。
起始位:
每开始一次通信时发送方先发出一个逻辑”0”的信号(低电平),表示传输字符的开始。因为总线空闲时为高电平所以开始一次通信时先发送一个明显区别于空闲状态的信号即低电平。
数据位:
起始位之后就是我们所要传输的数据,数据位可以是5、6、7、8,9位等,构成一个字符(一般都是8位)。如ASCII码(7位),扩展BCD码(8位)。先发送最低位,最后发送最高位,使用低电平表示‘0’高电平表示‘1’完成数据位的传输。
奇偶校验位:
数据位加上这一位后,使得“1”的位数应为偶数(偶校验)或奇数(奇校验),以此来校验数据传送的正确性。 校验位其实是调整个数,以下是奇偶校验两种方式:
- 奇校验(odd parity):如果数据位中“1”的数目是偶数,则校验位为“1”,如果“1”的数目是奇数,校验位为“0”。
- 偶校验(even parity):如果数据为中“1”的数目是偶数,则校验位为“0”,如果为奇数,校验位为“1”。
在代码设计中我们采用一位异或,将每两位相邻数据位异或后得到一位数据,再根据设置的奇校验偶校验来判断校验位的值。
停止位:
它是一个字符数据的结束标志。可以是1位、1.5位、2位的高电平。
2.1.2 传输速度
波特率:单位时间内传输的码元数量(码元:携带数据的信息单元)
2.1.2.1 什么是波特率
波特率等于每秒钟传输的数据位数,假如我们的全局时钟频率为100MHz,波特率设置为9600,那么意味着每秒该UART传输协议可以传输9600bits的数据,换句话说传输1比特需时间约为:10^9(ns)/9600=(ns)。
2.1.2.2 如何换算波特率
如上,时钟频率假如为100MHz,这意味着我们的时钟周期为10ns,因此10416个时钟周期我们就可以传输1bit数据,换言之我们需要一个大小为10416的分频电路来对100MHz时钟进行处理,因此在设计UART的过程中,我们需要使用分频电路依据波特率处理全局时钟,依据分频后的时钟节奏来发送数据和接收数据。
2.2 物理层
接口类型、电平标准
串口电平标准:
TTL电平的串口(3.3v)
RS232电平的串口(+3~+15v为低电平,-5~-15v为高电平)
串口按电气标准分包括:
• RS-232-C:TXD/RXD/GND、15 m/9600bps (全双工)
• RS-422:TX+/TX-/RX+/RX-/GND (全双工,差分信号)
• RS485:A/B/G 、1200 米/9600bps (半双工,差模信号)
三、工程实践
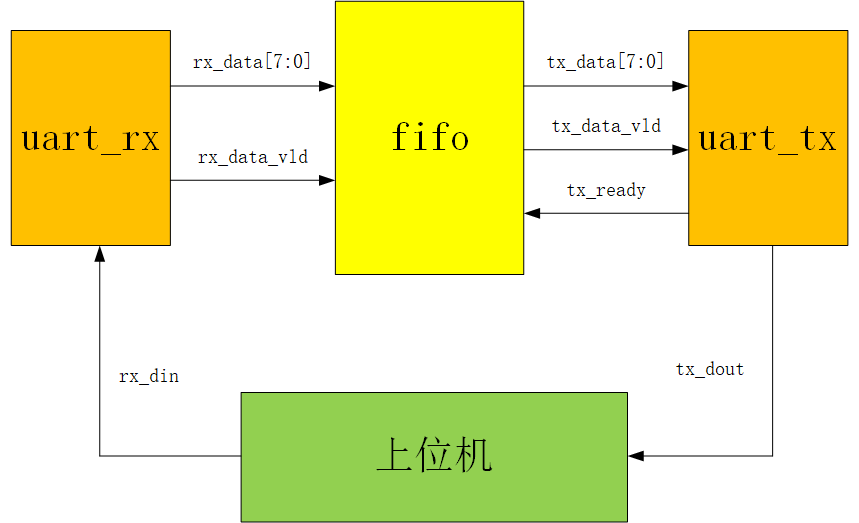
3.1系统框图
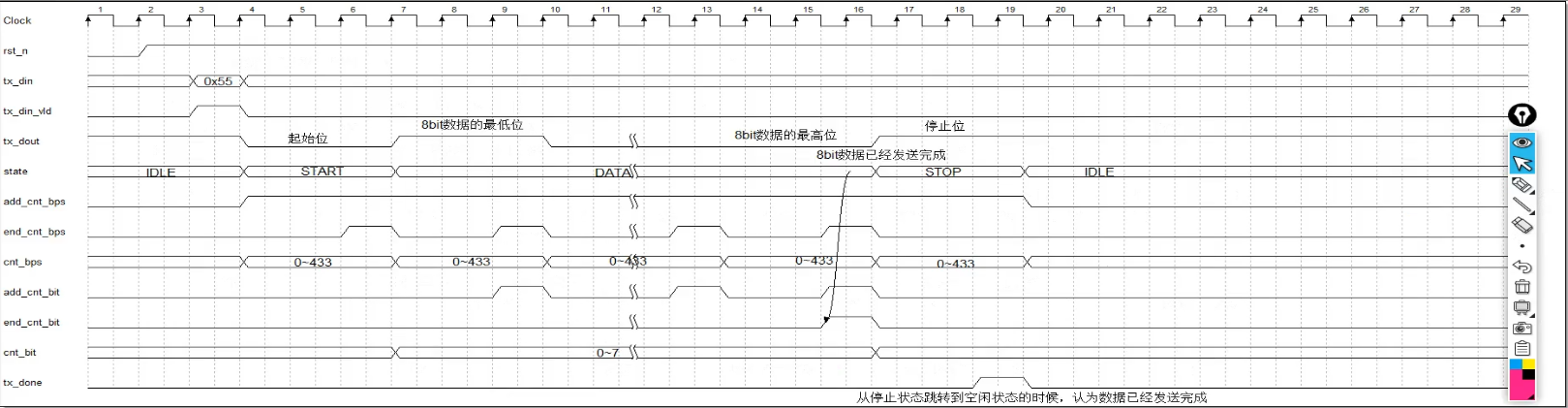
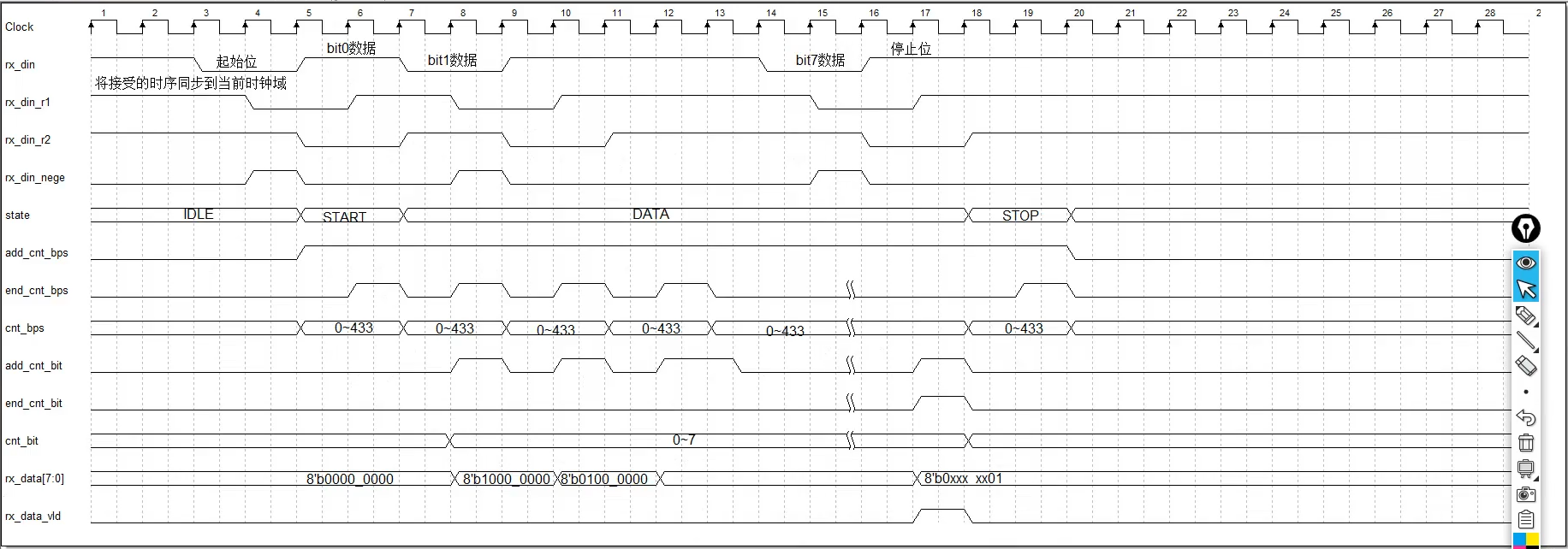
3.2时序图
3.2.1 发送时序
3.2.2 接收时序
3.3 代码设计
3.3.1 UART_RX
