大家好,欢迎来到IT知识分享网。
目录
一、经纬度坐标系
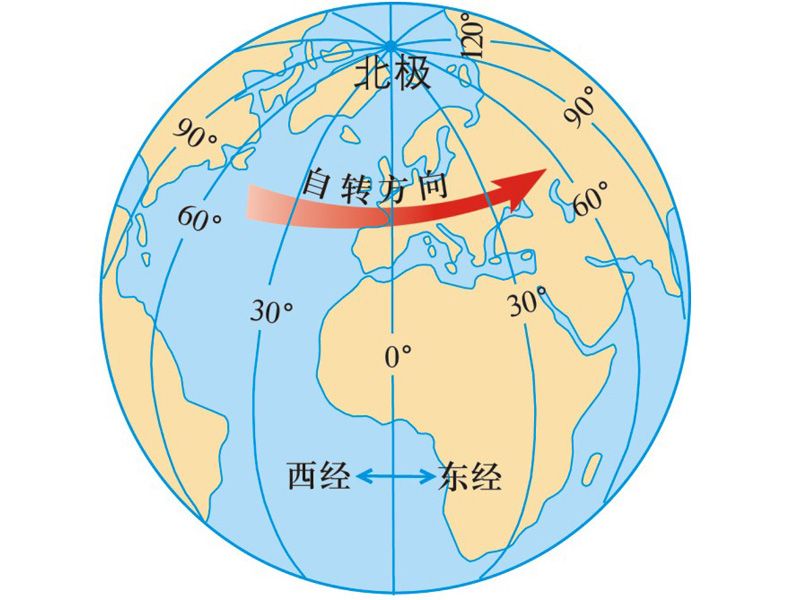
经纬度坐标系是一种地理坐标系统,用于描述地球表面上任意位置的坐标。它是基于地球的自转和赤道的划分而建立的。
经度(Longitude)表示地球表面上一个点相对于本初子午线的东西方向的位置。经度的度量单位是度(°),范围从0°到180°,以东经为正值,西经为负值。本初子午线位于英国伦敦的皇家格林尼治天文台,它被定义为经度0°。
纬度(Latitude)表示地球表面上一个点相对于赤道的北南方向的位置。纬度的度量单位也是度(°),范围从0°到90°,以北纬为正值,南纬为负值。赤道位于纬度0°。
经纬度坐标系统使用经度和纬度的组合来确定地球表面上的特定位置。一个点的经纬度坐标表示为两个数值的组合,例如:40°N,120°E 表示北纬40度,东经120度的位置。
经纬度坐标系统是全球通用的地理坐标系统,广泛应用于导航、地图制作、地理信息系统(GIS)等领域。
二、地心地固坐标系
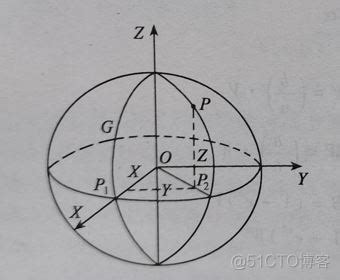
地心地固坐标系(Geocentric Cartesian Coordinate System)是一种用于描述地球上的位置和方向的坐标系统。它是一种笛卡尔坐标系,其中地球的中心被定义为原点,三个坐标轴固定在地球上,与地球自转轴对齐。
在地心地固坐标系中,三个坐标轴通常被定义如下:
- X轴:通过原点和经度为0度的子午线(通常是通过英国伦敦的本初子午线)。
- Y轴:通过原点、纬度为0度的赤道,与X轴垂直。
- Z轴:与地球自转轴对齐,指向地球北极,垂直于XY平面。
使用这种坐标系,可以准确描述地球上任意点的位置。例如,通过给定的经度、纬度和高度(相对于海平面),可以确定点在地心地固坐标系中的三维坐标。这对于导航、地理信息系统(GIS)、地图制作和天文学等领域非常重要。
需要注意的是,地心地固坐标系是一个相对于地球的固定坐标系,而非相对于太阳或其他天体的惯性坐标系。它主要用于地球表面的测量和定位,而在宇宙空间中,通常使用其他坐标系,如国际天文学联合会所定义的天球坐标系。
将经纬度坐标系下的坐标转换为地心固定坐标系ECEF下的坐标
(使用椭球体参数和坐标转换公式来进行计算。)
import math # 地球椭球体参数 a = .0 # 长半轴 f = 1 / 298. # 扁率 def deg2rad(deg): return deg * (math.pi / 180) def geodetic_to_geocentric(latitude, longitude, altitude): # 将纬度、经度、高度转换为弧度 lat_rad = deg2rad(latitude) lon_rad = deg2rad(longitude) # 计算地球椭球体上的参数 b = a * (1 - f) # 短半轴 e_squared = 1 - (b2) / (a2) # 第一偏心率的平方 # 计算地球椭球体上的坐标 N = a / math.sqrt(1 - e_squared * (math.sin(lat_rad)2)) X = (N + altitude) * math.cos(lat_rad) * math.cos(lon_rad) Y = (N + altitude) * math.cos(lat_rad) * math.sin(lon_rad) Z = (N * (1 - e_squared) + altitude) * math.sin(lat_rad) return X, Y, Z # 示例坐标:纬度为40.7128度,经度为-74.0060度,海拔高度为0米(纽约市) latitude = 40.7128 longitude = -74.0060 altitude = 0 x, y, z = geodetic_to_geocentric(latitude, longitude, altitude) print("X坐标:", x) print("Y坐标:", y) print("Z坐标:", z) 三、地球惯性坐标系
地球惯性坐标系是一种参考坐标系,用于描述地球在宇宙中的运动。它是一个以地球质心为原点的坐标系,其坐标轴与地球的自转轴和公转轴有关。
在地球惯性坐标系中,地球的自转轴被定义为坐标系的Z轴,它与地球的北极方向相对应。X轴则与春分点方向相切,并指向地球轨道上的某个固定点。Y轴则垂直于X轴和Z轴,与它们构成一个右手坐标系。
地球惯性坐标系是一个非旋转的坐标系,它随着地球的自转和公转而保持固定。因此,使用地球惯性坐标系可以方便地描述地球上的物理现象和天文现象,以及与地球有关的导航、定位和遥感等应用。
需要注意的是,地球惯性坐标系并不考虑地壳运动、地球自转的变化以及其他地球动力学效应,它主要用于研究地球的宏观运动和与地球运动相关的现象。
J2000坐标系是一种惯性坐标系,它是在2000年1月1日12时(格林威治时间)定义的。J2000坐标系的坐标轴与地球的自转轴和公转轴有关,类似于地球惯性坐标系。它的X轴指向春分点方向,Z轴与地球自转轴相对应,Y轴垂直于X轴和Z轴。J2000坐标系被广泛应用于天文学和航天领域。
地球惯性坐标系可以被看作是J2000坐标系的一个特例,它是一种以地球为中心的惯性坐标系。在地球惯性坐标系中,地球的自转轴被定义为Z轴,与地球的北极方向相对应。X轴与春分点方向相切,并指向地球轨道上的某个固定点。Y轴垂直于X轴和Z轴,构成一个右手坐标系。