module uart_rx #( parameter CLK_FREQ = 50_000_000, BPS = , CHECK = "NONE" //"Odd"为奇数校验,"Even"为偶数校验 )( input clk , input rst_n , input rx_din , output rx_data_vld , output reg [7:0] rx_data ); parameter MAX_BPS = CLK_FREQ/BPS; reg [4:0] state_c; reg [4:0] state_n; wire idle2start; wire start2data; wire data2stop ; wire data2parity; wire parity2stop; wire stop2idle ; reg [71:0] state_ascii; reg rx_din_r1; reg rx_din_r2; reg [8:0] cnt_bps; wire add_cnt_bps; wire end_cnt_bps; reg [2:0] cnt_bit; wire add_cnt_bit; wire end_cnt_bit; reg rx_check; reg error; wire rx_data_check; / 数据发送信号 / parameter IDLE = 5'b00001, START = 5'b00010, DATA = 5'b00100, Parity = 5'b01000, STOP = 5'b10000; / 仿真ASCII码显示 / always@(*) case(state_c) IDLE : state_ascii="IDLE "; START : state_ascii="START"; DATA : state_ascii="DATA "; Parity : state_ascii="Parity"; STOP : state_ascii="STOP "; default : state_ascii="IDLE "; endcase / 下降沿检测 / always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) if(!rst_n) begin rx_din_r1 <= 1; rx_din_r2 <= 1; end else begin rx_din_r1 <= rx_din; rx_din_r2 <= rx_din_r1; end assign rx_din_nege = !rx_din_r1 && rx_din_r2; //第一段状态机 always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin if(!rst_n)begin state_c <= IDLE; end else begin state_c <= state_n; end end //第二段状态机 always @(*)begin case(state_c) IDLE : if(idle2start) state_n = START ; else state_n = state_c; START : if(start2data) state_n = DATA ; else state_n = state_c; DATA : if(data2stop) state_n = STOP ; else if(data2parity) state_n = Parity; else state_n = state_c; Parity : if(parity2stop) state_n = STOP; else state_n = state_c; STOP : if(stop2idle) state_n = IDLE ; else state_n = state_c; default : state_n = state_c; endcase end //状态跳转条件 assign idle2start = state_c == IDLE && rx_din_nege ; assign start2data = state_c == START && end_cnt_bps ; assign data2stop = state_c == DATA && end_cnt_bit && (CHECK == "NONE"); assign data2parity = state_c == DATA && end_cnt_bit ; assign parity2stop = state_c == Parity&& end_cnt_bps ; assign stop2idle = state_c == STOP && (cnt_bps == MAX_BPS >>1); / 波特率控制 / always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) if(!rst_n) cnt_bps <= 'd0; else if(add_cnt_bps) begin if(end_cnt_bps) cnt_bps <= 'd0; else cnt_bps <= cnt_bps + 1'b1; end else cnt_bps = 'd0; assign add_cnt_bps = state_c != IDLE ; assign end_cnt_bps = add_cnt_bps && cnt_bps == MAX_BPS - 1 ; / 数据位控制 / always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) if(!rst_n) cnt_bit <= 'd0; else if(add_cnt_bit) begin if(end_cnt_bit) cnt_bit <= 'd0; else cnt_bit <= cnt_bit + 1'b1; end assign add_cnt_bit = end_cnt_bps && state_c == DATA; assign end_cnt_bit = add_cnt_bit && cnt_bit == 8 - 1; / 数据接收逻辑 / always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) if(!rst_n) rx_data <= 0; else if(state_c == DATA && cnt_bps == MAX_BPS >> 1) rx_data <= {rx_din_r2,rx_data[7:1]}; / 校验位计算 / generate if(CHECK == "NONE")begin assign rx_data_vld = stop2idle; end else begin //计算接收到的数据奇偶校验 assign rx_data_check = (CHECK == "Odd") ? ^rx_data : ~rx_data; //接收到的奇偶校验位 always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) if(!rst_n) rx_check <= 0; else if(state_c == Parity && (cnt_bps == MAX_BPS >> 1)) rx_check <= rx_din_r2; always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) if(!rst_n) error <= 0; else if(parity2stop) error <= rx_check != rx_data_check; assign rx_data_vld = stop2idle && !error; end endgenerate endmodule3.3.2 UART_TX
module uart_tx #( parameter CLK_FREQ = 50_000_000, BPS = , CHECK = "NONE" //"Odd"为奇数校验,"Even"为偶数校验 )( input clk , input rst_n , input [7:0] tx_din , input tx_din_vld , output tx_ready , output reg tx_dout ); parameter MAX_BPS = CLK_FREQ/BPS; reg [4:0] state_c; reg [4:0] state_n; wire idle2start; wire start2data; wire data2stop ; wire data2parity; wire parity2stop; wire stop2idle ; reg [71:0] state_ascii; reg [8:0] cnt_bps; wire add_cnt_bps; wire end_cnt_bps; reg [2:0] cnt_bit; wire add_cnt_bit; wire end_cnt_bit; //寄存tx_din reg [7:0] tx_din_r; //计算奇偶校验 (* keep *)wire uart_check; //(* keep *) signal tap仿真时用于防止优化掉wire信号;(*noprune*) 用于防止优化掉reg信号 parameter IDLE = 5'b00001, START = 5'b00010, DATA = 