import math # 输入地心固定坐标系下的点坐标 geocentric_x = . geocentric_y = -. geocentric_z = . # 输入当前时间(以儒略日表示) current_jd = .0 # 计算格林尼治恒星时角(以弧度表示) def calculate_greenwich_sidereal_time(jd): # 计算儒略世纪数 T = (jd - .0) / 36525.0 # 计算格林尼治恒星时角(以弧度表示) GST = (100. + 36000. * T + 0.000 * T2 - (T3 / .0)) * (math.pi / 180.0) # 将格林尼治恒星时角限制在0到2π之间 GST = GST % (2 * math.pi) return GST # 将地心固定坐标系下的点坐标转换为J2000坐标系下的坐标 def convert_to_j2000_coordinates(x, y, z, gst): # 定义J2000坐标系的旋转矩阵 rotation_matrix = [ [math.cos(gst), -math.sin(gst), 0], [math.sin(gst), math.cos(gst), 0], [0, 0, 1] ] # 进行矩阵乘法,得到J2000坐标系下的坐标 j2000_x = rotation_matrix[0][0] * x + rotation_matrix[0][1] * y + rotation_matrix[0][2] * z j2000_y = rotation_matrix[1][0] * x + rotation_matrix[1][1] * y + rotation_matrix[1][2] * z j2000_z = rotation_matrix[2][0] * x + rotation_matrix[2][1] * y + rotation_matrix[2][2] * z return j2000_x, j2000_y, j2000_z # 计算格林尼治恒星时角 gst = calculate_greenwich_sidereal_time(current_jd) # 将地心固定坐标系下的点坐标转换为J2000坐标系下的坐标 j2000_x, j2000_y, j2000_z = convert_to_j2000_coordinates(geocentric_x, geocentric_y, geocentric_z, gst) # 输出J2000坐标系下的坐标 print("J2000 X:", j2000_x) print("J2000 Y:", j2000_y) print("J2000 Z:", j2000_z) import datetime # 获取当前日期和时间 current_date_time = datetime.datetime.now() # 计算儒略日的函数 def calculate_julian_day(year, month, day, hour, minute, second): if month <= 2: year -= 1 month += 12 a = year // 100 b = a // 4 c = 2 - a + b e = 365.25 * (year + 4716) f = 30.6001 * (month + 1) jd = c + day + e + f - 1524.5 + (hour + minute / 60.0 + second / 3600.0) / 24.0 return jd # 提取当前日期和时间的年、月、日、时、分、秒 year = current_date_time.year month = current_date_time.month day = current_date_time.day hour = current_date_time.hour minute = current_date_time.minute second = current_date_time.second # 计算当前时间的儒略日 current_jd = calculate_julian_day(year, month, day, hour, minute, second) # 输出当前时间的儒略日 print("Current Julian Day:", current_jd) 四、卫星位置计算
import datetime import math # 常数定义 MU = 3.e14 # 地球引力常数 OMEGA_E_DOT = 7.e-5 # 地球自转角速度(rad/s) # 将角度转换为弧度 def deg2rad(deg): return deg * math.pi / 180.0 # 将弧度转换为角度 def rad2deg(rad): return rad * 180.0 / math.pi # 计算矢量点积 def dot(a, b): return sum([a[i] * b[i] for i in range(3)]) # 计算矢量差 def diff(a, b): return [a[i] - b[i] for i in range(3)] # 计算矢量叉积 def cross(a, b): return [ a[1] * b[2] - a[2] * b[1], a[2] * b[0] - a[0] * b[2], a[0] * b[1] - a[1] * b[0] ] # 计算向量模长 def norm(a): return math.sqrt(dot(a, a)) # 计算轨道的其他参数 def compute_orbital_params(a, e, i, RAAN, arg_per, M, t, t0): # 计算平均角速度 n = math.sqrt(MU / a 3) # 计算时间差 dt = (t - t0).total_seconds() # 计算平近点角 M = M + n * dt # 利用Kepler方程求解偏近点角 E = M for _ in range(10): E = M + e * math.sin(E) # 计算真近点角 v = 2 * math.atan(math.sqrt((1 + e) / (1 - e)) * math.tan(E / 2)) # 计算升交点赤经 RAAN = RAAN + (OMEGA_E_DOT * dt) # 计算卫星位置矢量 r = a * (1 - e * math.cos(E)) x = r * 1000.0 * (math.cos(RAAN) * math.cos(v + arg_per) - math.sin(RAAN) * math.sin(v + arg_per) * math.cos(i)) y = r * 1000.0 * (math.sin(RAAN) * math.cos(v + arg_per) + math.cos(RAAN) * math.sin(v + arg_per) * math.cos(i)) z = r * 1000.0 * (math.sin(i) * math.sin(v + arg_per)) # 返回卫星位置矢量 return x, y, z # 初始时间和初始轨道六根数 t0 = datetime.datetime(2023, 5, 1, 0, 0, 0) # 初始时间 a = 7000.0 e = 0.01 # 偏心率 i = deg2rad(60.0) # 轨道倾角 RAAN = deg2rad(30.0) # 升交点赤经 arg_per = deg2rad(45.0) # 近地点幅角 M = deg2rad(0.0) # 平近点角 # 当前时间 current_time = datetime.datetime.now() # 计算当前时刻的卫星位置 satellite_position = compute_orbital_params(a, e, i, RAAN, arg_per, M, current_time, t0) # 输出卫星位置 print("Satellite Position (X, Y, Z):", satellite_position) # 单位是m五、东北天坐标系
J2000转东北天
import math # 输入地理坐标 latitude = 40.7128 longitude = -74.0060 altitude = 0.0 # 海拔高度,此处假设为0 # 输入参考点的地理坐标 reference_latitude = 40.0 reference_longitude = -75.0 reference_altitude = 0.0 # 输入当前时间(UTC) current_time = # 时间戳,表示2021年5月12日00:00:00 # 定义地球半径(单位:米) earth_radius = # 将角度转换为弧度 def degrees_to_radians(degrees): return degrees * (math.pi / 180.0) # 将弧度转换为角度 def radians_to_degrees(radians): return radians * (180.0 / math.pi) # 计算地球自转角速度 def calculate_earth_rotation_rate(): return 2 * math.pi / 86400 # 地球自转周期约为86400秒 # 计算当前时间与J2000时刻的时间差(单位:秒) def calculate_time_difference(current_time): j2000_time = # J2000时刻的时间戳,表示2000年1月1日12:00:00 return current_time - j2000_time # 计算地球自转角(单位:弧度) def calculate_earth_rotation_angle(current_time): time_difference = calculate_time_difference(current_time) rotation_rate = calculate_earth_rotation_rate() return rotation_rate * time_difference # 将地理坐标转换为地心坐标系下的直角坐标(以米为单位) def convert_geographic_to_geocentric(latitude, longitude, altitude): latitude_rad = degrees_to_radians(latitude) longitude_rad = degrees_to_radians(longitude) x = (earth_radius + altitude) * math.cos(latitude_rad) * math.cos(longitude_rad) y = (earth_radius + altitude) * math.cos(latitude_rad) * math.sin(longitude_rad) z = (earth_radius + altitude) * math.sin(latitude_rad) return x, y, z # 将地心坐标系下的直角坐标转换为东北天坐标系下的坐标 def