5'b00100, Parity = 5'b01000, STOP = 5'b10000; / 仿真ASCII码显示 / always@(*) case(state_c) IDLE : state_ascii="IDLE "; START : state_ascii="START"; DATA : state_ascii="DATA "; Parity : state_ascii="Parity"; STOP : state_ascii="STOP "; default : state_ascii="IDLE "; endcase / 状态机 / //第一段状态机 always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin if(!rst_n)begin state_c <= IDLE; end else begin state_c <= state_n; end end //第二段状态机 always @(*)begin case(state_c) IDLE : if(idle2start) state_n = START ; else state_n = state_c; START : if(start2data) state_n = DATA ; else state_n = state_c; DATA : if(data2stop) state_n = STOP ; else if(data2parity) state_n = Parity; else state_n = state_c; Parity : if(parity2stop) state_n = STOP; else state_n = state_c; STOP : if(stop2idle) state_n = IDLE ; else state_n = state_c; default : state_n = state_c; endcase end //状态跳转条件 assign idle2start = state_c == IDLE && tx_din_vld ; assign start2data = state_c == START && end_cnt_bps ; assign data2stop = state_c == DATA && end_cnt_bit && (CHECK == "NONE"); assign data2parity = state_c == DATA && end_cnt_bit ; assign parity2stop = state_c == Parity&& end_cnt_bps ; assign stop2idle = state_c == STOP && end_cnt_bps ; / 波特率控制 / always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) if(!rst_n) cnt_bps <= 'd0; else if(add_cnt_bps) begin if(end_cnt_bps) cnt_bps <= 'd0; else cnt_bps <= cnt_bps + 1'b1; end assign add_cnt_bps = state_c != IDLE ; assign end_cnt_bps = add_cnt_bps && cnt_bps == MAX_BPS - 1 ; / 数据位控制 / always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) if(!rst_n) cnt_bit <= 'd0; else if(add_cnt_bit) begin if(end_cnt_bit) cnt_bit <= 'd0; else cnt_bit <= cnt_bit + 1'b1; end assign add_cnt_bit = end_cnt_bps && state_c == DATA; assign end_cnt_bit = add_cnt_bit && cnt_bit == 8 - 1; //寄存tx_din always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) if(!rst_n) tx_din_r <= 0; else if(tx_din_vld) tx_din_r <= tx_din; / 计算奇偶校验位 / assign uart_check = ^tx_din_r; //奇校验 缩位异或 0:奇数个1 1:偶数个1 / UART发送时序 / always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) if(!rst_n) tx_dout <= 1; else case(state_c) START : tx_dout <= 0; DATA : tx_dout <= tx_din_r[cnt_bit]; Parity : tx_dout <= (CHECK == "Odd") ? uart_check : ~uart_check; default : tx_dout <= 1; endcase assign tx_ready = (state_c == IDLE); endmodule3.3.3 fifo
module uart_ctrl_fifo ( input clk , input rst_n , input tx_ready , input rx_data_vld , input [7:0] rx_data , output [7:0] tx_din , output tx_din_vld ); wire fifo_wr_req; wire fifo_rd_req; wire fifo_empty ; wire fifo_full ; wire [7:0] fifo_wr_data; wire [7:0] fifo_rd_data; fifo_8x32 fifo_8x32_inst ( .aclr ( ~rst_n ), .clock ( clk ), .data ( fifo_wr_data), .rdreq ( fifo_rd_req ), .wrreq ( fifo_wr_req ), .empty ( fifo_empty ), .full ( fifo_full ), .q ( fifo_rd_data), .usedw ( ) ); assign fifo_wr_req = ~fifo_full && rx_data_vld; assign fifo_wr_data = rx_data; assign fifo_rd_req = ~fifo_empty && tx_ready; assign tx_din = fifo_rd_data; assign tx_din_vld = fifo_rd_req; endmodule3.3.4 Top
module top ( input clk , input rst_n , input rx_din , output clk_debug ,//debug 用于降低时钟频率,有利于signal tap仿真调试 output uart_tx_data ); //debug 用于降低时钟频率,有利于signal tap仿真调试 /* pll pll_inst ( */ /* .areset ( ~rst_n ), */ /* .inclk0 ( clk ), */ /* .c0 ( clk_debug ), */ /* .locked ( ) */ /* ); */ wire tx_ready ; wire rx_data_vld; wire [7:0] rx_data ; wire [7:0] tx_din ; wire tx_din_vld; uart_rx #( .CLK_FREQ(50_000_000), .BPS ( ), .CHECK ("Odd" ) )uart_rx_inst( /* input */ .clk (clk ) , /* input */ .rst_n (rst_n ) , /* input */ .rx_din (rx_din ) , /* output */ .rx_data_vld(rx_data_vld) , /* output reg [7:0] */ .rx_data (rx_data ) ); uart_ctrl_fifo uart_ctrl_fifo_inst( /* input */ .clk (clk ) , /* input */ .rst_n (rst_n ) , /* input */ .tx_ready (tx_ready ) , /* input */ .rx_data_vld(rx_data_vld) , /* input [7:0] */ .rx_data (rx_data ) , /* output [7:0] */ .tx_din (tx_din ) , /* output */ .tx_din_vld(tx_din_vld) ); uart_tx #( .CLK_FREQ(50_000_000), .BPS ( ), .CHECK ("Odd" ) ) uart_tx_inst( /* input */ .clk (clk ) , /* input */ .rst_n (rst_n ) , /* input [7:0] */ .tx_din (tx_din ) , /* input */ .tx_din_vld(tx_din_vld) , /* output reg */ .tx_ready (tx_ready ) , /* output reg */ .tx_dout (uart_tx_data ) ); endmodule3.4 仿真测试