convert_geocentric_to_topocentric(x, y, z, reference_latitude, reference_longitude): reference_latitude_rad = degrees_to_radians(reference_latitude) reference_longitude_rad = degrees_to_radians(reference_longitude) rotation_angle = reference_longitude_rad topocentric_x = -math.sin(reference_latitude_rad) * math.cos(reference_longitude_rad) * x - math.sin(reference_latitude_rad) * math.sin(reference_longitude_rad) * y + math.cos(reference_latitude_rad) * math.cos(reference_longitude_rad) * z topocentric_y = -math.sin(reference_longitude_rad) * x + math.cos(reference_longitude_rad) * y topocentric_z = math.cos(reference_latitude_rad) * math.cos(reference_longitude_rad) * x + math.cos(reference_latitude_rad) * math.sin(reference_longitude_rad) * y + math.sin(reference_latitude_rad) * z return topocentric_x, topocentric_y, topocentric_z # 计算地球自转角(单位:弧度) earth_rotation_angle = calculate_earth_rotation_angle(current_time) # 将地理坐标转换为地心坐标系下的直角坐标 geocentric_x, geocentric_y, geocentric_z = convert_geographic_to_geocentric(latitude, longitude, altitude) # 将参考点的地理坐标转换为地心坐标系下的直角坐标 reference_geocentric_x, reference_geocentric_y, reference_geocentric_z = convert_geographic_to_geocentric(reference_latitude, reference_longitude, reference_altitude) # 计算参考点的地球自转角(单位:弧度) reference_earth_rotation_angle = calculate_earth_rotation_angle(current_time) # 将地心坐标系下的直角坐标转换为东北天坐标系下的坐标 topocentric_x, topocentric_y, topocentric_z = convert_geocentric_to_topocentric( geocentric_x - reference_geocentric_x, geocentric_y - reference_geocentric_y, geocentric_z - reference_geocentric_z, reference_latitude, reference_longitude ) # 输出东北天坐标系下的坐标 print("东向(x):", topocentric_x) print("北向(y):", topocentric_y) print("天向(z):", topocentric_z) 地心地固转东北天
import math # 输入地心地固坐标系下的坐标 x = . y = -. z = . # 输入参考点的地心地固坐标系下的坐标 reference_x = .0 reference_y = 0.0 reference_z = 0.0 # 定义地球自转角速度(单位:弧度/秒) rotation_rate = 7.e-5 # 将地心地固坐标系下的坐标转换为东北天坐标系下的坐标 def convert_geocentric_to_topocentric(x, y, z, reference_x, reference_y, reference_z): dx = x - reference_x dy = y - reference_y dz = z - reference_z rotation_angle = rotation_rate * 0 # 这里假设时间差为0 topocentric_x = -math.sin(rotation_angle) * dx - math.cos(rotation_angle) * dy topocentric_y = math.cos(rotation_angle) * dx - math.sin(rotation_angle) * dy topocentric_z = dz return topocentric_x, topocentric_y, topocentric_z # 将地心地固坐标系下的坐标转换为东北天坐标系下的坐标 topocentric_x, topocentric_y, topocentric_z = convert_geocentric_to_topocentric(x, y, z, reference_x, reference_y, reference_z) # 输出东北天坐标系下的坐标 print("东向(x):", topocentric_x) print("北向(y):", topocentric_y) print("天向(z):", topocentric_z) 六、姿态角求解