3.4.1 测试代码设计
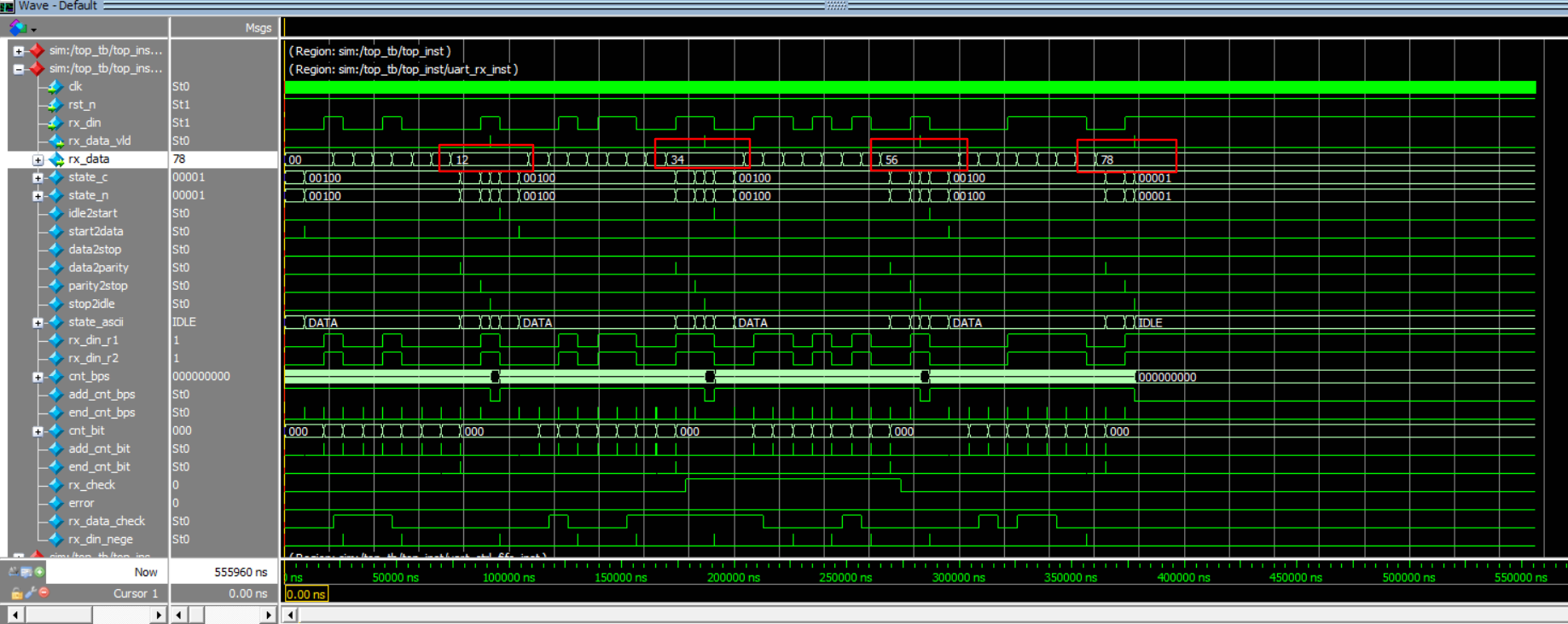
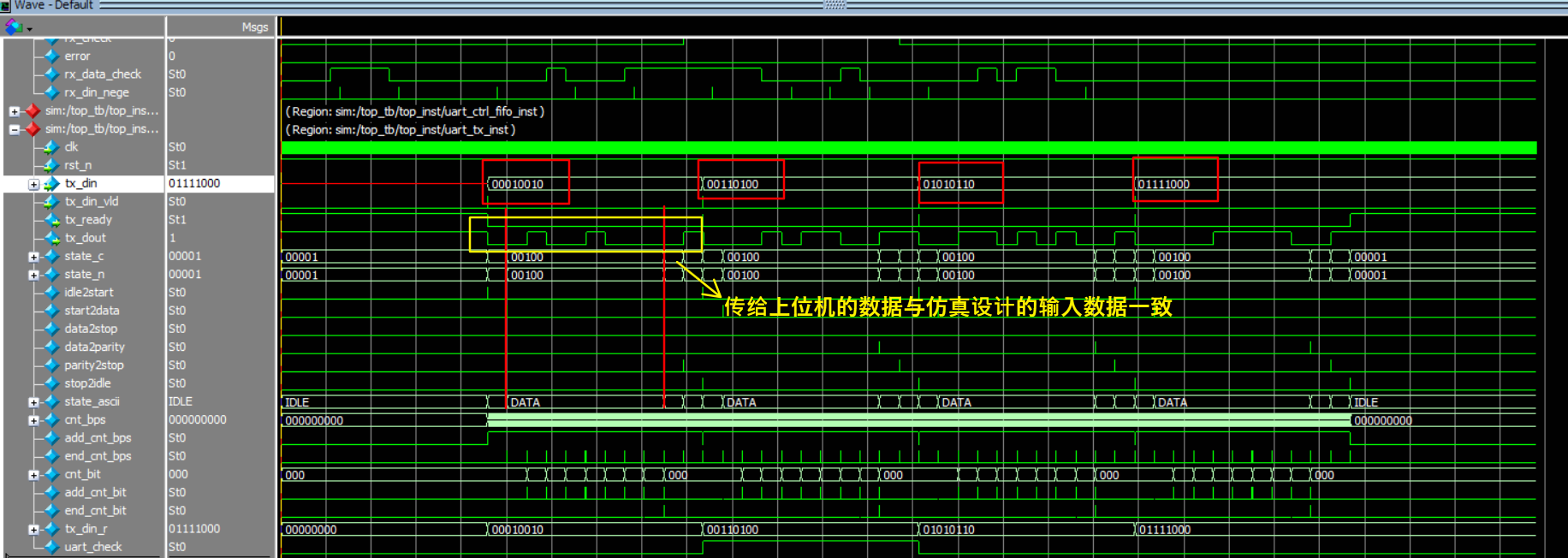
`timescale 1ns/1ps module top_tb(); parameter CLK_CYCLE = 20; reg sys_clk,sys_rst_n; reg rx_din; always #(CLK_CYCLE/2) sys_clk = ~sys_clk; initial begin sys_clk = 1'b1; sys_rst_n = 1'b0; #(CLK_CYCLE*2); sys_rst_n = 1'b1; end top top_inst( /* input */ .clk (sys_clk ) , /* input */ .rst_n (sys_rst_n ) , /* input */ .rx_din (rx_din ) , /* output */ .uart_tx_data() ); initial begin rx_din = 1; sys_clk = 1'b1; sys_rst_n = 1'b0; #(CLK_CYCLE*2); sys_rst_n = 1'b1; #(CLK_CYCLE*20); my_uart_tx(8'h12); my_uart_tx(8'h34); my_uart_tx(8'h56); my_uart_tx(8'h78); #(CLK_CYCLE*434*20); $stop; end integer i; task my_uart_tx; input [7:0] data_in; begin rx_din = 0; #(CLK_CYCLE*434); //数据位 for(i=0;i<=7;i=i+1)begin rx_din = data_in[i]; #(CLK_CYCLE*434); end //奇偶校验位 rx_din = ^data_in; #(CLK_CYCLE*434); //停止位 rx_din = 1; #(CLK_CYCLE*434); end endtask endmodule3.4.2 仿真波形
如上图,给仿真模拟上位机的一个输入数据,观察模拟输出给上位机的数据是否一致。
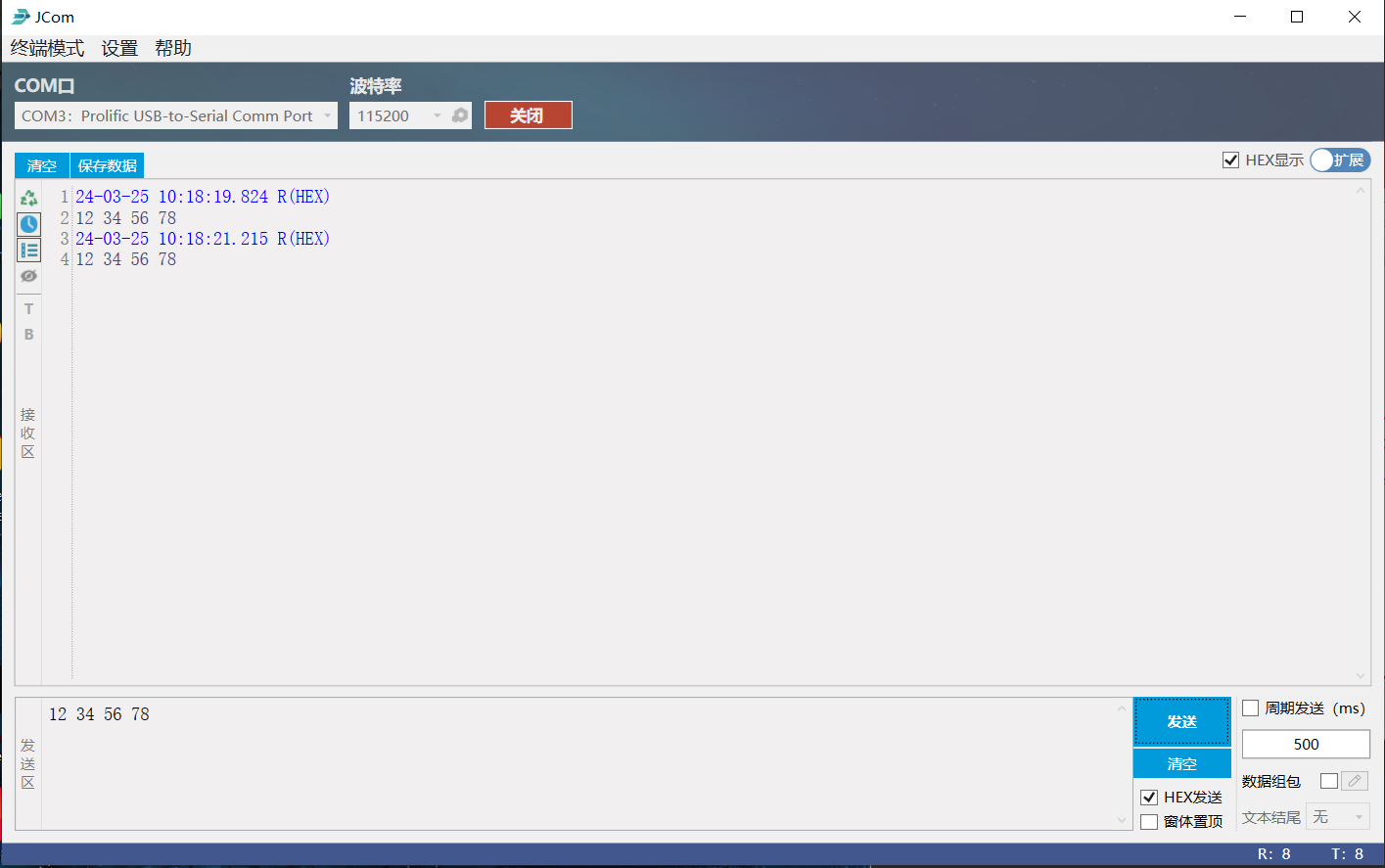
3.5板级测试
本次测试采用JCOM上位机,观察下图可见,输入数据与输出数据一致,至此UART协议代码设计完成。
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/110990.html