import math # 输入卫星的J2000坐标系下的坐标 satellite_x = 1000.0 satellite_y = 2000.0 satellite_z = 3000.0 # 输入目标点的J2000坐标系下的坐标 target_x = 500.0 target_y = 1000.0 target_z = 1500.0 # 计算卫星相对于目标点的俯仰角 def calculate_elevation_angle(satellite_x, satellite_y, satellite_z, target_x, target_y, target_z): dx = target_x - satellite_x dy = target_y - satellite_y dz = target_z - satellite_z distance = math.sqrt(dx2 + dy2 + dz2) elevation_angle = math.asin(dz / distance) return elevation_angle # 计算卫星相对于目标点的侧摆角 def calculate_azimuth_angle(satellite_x, satellite_y, satellite_z, target_x, target_y, target_z): dx = target_x - satellite_x dy = target_y - satellite_y azimuth_angle = math.atan2(dy, dx) return azimuth_angle # 计算卫星相对于目标点的偏航角 def calculate_yaw_angle(): # 这里假设偏航角为0 return 0.0 # 计算卫星相对于目标点的俯仰角、侧摆角和偏航角 elevation_angle = calculate_elevation_angle(satellite_x, satellite_y, satellite_z, target_x, target_y, target_z) azimuth_angle = calculate_azimuth_angle(satellite_x, satellite_y, satellite_z, target_x, target_y, target_z) yaw_angle = calculate_yaw_angle() # 将弧度转换为角度 elevation_angle_deg = math.degrees(elevation_angle) azimuth_angle_deg = math.degrees(azimuth_angle) yaw_angle_deg = math.degrees(yaw_angle) # 输出卫星相对于目标点的俯仰角、侧摆角和偏航角 print("俯仰角(Elevation Angle):", elevation_angle_deg) print("侧摆角(Azimuth Angle):", azimuth_angle_deg) print("偏航角(Yaw Angle):", yaw_angle_deg) 七、计算某一时间的儒略日
def calculate_julian_date(year, month, day): if month <= 2: year -= 1 month += 12 A = year // 100 B = A // 4 C = 2 - A + B julian_day = ( int(365.25 * (year + 4716)) + int(30.6001 * (month + 1)) + day + C - 1524.5 ) return julian_day # 示例用法 year = 2023 month = 5 day = 12 julian_date = calculate_julian_date(year, month, day) print("儒略日:", julian_date) 在上述示例中,calculate_julian_date函数接收年份、月份和日期作为参数,并返回计算得到的儒略日。
函数中的计算遵循儒略日计算的公式和规则,包括对闰年的处理。首先,根据月份的值进行修正,将一月和二月看作前一年的十三月和十四月。然后,根据公式进行计算,包括年份的转换、月份的调整和一些常量的计算。
在示例用法中,我们定义了一个日期(2023年5月12日),然后调用calculate_julian_date函数来计算儒略日,并将结果打印出来。
请注意,这个示例是一个简化的实现,没有考虑一些特殊情况(如公元前的日期)和其他修正因素。在实际应用中,可能需要使用更复杂的算法和规则来计算儒略日,以获得更准确的结果。
免责声明:本站所有文章内容,图片,视频等均是来源于用户投稿和互联网及文摘转载整编而成,不代表本站观点,不承担相关法律责任。其著作权各归其原作者或其出版社所有。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,侵犯到您的权益,请在线联系站长,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 本文来自网络,若有侵权,请联系删除,如若转载,请注明出处:https://haidsoft.com/140695.html